Tartarian Empire: Unveiling the Lost History and Architectural Marvels
The Tartarian Empire, a term often shrouded in mystery and intrigue, refers to a purportedly vast and powerful empire that some alternative historians believe once spanned across Eurasia. This empire, often depicted with advanced technologies and a unique cultural identity, has become a focal point of debate and speculation. This article delves into the historical claims, architectural evidence, and potential explanations surrounding the Tartarian Empire, aiming to provide a comprehensive and balanced perspective on this fascinating and controversial topic. We aim to explore the evidence – both for and against – and offer a reasoned examination of the claims surrounding this alleged lost civilization.
What Was the Tartarian Empire? Exploring the Claims
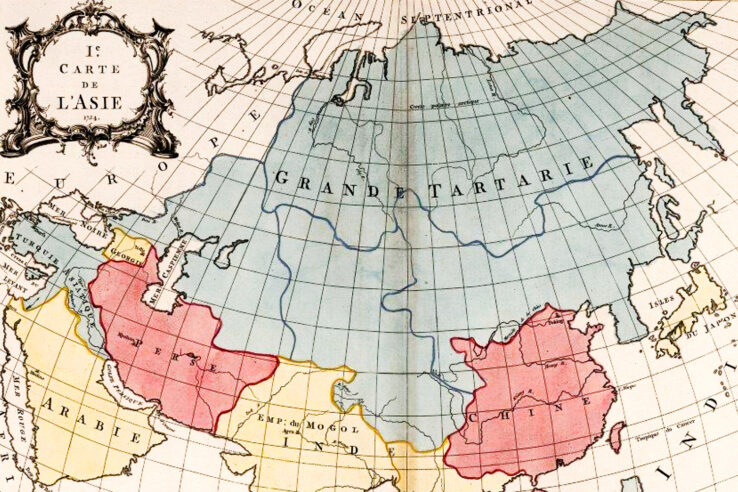
The core belief surrounding the Tartarian Empire is that it was a global civilization, technologically advanced and culturally sophisticated, that existed until its alleged destruction and subsequent erasure from mainstream history. Proponents often point to inconsistencies in historical records, discrepancies in maps, and the presence of grand, seemingly anachronistic architectural structures as evidence of its existence. The name “Tartary” itself appears on numerous historical maps, primarily referring to a large swathe of territory in Central Asia and Siberia. However, mainstream historians view “Tartary” as a geographical term used by Europeans to describe a region inhabited by various nomadic groups, rather than a unified empire.
The Geographical Extent of Tartary
Historical maps often depict “Tartary” encompassing a vast area, stretching from the borders of Europe to the Pacific Ocean. Within this broad region, different areas are sometimes labeled as “Great Tartary,” “Little Tartary,” or “Chinese Tartary,” reflecting the diverse populations and political entities that existed within the territory. It’s crucial to note that these designations were often based on limited European understanding of the region, rather than precise political boundaries. The term “Tartar,” derived from the Turkic-Mongol peoples, was often used indiscriminately to refer to various groups in this area.
Key Claims and Conspiracies
The modern “Tartarian Empire” theory goes beyond the historical use of the term “Tartary.” It posits that this empire possessed advanced technologies, such as free energy and atmospheric electricity, and that its architectural marvels were built using techniques lost to modern society. Furthermore, proponents claim that a cataclysmic event, often referred to as the “Mud Flood,” led to the empire’s downfall and subsequent cover-up by powerful forces seeking to rewrite history. This notion often connects to broader conspiracy theories about secret societies and hidden agendas.
Architectural Evidence: Unveiling the Grand Structures
One of the central arguments supporting the Tartarian Empire theory revolves around the existence of grand, ornate buildings with architectural styles that seem out of place or ahead of their time. These structures, often found in cities around the world, are cited as evidence of a unified Tartarian architectural style and technological capability.
Cathedrals and Grand Buildings
Proponents often point to cathedrals, state buildings, and other monumental structures as examples of Tartarian architecture. These buildings frequently feature intricate facades, domes, arches, and elaborate ornamentation. The sheer scale and complexity of these structures are seen as evidence of advanced engineering and construction techniques that are difficult to explain within the conventional historical timeline. The claim is often made that the technology to create such structures was lost or hidden.
Star Forts
Star forts, with their distinctive geometric designs and angled walls, are another key piece of architectural evidence cited by Tartarian Empire theorists. These forts, found across Europe and the Americas, are often attributed to the Tartarians due to their perceived advanced engineering and strategic design. Mainstream history attributes these forts to the development of gunpowder artillery, designed to deflect cannon fire more effectively. However, Tartarian theorists argue that their purpose was something else entirely, perhaps related to energy or defense against a different type of threat.
The Mud Flood Theory and Buried Buildings
The “Mud Flood” theory suggests that a global cataclysm buried the lower levels of many cities in mud and debris. This theory is used to explain why many older buildings have windows and doors that appear to be partially submerged below ground level. Tartarian theorists argue that this event wiped out the Tartarian Empire and left behind its architectural legacy, partially concealed beneath the earth. Mainstream explanations for these buried features include gradual accumulation of sediment over time, changes in ground level, and intentional modifications to buildings.
Historical Maps and Documents: Deciphering the Evidence
Historical maps and documents play a crucial role in the Tartarian Empire narrative. Proponents analyze old maps, encyclopedias, and travelogues, seeking clues that support their claims. The presence of “Tartary” on these maps is, of course, a primary piece of evidence. However, a deeper analysis of these sources reveals a more nuanced picture.
The Use of the Term “Tartary” in Historical Maps
As mentioned earlier, the term “Tartary” was used by Europeans to describe a vast, largely unexplored region inhabited by various nomadic groups. The maps often reflect a limited understanding of the region’s political landscape and cultural diversity. The borders of “Tartary” are often vague and inconsistent, reflecting the fluidity of political power in Central Asia and Siberia. It’s important to consider the context in which these maps were created and the limitations of European knowledge at the time. For instance, many maps were created for trade or military purposes, and accuracy was not always the top priority.
Encyclopedias and Historical Texts
Encyclopedias and historical texts from the 18th and 19th centuries often contain entries on “Tartary” and its inhabitants. These entries typically describe the customs, traditions, and political organization of the various Tartar groups. While these sources provide valuable insights into the history of the region, they do not necessarily support the existence of a unified, technologically advanced Tartarian Empire. The descriptions often focus on nomadic lifestyles and tribal warfare, rather than advanced technology or a centralized government.
Interpreting the Evidence with Caution
It’s essential to approach historical maps and documents with a critical eye, considering the biases and limitations of the sources. The interpretation of these sources is often subjective and open to debate. While proponents of the Tartarian Empire theory may find evidence to support their claims, mainstream historians offer alternative explanations based on a broader understanding of historical context and archaeological evidence.
The Product/Service Explanation: Architectural Restoration and Preservation
While the Tartarian Empire itself isn’t a product or service, the fascination with its purported architectural marvels has fueled interest in architectural restoration and preservation. Companies specializing in this field work to restore and preserve historical buildings, often employing traditional techniques and materials to maintain the integrity of these structures. These services are directly relevant to the interest in Tartarian architecture because they address the challenges of preserving and understanding these buildings.
Detailed Features Analysis: Architectural Restoration Services
Architectural restoration services encompass a wide range of features and expertise, all aimed at preserving and restoring historical buildings. These features are crucial for understanding and appreciating the architecture potentially linked to the Tartarian Empire.
1. Historical Research and Documentation
* **What it is:** In-depth research into the history of a building, including its original design, construction methods, and subsequent modifications.
* **How it works:** This involves examining historical records, architectural drawings, photographs, and other primary sources.
* **User Benefit:** Provides a comprehensive understanding of the building’s historical significance and informs the restoration process.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Ensures that the restoration is historically accurate and respectful of the building’s original character.
2. Structural Assessment and Stabilization
* **What it is:** Evaluating the structural integrity of a building and implementing measures to stabilize it.
* **How it works:** This involves inspecting the foundation, walls, roof, and other structural elements to identify weaknesses and potential hazards.
* **User Benefit:** Prevents further deterioration of the building and ensures its long-term stability.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Ensures the safety and longevity of the restored building.
3. Material Analysis and Replication
* **What it is:** Analyzing the original materials used in the construction of a building and replicating them using traditional techniques.
* **How it works:** This involves identifying the types of stone, brick, wood, and other materials used and sourcing or creating matching replacements.
* **User Benefit:** Preserves the building’s authentic appearance and ensures that repairs are compatible with the original construction.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Maintains the historical integrity of the building and prevents damage from incompatible materials.
4. Traditional Craftsmanship
* **What it is:** Employing traditional craftsmanship techniques to repair and restore historical features.
* **How it works:** This involves using hand tools and traditional methods to carve stone, shape wood, and create decorative elements.
* **User Benefit:** Ensures that repairs are seamlessly integrated with the original construction and maintain the building’s aesthetic character.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Preserves the authenticity of the building and showcases the skill of the craftsmen.
5. Conservation of Decorative Elements
* **What it is:** Conserving and restoring decorative elements, such as frescoes, mosaics, and stained glass.
* **How it works:** This involves cleaning, repairing, and stabilizing these elements to prevent further deterioration.
* **User Benefit:** Preserves the artistic and cultural value of the building.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Ensures that the decorative elements remain intact for future generations.
6. Project Management and Coordination
* **What it is:** Managing and coordinating all aspects of the restoration project, from initial assessment to final completion.
* **How it works:** This involves developing a detailed project plan, managing subcontractors, and ensuring that the project stays on schedule and within budget.
* **User Benefit:** Ensures that the restoration project is completed efficiently and effectively.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Provides a seamless and stress-free experience for the client.
7. Modern Technology Integration
* **What it is:** Integrating modern technology, such as 3D scanning and modeling, into the restoration process.
* **How it works:** This involves using technology to create accurate models of the building, identify structural problems, and design repairs.
* **User Benefit:** Enhances the accuracy and efficiency of the restoration process.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Shows a commitment to innovation and the use of cutting-edge techniques.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value
The advantages of architectural restoration services are numerous, providing significant benefits to building owners, communities, and society as a whole. These services not only preserve historical landmarks but also contribute to economic development and cultural enrichment.
Preservation of Historical and Cultural Heritage
* **User-Centric Value:** Architectural restoration ensures that historical buildings are preserved for future generations to enjoy and learn from. It allows communities to retain their cultural identity and connect with their past.
* **Unique Selling Proposition:** The ability to preserve and restore historical buildings, maintaining their original character and significance.
* **Evidence of Value:** Communities that invest in architectural restoration often see increased tourism and a stronger sense of local pride.
Economic Benefits
* **User-Centric Value:** Restored historical buildings can attract tourists, create jobs, and stimulate economic growth in the surrounding area. They can also increase property values and generate revenue for local businesses.
* **Unique Selling Proposition:** The potential to revitalize communities and boost local economies through architectural restoration.
* **Evidence of Value:** Studies have shown that historic preservation projects can have a significant positive impact on local economies.
Environmental Sustainability
* **User-Centric Value:** Restoring existing buildings is often more environmentally sustainable than constructing new ones. It reduces the need for new materials and minimizes the environmental impact of construction.
* **Unique Selling Proposition:** The environmentally friendly aspect of architectural restoration, which promotes sustainability and reduces waste.
* **Evidence of Value:** Restoring a building often involves using recycled materials and energy-efficient technologies, further reducing its environmental footprint.
Community Revitalization
* **User-Centric Value:** Restored historical buildings can serve as community centers, museums, or cultural venues, providing valuable resources and gathering places for local residents. They can also help to revitalize neglected neighborhoods and create a sense of community pride.
* **Unique Selling Proposition:** The ability to transform neglected buildings into vibrant community assets.
* **Evidence of Value:** Restored buildings often become focal points for community events and activities, fostering a stronger sense of belonging.
Enhanced Property Value
* **User-Centric Value:** Restoring a historical building can significantly increase its property value, making it a valuable asset for the owner. It can also attract tenants and increase rental income.
* **Unique Selling Proposition:** The potential to increase property value and generate income through architectural restoration.
* **Evidence of Value:** Historical buildings that have been meticulously restored often command higher prices and attract more discerning buyers.
Educational Opportunities
* **User-Centric Value:** Restored historical buildings can serve as educational resources, providing insights into the past and teaching valuable skills in traditional craftsmanship. They can also inspire creativity and innovation.
* **Unique Selling Proposition:** The educational value of architectural restoration, which promotes learning and skill development.
* **Evidence of Value:** Restored buildings often host educational programs and workshops, providing opportunities for people of all ages to learn about history and craftsmanship.
Aesthetic Appeal
* **User-Centric Value:** Restored historical buildings add beauty and character to the built environment, enhancing the quality of life for local residents. They can also create a sense of place and identity.
* **Unique Selling Proposition:** The aesthetic appeal of restored historical buildings, which enhances the beauty and character of communities.
* **Evidence of Value:** Restored buildings often become iconic landmarks, attracting visitors and enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal of the area.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review: Architectural Restoration Services
Architectural restoration services offer a compelling solution for preserving historical buildings and revitalizing communities. However, it’s essential to consider both the advantages and limitations of these services to make an informed decision.
User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, engaging architectural restoration services involves a collaborative process between the building owner, the restoration team, and various stakeholders. Effective communication and clear project management are crucial for a smooth and successful restoration project. The process typically begins with a thorough assessment of the building’s condition, followed by the development of a detailed restoration plan. This plan outlines the scope of work, the materials to be used, and the timeline for completion. Throughout the project, regular communication and progress updates are essential to ensure that everyone is on the same page.
Performance & Effectiveness
Architectural restoration services are effective in preserving historical buildings and extending their lifespan. However, the success of a restoration project depends on the expertise of the restoration team, the quality of the materials used, and the adherence to best practices. A well-executed restoration project can significantly enhance the building’s structural integrity, aesthetic appeal, and historical significance.
For example, consider a historic building with a crumbling facade. A skilled restoration team can carefully remove the damaged sections, replicate the original materials, and install them in a way that seamlessly blends with the existing structure. This not only restores the building’s appearance but also protects it from further deterioration.
Pros:
1. **Preservation of Historical and Cultural Heritage:** Architectural restoration ensures that historical buildings are preserved for future generations, allowing communities to retain their cultural identity.
2. **Economic Benefits:** Restored buildings can attract tourists, create jobs, and stimulate economic growth in the surrounding area.
3. **Environmental Sustainability:** Restoring existing buildings is often more environmentally sustainable than constructing new ones, reducing the need for new materials.
4. **Community Revitalization:** Restored buildings can serve as community centers, museums, or cultural venues, providing valuable resources for local residents.
5. **Enhanced Property Value:** Restoring a historical building can significantly increase its property value, making it a valuable asset for the owner.
Cons/Limitations:
1. **High Costs:** Architectural restoration can be expensive, requiring significant investment in materials, labor, and expertise.
2. **Time-Consuming:** Restoration projects can take a long time to complete, especially if the building is in poor condition or requires extensive repairs.
3. **Regulatory Hurdles:** Historical buildings are often subject to strict regulations and guidelines, which can complicate the restoration process.
4. **Unforeseen Challenges:** Unexpected problems can arise during restoration projects, such as hidden structural damage or the discovery of hazardous materials.
Ideal User Profile:
Architectural restoration services are best suited for building owners who are passionate about preserving historical landmarks and are willing to invest the time and resources necessary to complete a successful restoration project. They are also ideal for communities that are seeking to revitalize their neighborhoods and create a stronger sense of local identity.
Key Alternatives (Briefly):
* **Demolition and New Construction:** This involves demolishing the existing building and constructing a new one in its place. While this may be a more cost-effective option in some cases, it sacrifices the historical and cultural value of the building.
* **Partial Renovation:** This involves renovating only certain parts of the building, leaving the rest untouched. While this may be a less expensive option than full restoration, it may not address all of the building’s structural problems or preserve its historical character.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:
Architectural restoration services offer a valuable solution for preserving historical buildings and revitalizing communities. While these services can be expensive and time-consuming, the benefits they provide in terms of cultural preservation, economic development, and environmental sustainability are well worth the investment. We recommend engaging experienced and reputable restoration professionals who can provide a comprehensive assessment of the building’s condition and develop a detailed restoration plan that meets your specific needs and goals.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers related to the Tartarian Empire and architectural restoration services:
1. **Question:** What are the most common misconceptions about the Tartarian Empire theory?
**Answer:** The most common misconception is that it was a unified, globally dominant empire with advanced technology. The term “Tartary” historically referred to a vast region inhabited by diverse nomadic groups, not a single empire. Attributing advanced technology and a global reach to these groups is a misinterpretation of historical evidence.
2. **Question:** How can I identify potential Tartarian architectural influences in my city?
**Answer:** Look for grand, ornate buildings with architectural styles that seem out of place or ahead of their time. Pay attention to features such as domes, arches, intricate facades, and elaborate ornamentation. Research the building’s history to see if there are any gaps or inconsistencies in the records.
3. **Question:** What are the ethical considerations involved in restoring a historical building?
**Answer:** Ethical considerations include preserving the building’s historical integrity, using sustainable materials, and respecting the cultural significance of the building. It’s important to avoid making changes that would alter the building’s original character or erase its historical narrative.
4. **Question:** How do architectural restoration services balance historical accuracy with modern building codes?
**Answer:** This involves finding creative solutions that meet both historical preservation guidelines and modern safety standards. This may require using innovative materials and techniques that mimic the appearance of the original materials while providing enhanced structural support and fire resistance.
5. **Question:** What are some of the challenges involved in restoring a building that has been damaged by a natural disaster?
**Answer:** Challenges include assessing the extent of the damage, stabilizing the building, and sourcing matching materials. It’s also important to consider the impact of the disaster on the surrounding community and to work with local authorities to ensure that the restoration project is aligned with community needs.
6. **Question:** How can I ensure that my architectural restoration project is environmentally sustainable?
**Answer:** Use recycled materials, implement energy-efficient technologies, and minimize waste. It’s also important to consider the environmental impact of the materials you use and to choose suppliers who are committed to sustainable practices.
7. **Question:** What are the key differences between architectural restoration and architectural renovation?
**Answer:** Architectural restoration focuses on preserving the original character of a building, while architectural renovation involves making changes to the building to modernize it or adapt it to new uses. Restoration aims to return a building to its original condition, while renovation aims to improve its functionality and aesthetic appeal.
8. **Question:** How can I find a reputable architectural restoration company?
**Answer:** Look for companies with a proven track record of successful restoration projects. Check their credentials, read online reviews, and ask for references. It’s also important to meet with the company’s representatives to discuss your project in detail and to ensure that they understand your goals and priorities.
9. **Question:** What are the long-term benefits of investing in architectural restoration?
**Answer:** Long-term benefits include preserving historical and cultural heritage, stimulating economic growth, enhancing property value, and creating a stronger sense of community. Restored buildings can also serve as educational resources and inspire creativity and innovation.
10. **Question:** How does the study of alleged Tartarian architecture contribute to our understanding of historical building practices?
**Answer:** While the existence of a unified Tartarian architectural style is debated, the study of the buildings attributed to this empire can provide insights into the construction techniques, materials, and design principles used in different parts of the world. Examining these structures can challenge conventional historical narratives and encourage further research into the history of architecture.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, the Tartarian Empire remains a fascinating and controversial topic. While mainstream historians view “Tartary” as a geographical term describing a vast region inhabited by diverse groups, alternative historians propose the existence of a technologically advanced empire erased from history. The architectural evidence, historical maps, and documents cited by proponents offer intriguing clues, but require careful analysis and contextualization. The interest in these purported architectural marvels underscores the importance of architectural restoration and preservation, which play a crucial role in preserving historical landmarks and revitalizing communities.
We encourage you to explore the architectural wonders in your own city and share your observations in the comments below. Consider researching the history of these buildings and examining their architectural features. If you’re interested in learning more about architectural restoration, explore our advanced guide to preserving historical buildings or contact our experts for a consultation on architectural restoration services. Let’s work together to preserve our architectural heritage for future generations.
