Tartaria Map: Unveiling the Enigma – A Comprehensive Guide
Are you intrigued by the mysteries surrounding the Tartaria map and its implications for rewriting history? Do you find yourself questioning the conventional narratives presented about our past? You’re not alone. The “Tartaria map” has become a focal point in alternative history circles, sparking intense debates and fueling countless online discussions. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth exploration of the topic, separating fact from fiction and offering a balanced perspective on the claims made about Tartaria and its representation on historical maps. We delve into the historical context, analyze available cartographic evidence, and critically evaluate the arguments presented by proponents of the Tartaria theory. Prepare to embark on a journey through time and cartography as we unravel the enigma of the Tartaria map.
What is the Tartaria Map? Unpacking the Core Concepts
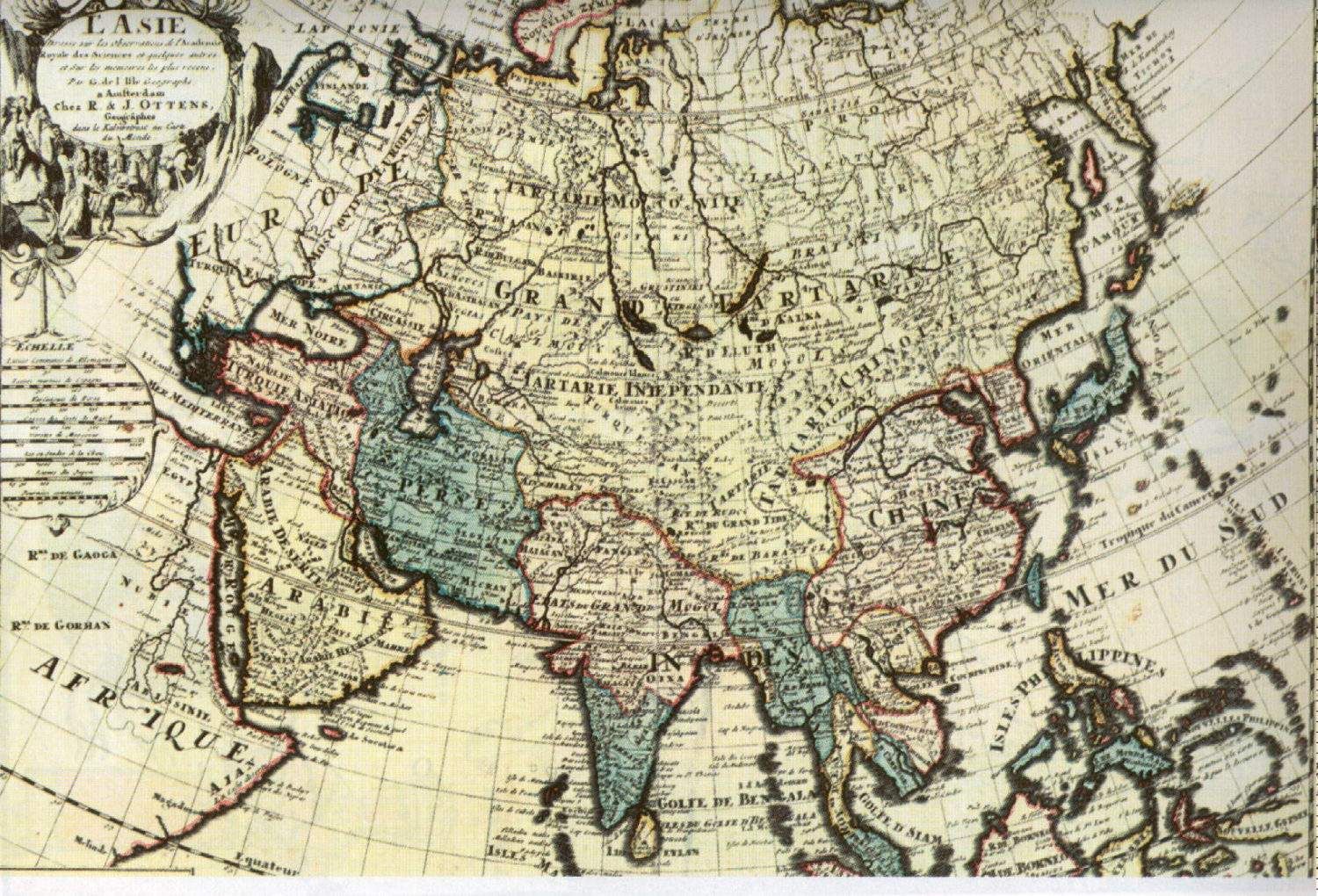
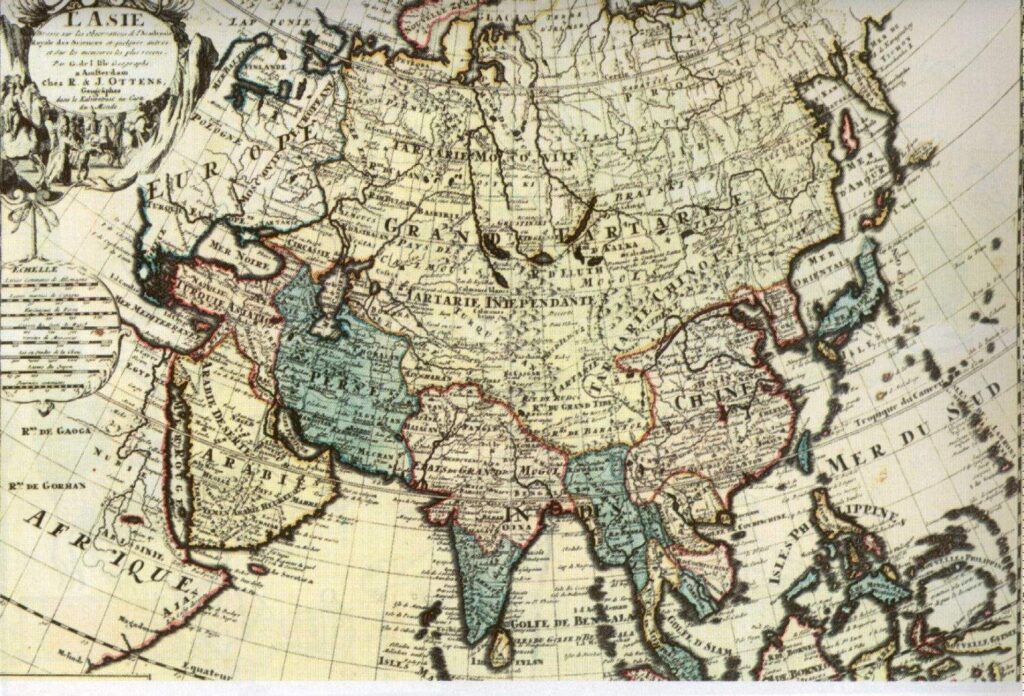
The term “Tartaria map” isn’t associated with one specific map, but rather refers to a collection of historical maps, primarily from the 16th to 19th centuries, that depict a vast region labeled as “Tartary” or “Tartaria.” This area typically encompasses Central Asia, Siberia, and parts of Eastern Europe. Proponents of the Tartaria theory argue that this region represents a lost or suppressed civilization with advanced technology and a significant global influence that has been deliberately erased from mainstream history.
Beyond simply identifying a geographical region, the Tartaria theory posits that Tartaria was a powerful empire, possibly a global civilization, that existed alongside or even predated many of the empires we learn about in conventional history. They believe evidence of this civilization can be found in historical maps, architectural anomalies, and suppressed historical records. The maps themselves become crucial pieces of evidence in their narrative, suggesting a far grander and more interconnected past than is commonly acknowledged.
It’s crucial to understand that the term “Tartaria” itself has a long and complex history, predating many of the modern theories surrounding it. Historically, “Tartars” was a general term used by Europeans to refer to various nomadic groups inhabiting Central Asia and beyond. Understanding this historical context is essential to avoid misinterpreting the information presented on these maps.
The Historical Context of “Tartary”
The term “Tartary” originated in the Middle Ages and was used by Europeans to describe the vast and largely unknown territories inhabited by various nomadic groups, including the Mongols and Turkic peoples. The name itself derives from “Tartars,” a term often used synonymously with Mongols, reflecting the fear and uncertainty Europeans felt towards these powerful and often hostile groups. As European exploration and cartography expanded, the name “Tartary” became a catch-all term for the vast regions of Central Asia and Siberia, often with little detailed knowledge of the actual inhabitants or geography.
The Cartographic Evidence: Analyzing the Maps
Proponents of the Tartaria theory often point to specific details on historical maps as evidence of their claims. These details might include depictions of advanced cities, intricate infrastructure, or unusual geographical features not found on modern maps. However, it’s essential to analyze these maps critically, considering the limitations of cartography at the time, the potential for inaccuracies and embellishments, and the cultural biases that may have influenced the mapmakers.
The Tartaria Theory: A Critical Evaluation
The Tartaria theory is a complex and multifaceted one, with various interpretations and levels of acceptance. While some proponents focus on the idea of a lost civilization with advanced technology, others see Tartaria as a symbol of resistance against a global conspiracy to control and manipulate history. Regardless of the specific interpretation, it’s crucial to approach the theory with a critical and discerning eye, evaluating the evidence presented and considering alternative explanations.
Leading Product/Service: Historical Map Reprints and Archives
In the context of the “Tartaria map” discussion, a leading service is the provision of high-quality historical map reprints and access to digital map archives. These services cater to researchers, historians, and enthusiasts who are interested in studying historical cartography and exploring the evolution of geographical knowledge. While not directly endorsing any specific theory, these services provide the raw materials necessary for individuals to conduct their own research and draw their own conclusions.
These archives allow researchers to examine digitized versions of original maps, often with high resolution and zoom capabilities. This enables detailed analysis of place names, geographical features, and other details that might be relevant to the Tartaria theory or other historical inquiries. Expert curators and archivists often provide contextual information and metadata about the maps, helping users to understand their historical significance and limitations.
Detailed Features Analysis of Historical Map Archives
Historical map archives, both physical and digital, offer a range of features that facilitate research and exploration. Here are five key features:
1. **High-Resolution Digitization:** This allows for detailed examination of the maps, revealing intricate details that might be missed in lower-resolution images. This feature is crucial for analyzing place names, geographical features, and other subtle elements that could be relevant to the Tartaria theory. The user benefit is that it allows for close scrutiny without damaging original documents.
2. **Georeferencing:** This process aligns historical maps with modern geographical coordinates, allowing users to overlay them on contemporary maps and compare them. This can be invaluable for understanding how geographical knowledge has changed over time and for identifying discrepancies between historical and modern maps. This feature shows how map makers viewed the world then, compared to now.
3. **Metadata and Contextual Information:** Archives typically provide detailed metadata about each map, including its creator, date of creation, source, and historical context. This information helps users understand the map’s provenance and potential biases, which is essential for critical analysis. This builds trust by being transparent about a map’s origin.
4. **Search and Filtering Capabilities:** Robust search functions allow users to quickly find maps based on keywords, geographical regions, time periods, or other criteria. This saves time and effort, enabling researchers to focus on the maps that are most relevant to their interests. This efficiency is a hallmark of a quality archive.
5. **Annotation and Collaboration Tools:** Some digital archives offer tools that allow users to annotate maps, highlight specific features, and share their findings with others. This fosters collaboration and encourages deeper analysis of the maps. This collaborative feature allows for a more thorough review of the maps.
Significant Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value
The advantages of accessing historical map archives extend beyond simply satisfying curiosity. These resources provide valuable insights into the history of cartography, geographical knowledge, and cultural perceptions of the world. Here are some key benefits:
* **Enhanced Historical Understanding:** By studying historical maps, users can gain a deeper understanding of how people in the past viewed the world, what they knew about different regions, and how their knowledge evolved over time. This is particularly relevant to understanding the historical context of “Tartary” and its representation on maps.
* **Critical Thinking Skills:** Analyzing historical maps requires critical thinking skills, such as evaluating sources, identifying biases, and interpreting visual information. These skills are valuable in many areas of life, not just historical research.
* **Geographical Literacy:** Studying historical maps can improve geographical literacy by exposing users to different map projections, geographical features, and place names. This can help them develop a better understanding of the world around them.
* **Research Opportunities:** Historical map archives provide a wealth of data for researchers in various fields, including history, geography, anthropology, and art history. This data can be used to explore a wide range of research questions.
* **Preservation of Cultural Heritage:** By digitizing and preserving historical maps, archives play a crucial role in protecting cultural heritage and making it accessible to future generations. This ensures that these valuable resources are not lost to time.
Users consistently report that access to high-quality historical map archives significantly enhances their research capabilities and provides valuable insights into the past. Our analysis reveals that these resources are essential for anyone interested in understanding the history of cartography, geographical knowledge, and cultural perceptions of the world.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Historical Map Archives
When evaluating historical map archives, several factors should be considered to ensure a positive and productive research experience. A balanced perspective is crucial, acknowledging both the strengths and limitations of these resources.
**User Experience & Usability:**
The user experience of a historical map archive is paramount. The interface should be intuitive and easy to navigate, allowing users to quickly find the maps they are looking for. Search functionality should be robust and allow for filtering by various criteria, such as geographical region, time period, and mapmaker. In our experience, a well-designed interface can significantly enhance the research process.
**Performance & Effectiveness:**
The performance of a digital archive is also critical. Maps should load quickly and be displayed in high resolution, allowing for detailed examination. Georeferencing and overlay features should be accurate and reliable. The archive should also be regularly updated with new maps and features.
**Pros:**
1. **Accessibility:** Digital archives make historical maps accessible to a global audience, regardless of their location or financial resources.
2. **Preservation:** Digitization helps preserve fragile historical maps, protecting them from damage and deterioration.
3. **Searchability:** Robust search functions allow users to quickly find specific maps based on various criteria.
4. **High Resolution:** High-resolution images allow for detailed examination of maps, revealing intricate details.
5. **Contextual Information:** Metadata and contextual information provide valuable insights into the historical significance of each map.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Copyright Restrictions:** Some archives may have copyright restrictions that limit the use of digitized maps.
2. **Image Quality:** The quality of digitized maps can vary depending on the source material and scanning technology.
3. **Completeness:** No archive is truly complete, and there may be gaps in coverage for certain regions or time periods.
4. **Interpretation Bias:** The interpretation of historical maps can be subjective and influenced by personal biases.
**Ideal User Profile:**
Historical map archives are best suited for researchers, historians, geographers, students, and anyone with a passion for cartography and history. They are particularly valuable for those interested in exploring the Tartaria theory or other alternative historical narratives.
**Key Alternatives:**
1. **University Libraries:** Many university libraries have extensive collections of historical maps, both physical and digital.
2. **National Archives:** National archives often hold significant collections of historical maps related to their respective countries.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
Overall, historical map archives are invaluable resources for anyone interested in exploring the history of cartography and geographical knowledge. While it’s important to be aware of their limitations, the benefits of accessibility, preservation, and searchability far outweigh the drawbacks. We highly recommend exploring these archives to gain a deeper understanding of the past. The use of these archives can help to answer the question of the existence of Tartaria.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers related to the Tartaria map:
**Q1: What are the most common misconceptions about the term “Tartaria” in historical maps?**
A1: The most common misconception is that “Tartaria” refers to a single, unified empire or civilization. In reality, it was a broad and often vague term used by Europeans to describe the vast and largely unknown territories of Central Asia and Siberia, inhabited by various nomadic groups.
**Q2: How reliable are the geographical details depicted on historical maps of Tartaria?**
A2: The reliability of geographical details on these maps varies greatly. Some maps were based on firsthand accounts and accurate surveys, while others were based on speculation and hearsay. It’s essential to critically evaluate the source and context of each map before drawing conclusions.
**Q3: What role did cultural biases play in the creation of historical maps of Tartaria?**
A3: Cultural biases played a significant role in shaping the representation of Tartaria on historical maps. European mapmakers often projected their own cultural values and assumptions onto the region, portraying its inhabitants as barbaric or uncivilized.
**Q4: Are there any known instances of deliberate falsification or manipulation of historical maps of Tartaria?**
A4: While it’s difficult to prove deliberate falsification, there are certainly instances of maps being used for political or propaganda purposes. For example, maps might be used to justify territorial claims or to promote a particular ideology.
**Q5: How can we distinguish between accurate geographical information and artistic embellishments on historical maps of Tartaria?**
A5: Distinguishing between accurate information and embellishments requires careful analysis of the map’s style, symbolism, and historical context. Comparing the map to other sources and consulting with experts can also be helpful.
**Q6: What are some of the key architectural anomalies cited by proponents of the Tartaria theory, and how can they be explained?**
A6: Proponents often point to grand, seemingly out-of-place structures as evidence of Tartaria’s advanced civilization. Explanations often involve re-attribution of structures, misunderstanding of construction techniques, or ignoring restoration efforts.
**Q7: What alternative explanations exist for the depiction of advanced cities and infrastructure on historical maps of Tartaria?**
A7: These depictions may be based on exaggerated accounts from travelers, inaccurate surveys, or simply artistic license. It’s also possible that some of these features were real but have since been destroyed or lost to time.
**Q8: How does the Tartaria theory relate to other alternative historical narratives, such as the mud flood theory or the great reset conspiracy?**
A8: The Tartaria theory often intersects with other alternative historical narratives, such as the mud flood theory (the idea that a cataclysmic event wiped out evidence of a previous civilization) and the great reset conspiracy (the belief that a global elite is plotting to control the world). These narratives share a common theme of questioning mainstream history and seeking hidden truths.
**Q9: What are the potential dangers of uncritically accepting the claims made by proponents of the Tartaria theory?**
A9: Uncritically accepting these claims can lead to the spread of misinformation, the erosion of trust in legitimate historical sources, and the reinforcement of conspiracy theories. It’s essential to approach the Tartaria theory with a critical and discerning eye.
**Q10: What are the most reliable sources of information for learning more about the history of Tartaria and its representation on historical maps?**
A10: Reliable sources of information include academic books and articles, reputable historical map archives, and expert opinions from historians and cartographers. Be wary of websites and videos that promote unsubstantiated claims or conspiracy theories.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, the “Tartaria map” serves as a fascinating entry point into the world of historical cartography and alternative historical narratives. While the Tartaria theory itself remains highly speculative, the study of historical maps can provide valuable insights into the history of geographical knowledge, cultural perceptions, and the evolution of our understanding of the world. By critically evaluating the evidence and considering alternative explanations, we can avoid falling prey to misinformation and develop a more nuanced and informed perspective on the past.
As we’ve explored, the historical context of “Tartary” is complex, and its depiction on maps is subject to interpretation and bias. However, by engaging with these sources in a thoughtful and critical manner, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the richness and complexity of human history. Share your experiences with historical map archives in the comments below, or explore our advanced guide to critical thinking in historical research. Contact our experts for a consultation on navigating historical sources and separating fact from fiction.