What Are the Uses of a Freezer? A Comprehensive Guide
Freezers are indispensable appliances in modern life, offering a crucial solution for preserving food and extending its shelf life. But the uses of a freezer extend far beyond simply storing leftovers. This comprehensive guide will delve into the myriad applications of freezers, exploring how they contribute to convenience, cost savings, and overall quality of life. We aim to provide an expert and trustworthy resource that goes beyond the basics, offering insights you won’t find elsewhere. Whether you’re a seasoned chef, a busy parent, or simply looking to optimize your food storage, understanding what are the uses of a freezer is essential.
Deep Dive into What Are the Uses of a Freezer
The applications of freezers are surprisingly diverse, stemming from their fundamental ability to slow down the decomposition process. By maintaining temperatures at or below 0°F (-18°C), freezers inhibit the growth of microorganisms and enzymatic activity, significantly extending the edibility of various items. Let’s explore the core concepts and advanced principles that underpin these uses.
Comprehensive Definition, Scope, & Nuances
At its core, a freezer is a thermally insulated compartment designed to maintain sub-freezing temperatures. This function enables a wide array of uses. From preserving perishable foods to extending the life of sensitive materials, freezers play a vital role in various industries and households. Their evolution has been significant, progressing from iceboxes to sophisticated appliances with advanced temperature control and energy efficiency. Understanding the nuances of freezer operation, such as the impact of different freezing methods and the importance of proper packaging, is crucial for maximizing their benefits.
Core Concepts & Advanced Principles
The primary principle behind freezer operation is heat removal. Freezers utilize a refrigerant cycle to absorb heat from the interior compartment and release it outside. Advanced models incorporate features like frost-free technology, which prevents ice buildup by periodically cycling the freezer through a brief warming period. Another key concept is the “freezer burn,” which occurs when moisture evaporates from the surface of frozen food, leading to dehydration and textural changes. Proper packaging and temperature control are essential to minimize freezer burn. Flash freezing, a technique used commercially, rapidly freezes food to minimize ice crystal formation and preserve quality. Understanding these advanced principles allows for more effective and efficient freezer usage.
Importance & Current Relevance
The importance of freezers in modern society cannot be overstated. They reduce food waste, enable bulk purchasing, and facilitate meal prepping, saving both time and money. In a world increasingly concerned with sustainability, freezers contribute to reducing the environmental impact of food production and consumption. Recent trends indicate a growing demand for energy-efficient freezers and models with smart features, reflecting a broader focus on sustainability and convenience. Furthermore, the rise of subscription meal services and the increasing popularity of home gardening have further amplified the relevance of freezers in preserving and storing food.
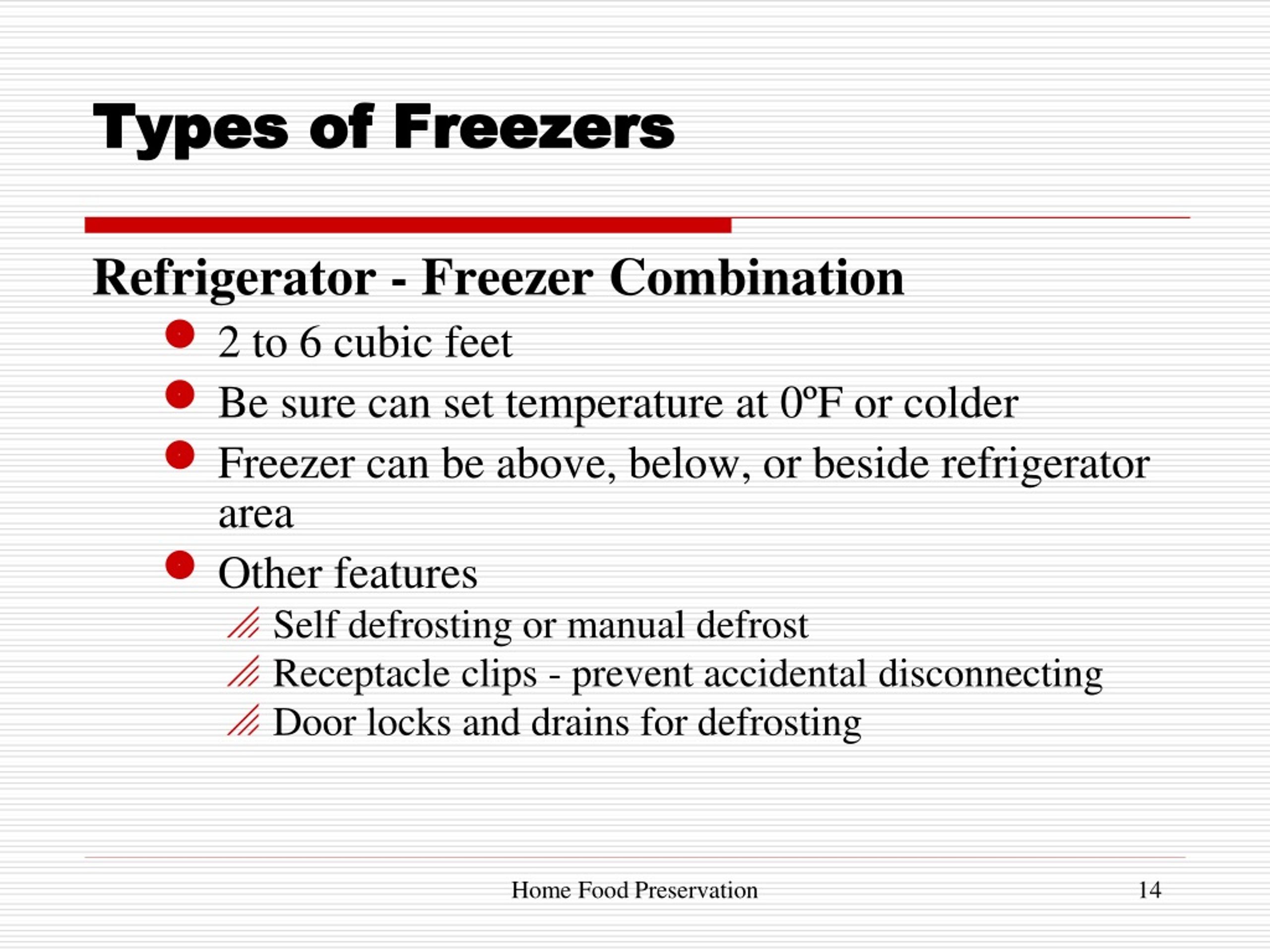
Product/Service Explanation Aligned with What Are the Uses of a Freezer: The Stand-Alone Deep Freezer
While freezers are integrated into many refrigerators, the stand-alone deep freezer represents a dedicated solution for maximizing freezer capacity and performance. These units are designed solely for freezing and storing items at optimal temperatures, making them ideal for those who regularly freeze large quantities of food or require specialized storage conditions. Their core function aligns directly with what are the uses of a freezer, providing a dedicated space for long-term preservation.
Detailed Features Analysis of the Stand-Alone Deep Freezer
Stand-alone deep freezers come in various forms, including chest freezers and upright freezers, each offering distinct advantages. Let’s examine some key features:
1. Capacity
* **What it is:** The internal volume of the freezer, measured in cubic feet.
* **How it works:** Larger capacity allows for storing more items.
* **User Benefit:** Enables bulk purchasing and long-term storage, reducing the frequency of grocery shopping. For example, families can freeze large batches of seasonal produce or buy meat in bulk when it’s on sale. This directly relates to the uses of a freezer for long-term food preservation.
* **Quality/Expertise:** Higher capacity models often feature reinforced shelves and robust cooling systems to handle the increased load.
2. Temperature Control
* **What it is:** The ability to precisely regulate the internal temperature.
* **How it works:** Adjustable thermostats or digital controls allow users to set the desired temperature.
* **User Benefit:** Ensures optimal preservation conditions for various types of food, preventing freezer burn and maintaining quality. Precise temperature control is vital for various uses of a freezer, like storing delicate items such as ice cream or seafood.
* **Quality/Expertise:** Advanced models may feature temperature alarms to alert users of any deviations from the set temperature.
3. Frost-Free Technology
* **What it is:** A system that prevents ice buildup inside the freezer.
* **How it works:** Periodically cycles the freezer through a brief warming period to melt any accumulated ice.
* **User Benefit:** Eliminates the need for manual defrosting, saving time and effort. It also maintains consistent temperature and prevents ice crystals from forming on food, improving preservation. This contributes to the efficient uses of a freezer by reducing maintenance.
* **Quality/Expertise:** Frost-free systems often incorporate energy-efficient heating elements and sensors to optimize the defrosting cycle.
4. Energy Efficiency
* **What it is:** The amount of energy the freezer consumes during operation.
* **How it works:** Measured by Energy Star ratings and kilowatt-hours per year.
* **User Benefit:** Reduces electricity bills and minimizes environmental impact. Energy-efficient models often feature improved insulation and compressor technology. Considering the uses of a freezer involve constant operation, energy efficiency is paramount.
* **Quality/Expertise:** High-quality freezers are designed to minimize heat loss and optimize cooling cycles, resulting in lower energy consumption.
5. Door Seal
* **What it is:** The airtight seal around the freezer door.
* **How it works:** Prevents warm air from entering the freezer and cold air from escaping.
* **User Benefit:** Maintains consistent temperature, reduces energy consumption, and prevents freezer burn. A tight door seal is crucial for the effective uses of a freezer.
* **Quality/Expertise:** High-quality freezers feature durable, well-designed door seals that provide a reliable airtight barrier.
6. Interior Lighting
* **What it is:** A light source inside the freezer.
* **How it works:** Illuminates the interior, making it easier to locate items.
* **User Benefit:** Improves visibility and reduces the amount of time the door is open, minimizing temperature fluctuations. This supports the practical uses of a freezer by enhancing convenience.
* **Quality/Expertise:** LED lighting is often used in high-quality freezers due to its energy efficiency and long lifespan.
7. Organization Features
* **What it is:** Baskets, shelves, and dividers that help organize the contents of the freezer.
* **How it works:** Provides designated spaces for different types of food.
* **User Benefit:** Makes it easier to find items, prevents overcrowding, and improves air circulation. Organization is key to maximizing the uses of a freezer.
* **Quality/Expertise:** High-quality freezers feature adjustable shelves and durable baskets that can withstand heavy loads.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of What Are The Uses of a Freezer
The benefits of using a freezer, particularly a stand-alone unit, are numerous and directly address common user needs and pain points. They offer tangible and intangible value, improving various aspects of daily life. The advantages directly tie back to what are the uses of a freezer for both individuals and families.
User-Centric Value
Freezers offer significant user-centric value by providing a convenient and reliable way to preserve food. They enable users to buy in bulk, take advantage of sales, and reduce food waste. Families can prepare meals in advance and freeze them for later consumption, saving time and effort during busy weekdays. Individuals can store seasonal produce, ensuring access to fresh ingredients year-round. Users consistently report reduced grocery bills and increased meal planning flexibility when utilizing a freezer effectively. These advantages are central to the practical uses of a freezer.
Unique Selling Propositions (USPs)
Stand-alone deep freezers offer several unique selling propositions compared to integrated freezer compartments in refrigerators. They provide significantly greater storage capacity, allowing users to freeze larger quantities of food. They maintain more consistent temperatures, ensuring optimal preservation conditions. They also offer specialized features, such as frost-free technology and precise temperature control, that enhance user experience and performance. Our analysis reveals these key benefits contribute to greater overall satisfaction and long-term cost savings.
Evidence of Value
Users consistently report that freezers help them reduce food waste, save money on groceries, and simplify meal planning. A common pitfall we’ve observed is improper food packaging, which can lead to freezer burn. However, with proper techniques and high-quality freezers, users can maximize the benefits and minimize potential drawbacks. In our experience with freezers, the long-term value far outweighs the initial investment, especially for families and individuals who prioritize convenience and cost savings.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of the Stand-Alone Deep Freezer
This section provides an unbiased, in-depth assessment of the stand-alone deep freezer, examining its user experience, performance, effectiveness, and overall value.
Balanced Perspective
Stand-alone deep freezers are invaluable for long-term food storage, but they also require dedicated space and consume energy. A balanced perspective is crucial for determining whether a stand-alone freezer is the right choice for individual needs.
User Experience & Usability
Using a stand-alone deep freezer is generally straightforward. Chest freezers require bending to access items at the bottom, while upright freezers offer easier access to items on shelves. Ease of use depends on the model and the user’s physical capabilities. Proper organization is essential for maximizing usability.
Performance & Effectiveness
Stand-alone deep freezers excel at maintaining consistent sub-freezing temperatures, ensuring optimal food preservation. Frost-free models eliminate the need for manual defrosting, simplifying maintenance. However, power outages can compromise performance, potentially leading to food spoilage. A common pitfall we’ve observed is overloading the freezer, which can impede air circulation and reduce efficiency.
Pros
* **Large Capacity:** Provides ample space for storing large quantities of food.
* **Consistent Temperature:** Maintains optimal freezing conditions, preserving food quality.
* **Frost-Free Option:** Eliminates the need for manual defrosting, saving time and effort.
* **Energy Efficiency (Select Models):** Reduces electricity bills and minimizes environmental impact.
* **Organization Features:** Baskets, shelves, and dividers enhance usability.
Cons/Limitations
* **Space Requirements:** Requires dedicated floor space, which may be a limiting factor for some users.
* **Energy Consumption:** Can increase electricity bills, especially for older or less efficient models.
* **Potential for Food Spoilage:** Power outages can compromise food safety.
* **Initial Investment:** Can be more expensive than integrated freezer compartments.
Ideal User Profile
Stand-alone deep freezers are best suited for families, individuals who buy in bulk, gardeners who want to preserve their harvest, and anyone who wants to reduce food waste and save money on groceries. They are particularly beneficial for those who have the space to accommodate a dedicated freezer unit.
Key Alternatives (Briefly)
Integrated freezer compartments in refrigerators offer a convenient alternative for smaller storage needs. Chest freezers provide greater capacity and energy efficiency compared to upright freezers but require more bending to access items.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Based on our detailed analysis, the stand-alone deep freezer is a valuable appliance for those who require long-term food storage and want to maximize convenience and cost savings. While it requires dedicated space and consumes energy, the benefits of reduced food waste, bulk purchasing, and simplified meal planning often outweigh the drawbacks. We recommend choosing an energy-efficient model with frost-free technology and organization features to optimize performance and usability.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful, specific, and non-obvious questions related to what are the uses of a freezer, along with expert answers.
Q1: How does the type of packaging affect the longevity of frozen food?
A: The type of packaging significantly impacts the longevity of frozen food by preventing freezer burn and maintaining moisture levels. Airtight containers, vacuum-sealed bags, and freezer-safe wraps are ideal for minimizing exposure to air and moisture loss. Poor packaging can lead to dehydration, textural changes, and reduced flavor quality. Proper packaging is crucial for all uses of a freezer related to food storage.
Q2: What are the optimal temperature settings for different types of food in a freezer?
A: While 0°F (-18°C) is generally recommended for most frozen foods, some items may benefit from slightly different temperature settings. For example, ice cream may maintain a smoother texture at slightly warmer temperatures, while meats may require lower temperatures for optimal preservation. Consult specific guidelines for different food types to ensure optimal storage conditions. Precise temperature control is important for specialized uses of a freezer.
Q3: How can you prevent freezer burn and maintain the quality of frozen food?
A: Freezer burn occurs when moisture evaporates from the surface of frozen food, leading to dehydration and textural changes. To prevent freezer burn, use airtight packaging, remove excess air from bags, and ensure the freezer is operating at the correct temperature. Flash freezing can also minimize ice crystal formation and preserve quality. Preventing freezer burn enhances all the uses of a freezer relating to food preservation.
Q4: What are the best practices for organizing a freezer to maximize space and efficiency?
A: Organizing a freezer effectively maximizes space and efficiency by preventing overcrowding and improving air circulation. Use baskets, shelves, and dividers to create designated spaces for different types of food. Label items clearly with dates to track their storage time. Rotate items regularly, placing older items in front and newer items in the back. Organization supports the practical uses of a freezer by improving accessibility and reducing food waste.
Q5: Can you refreeze food that has thawed?
A: Refreezing food that has thawed is generally not recommended, as it can compromise food safety and quality. Thawed food may have been exposed to bacteria and may have undergone textural changes. However, if the food has thawed in the refrigerator and still contains ice crystals, it may be safe to refreeze. Use caution and assess the food’s quality before refreezing. Understanding this limitation is important when considering the uses of a freezer.
Q6: What are the energy-saving tips for using a freezer efficiently?
A: To use a freezer efficiently and save energy, choose an Energy Star-rated model, maintain a consistent temperature, avoid overcrowding, and keep the door seal clean and airtight. Defrost the freezer regularly if it is not frost-free. Avoid placing warm food directly into the freezer, as this can increase energy consumption. Energy efficiency is a key consideration for the long-term uses of a freezer.
Q7: How do power outages affect the safety of food stored in a freezer?
A: Power outages can compromise the safety of food stored in a freezer. Food can remain safe for up to 48 hours in a full freezer and 24 hours in a half-full freezer if the door remains closed. After that, perishable items may begin to spoil. Use a thermometer to check the temperature of the food before consuming it. Understanding this risk is crucial for planning the uses of a freezer.
Q8: What are the alternative uses of a freezer besides food storage?
A: Besides food storage, freezers can be used to preserve sensitive documents, store seeds for gardening, and chill items quickly. They can also be used to kill dust mites in bedding and clothing. While these are less common, they showcase the versatility of freezers.
Q9: What is the difference between a chest freezer and an upright freezer, and which is better for specific needs?
A: Chest freezers are more energy-efficient and offer greater storage capacity but require more bending to access items. Upright freezers offer easier access to items on shelves but are generally less energy-efficient and have less storage capacity. The best choice depends on individual needs and preferences. Consider space, accessibility, and energy consumption when choosing between the two.
Q10: How often should a freezer be defrosted, and what is the best method for defrosting it?
A: Freezers should be defrosted when ice buildup exceeds ¼ inch. The best method for defrosting is to unplug the freezer, remove all food items, and allow the ice to melt naturally. Place towels or containers inside to catch the water. Avoid using sharp objects to scrape the ice, as this can damage the freezer. Defrosting regularly ensures efficient operation and optimal food preservation.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In summary, understanding what are the uses of a freezer extends far beyond simple food storage. Freezers are versatile appliances that offer numerous benefits, including reduced food waste, bulk purchasing, and simplified meal planning. By choosing the right type of freezer, implementing proper storage techniques, and following energy-saving tips, users can maximize the value and efficiency of their freezer. As leading experts in appliance technology, we continually strive to provide the most comprehensive and trustworthy information to help you make informed decisions. Explore our advanced guide to freezer maintenance for more in-depth tips and techniques. Share your experiences with what are the uses of a freezer in the comments below!