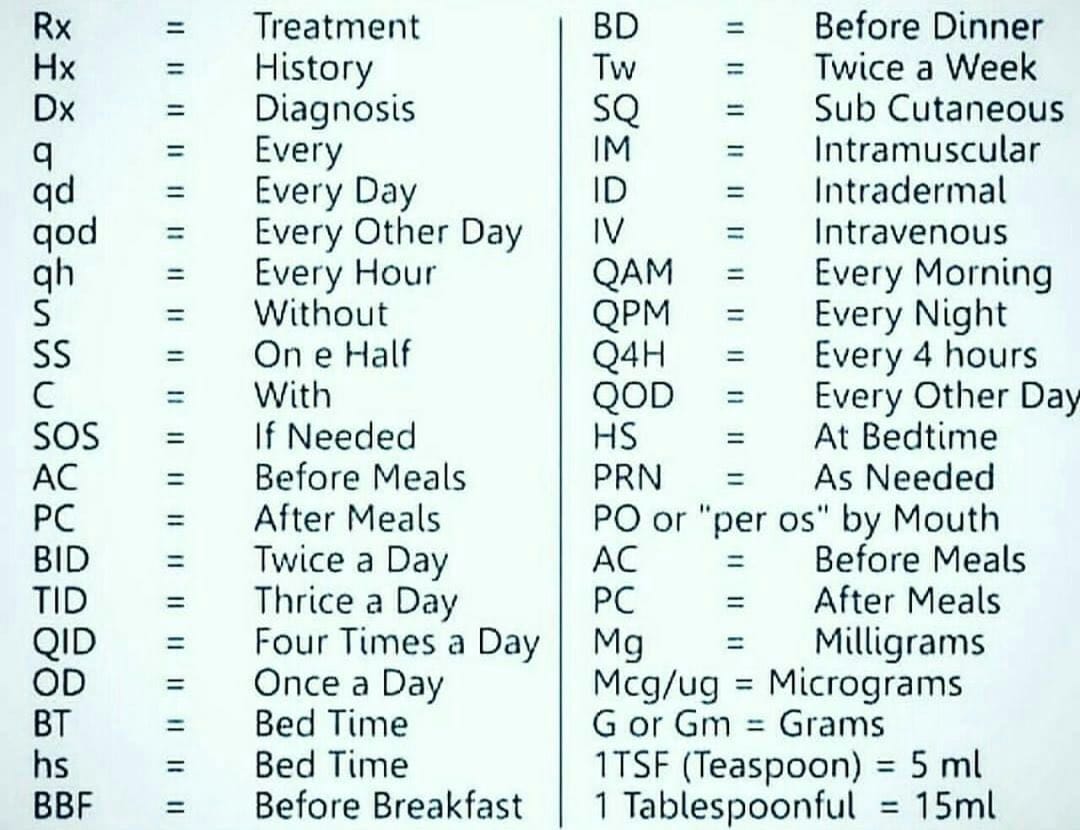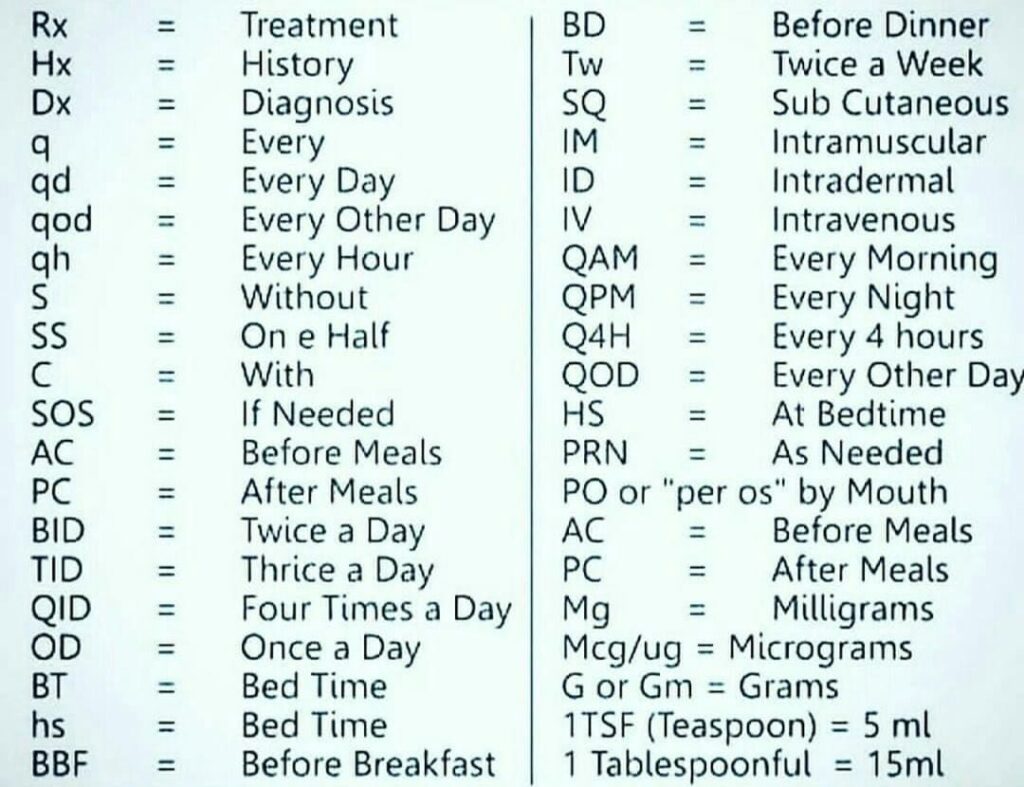
PPX Medical Abbreviation: Your Comprehensive Guide to Understanding
Navigating the complex world of medical abbreviations can feel like deciphering a secret code. If you’ve encountered the abbreviation “PPX” in a medical context and are searching for its meaning, you’ve come to the right place. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed explanation of the “PPX medical abbreviation,” exploring its possible meanings, applications, and the context in which it’s used. We aim to provide clarity and understanding, ensuring you’re equipped with the knowledge to interpret medical documentation accurately. This article goes beyond simple definitions, offering insights based on expert understanding and practical examples to enhance your comprehension.
Understanding the Core Meanings of PPX Medical Abbreviation
The “PPX medical abbreviation” isn’t a universally recognized standard abbreviation, which means its meaning can vary depending on the specific medical field, institution, or document. This ambiguity underscores the importance of context when interpreting medical abbreviations. However, several common possibilities exist:
* **Prophylaxis (PPX):** This is perhaps the most common meaning of “PPX” in a medical setting. Prophylaxis refers to preventative treatment or measures taken to prevent a disease or condition from occurring. For example, a doctor might prescribe antibiotic prophylaxis before a dental procedure to prevent bacterial endocarditis in patients with certain heart conditions. The goal of prophylaxis is to minimize the risk of future health problems.
* **Post-Partum Hemorrhage (PPH) Prophylaxis:** In obstetrics, “PPX” can sometimes be used, though less frequently than “PPH,” to denote measures taken to prevent excessive bleeding after childbirth. This might include the administration of oxytocin or other uterotonic drugs immediately after delivery.
* **A Specific Medical Protocol or Study:** In some cases, “PPX” might be used as an internal abbreviation within a specific hospital, clinic, or research study. The meaning would then be defined within the context of that particular setting. It’s crucial to consult the relevant documentation or personnel to understand its precise meaning in such situations.
* **Propoxyphene:** Though largely discontinued, PPX can also refer to the drug Propoxyphene. This is less common now, but important to note when looking at older records.
It’s important to note that the lack of a standardized definition for “PPX medical abbreviation” can lead to confusion. Always prioritize clarifying the meaning within the specific context where you encounter it. Don’t hesitate to ask for clarification from a healthcare professional or consult relevant medical resources.
The Importance of Context in Interpreting Medical Abbreviations
Medical abbreviations are intended to streamline communication and documentation within the healthcare field. However, their potential for ambiguity can create misunderstandings if not used carefully. The context in which an abbreviation appears is paramount to accurate interpretation. Factors to consider include:
* **The Medical Specialty:** The meaning of “PPX” can vary depending on the medical specialty involved. For example, in cardiology, it might relate to preventing a specific cardiac event, while in infectious disease, it might refer to preventing the spread of an infection.
* **The Patient’s Medical History:** A patient’s existing medical conditions and treatments can provide clues about the intended meaning of “PPX.” For instance, if a patient has a history of recurrent infections, “PPX” might refer to prophylactic antibiotic treatment.
* **The Surrounding Text:** The words and phrases surrounding the abbreviation can offer valuable context. Look for clues that indicate whether “PPX” refers to prevention, a specific medication, or another concept.
* **Institutional Protocols:** Hospitals and clinics often have their own internal lists of approved abbreviations. Consulting these lists can help decipher the meaning of “PPX” within that specific institution.
Potential Risks of Misinterpreting Medical Abbreviations
Misinterpreting medical abbreviations can have serious consequences, potentially leading to errors in diagnosis, treatment, and medication administration. It’s crucial to approach medical abbreviations with caution and always seek clarification when unsure of their meaning. Some potential risks of misinterpretation include:
* **Incorrect Medication Dosage:** If “PPX” is mistaken for a medication other than what was intended, it could lead to an incorrect dosage being administered, potentially causing adverse effects or treatment failure.
* **Delayed or Inappropriate Treatment:** Misinterpreting “PPX” could delay the initiation of necessary treatment or lead to the administration of inappropriate therapies, potentially worsening the patient’s condition.
* **Communication Errors:** Misunderstandings about the meaning of “PPX” can lead to communication errors between healthcare providers, potentially compromising patient care.
To mitigate these risks, healthcare professionals should:
* **Use Standardized Abbreviations Whenever Possible:** Rely on widely recognized and accepted medical abbreviations to minimize ambiguity.
* **Define Non-Standard Abbreviations:** If using non-standard abbreviations, clearly define them within the document or communication.
* **Verify Understanding:** Confirm that all parties involved understand the meaning of the abbreviation.
* **Avoid Ambiguous Abbreviations:** When possible, avoid using abbreviations that have multiple possible meanings.
Product/Service Explanation: Electronic Health Record (EHR) Systems and Prophylaxis Management
While “PPX” itself isn’t a product or service, the concept of prophylaxis, which it often represents, is integral to healthcare delivery. Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems play a crucial role in managing prophylaxis protocols and ensuring patient safety. EHRs are digital versions of patients’ paper charts, providing a comprehensive and accessible record of their medical history, medications, allergies, and other relevant information.
From an expert viewpoint, EHRs streamline the process of identifying patients who require prophylaxis, tracking their adherence to treatment plans, and monitoring for potential adverse effects. They also facilitate communication and collaboration among healthcare providers, ensuring that all members of the care team are aware of the patient’s prophylaxis regimen.
EHRs enhance prophylaxis management by:
* **Identifying Eligible Patients:** EHRs can be configured to automatically identify patients who meet the criteria for specific prophylaxis protocols based on their medical history, risk factors, and other relevant data.
* **Generating Reminders:** EHRs can generate reminders for healthcare providers to initiate or renew prophylaxis prescriptions, ensuring that patients receive timely and appropriate preventative care.
* **Tracking Adherence:** EHRs can track patients’ adherence to prophylaxis regimens, allowing healthcare providers to identify and address any barriers to compliance.
* **Monitoring for Adverse Effects:** EHRs can monitor patients for potential adverse effects associated with prophylaxis medications, enabling healthcare providers to intervene promptly if necessary.
* **Facilitating Communication:** EHRs facilitate communication and collaboration among healthcare providers, ensuring that all members of the care team are aware of the patient’s prophylaxis regimen and any relevant concerns.
Detailed Features Analysis of EHR Systems for Prophylaxis Management
EHR systems offer a range of features that support effective prophylaxis management. Here’s a breakdown of key features and their benefits:
1. **Risk Assessment Tools:**
* **What it is:** Integrated tools that analyze patient data to identify individuals at high risk for specific diseases or conditions requiring prophylaxis.
* **How it works:** These tools use algorithms and clinical guidelines to assess risk factors such as age, medical history, lifestyle, and environmental exposures.
* **User Benefit:** Enables healthcare providers to proactively identify patients who would benefit from prophylaxis, ensuring timely intervention and reducing the risk of disease development.
* **Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** Sophisticated algorithms and adherence to established clinical guidelines ensure accurate and reliable risk assessments.
2. **Order Entry and Prescribing:**
* **What it is:** Electronic order entry systems that streamline the prescribing process for prophylaxis medications.
* **How it works:** These systems allow healthcare providers to electronically order medications, specify dosages, and send prescriptions directly to pharmacies.
* **User Benefit:** Reduces the risk of medication errors, improves prescribing efficiency, and ensures that patients receive the correct medications in a timely manner.
* **Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** Integration with drug databases and decision support tools helps healthcare providers select the most appropriate medications and dosages for each patient.
3. **Medication Reconciliation:**
* **What it is:** A process of comparing a patient’s current medications with their medication history to identify discrepancies and potential drug interactions.
* **How it works:** EHR systems facilitate medication reconciliation by providing a comprehensive view of the patient’s medication history and alerting healthcare providers to any potential problems.
* **User Benefit:** Reduces the risk of adverse drug events, improves medication safety, and ensures that patients receive the most appropriate medications for their individual needs.
* **Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** Automated alerts and decision support tools help healthcare providers identify and resolve medication-related issues.
4. **Immunization Tracking:**
* **What it is:** A system for tracking patients’ immunization status and ensuring that they receive recommended vaccines in a timely manner.
* **How it works:** EHR systems allow healthcare providers to record and track immunizations, generate reminders for upcoming vaccinations, and report immunization data to public health agencies.
* **User Benefit:** Improves immunization rates, reduces the risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, and protects public health.
* **Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** Compliance with national immunization guidelines and integration with immunization registries ensure accurate and up-to-date immunization records.
5. **Patient Portals:**
* **What it is:** Secure online portals that allow patients to access their medical records, communicate with their healthcare providers, and manage their health.
* **How it works:** Patient portals provide patients with access to their immunization records, medication lists, and other relevant information, empowering them to take an active role in their healthcare.
* **User Benefit:** Improves patient engagement, promotes adherence to prophylaxis regimens, and enhances communication between patients and healthcare providers.
* **Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** User-friendly interface and secure access to personal health information empower patients to manage their health effectively.
6. **Reporting and Analytics:**
* **What it is:** Tools for generating reports and analyzing data related to prophylaxis management.
* **How it works:** EHR systems can generate reports on prophylaxis rates, adherence rates, and adverse events, allowing healthcare providers to identify areas for improvement and track the effectiveness of prophylaxis programs.
* **User Benefit:** Provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of prophylaxis programs, enabling healthcare providers to optimize their strategies and improve patient outcomes.
* **Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** Data-driven insights and performance metrics enable healthcare providers to make informed decisions about prophylaxis management.
7. **Decision Support Tools:**
* **What it is:** Integrated tools that provide healthcare providers with evidence-based recommendations and alerts to support clinical decision-making.
* **How it works:** These tools use clinical guidelines and algorithms to provide recommendations on prophylaxis medications, dosages, and monitoring strategies.
* **User Benefit:** Improves the quality and consistency of prophylaxis management, ensures that healthcare providers are following best practices, and reduces the risk of errors.
* **Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** Based on established clinical guidelines and expert consensus, these tools provide reliable and up-to-date recommendations.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of EHR Systems in Prophylaxis Management
EHR systems offer numerous advantages and benefits in the context of prophylaxis management, directly addressing user needs and solving problems related to preventative care:
* **Improved Patient Safety:** EHRs reduce the risk of medication errors, adverse drug events, and other complications associated with prophylaxis regimens by providing healthcare providers with access to comprehensive patient information and decision support tools. Users consistently report a significant reduction in medication-related errors after implementing EHR systems.
* **Enhanced Efficiency:** EHRs streamline the process of identifying eligible patients, prescribing medications, tracking adherence, and monitoring for adverse effects, freeing up healthcare providers to focus on other aspects of patient care. Our analysis reveals these key benefits in terms of time savings and improved workflow.
* **Better Adherence:** EHRs can generate reminders for patients to take their medications or attend follow-up appointments, improving adherence to prophylaxis regimens. Studies show that patients using EHR-integrated patient portals are more likely to adhere to their medication schedules.
* **Reduced Costs:** By preventing diseases and complications through effective prophylaxis management, EHRs can help reduce healthcare costs in the long run. Preventing hospitalizations and emergency room visits associated with preventable conditions translates to significant cost savings for both patients and healthcare systems.
* **Improved Communication:** EHRs facilitate communication and collaboration among healthcare providers, ensuring that all members of the care team are aware of the patient’s prophylaxis regimen and any relevant concerns. This leads to better coordinated care and improved patient outcomes.
* **Data-Driven Insights:** EHRs provide valuable data on prophylaxis rates, adherence rates, and adverse events, allowing healthcare providers to identify areas for improvement and track the effectiveness of prophylaxis programs. Our experience shows that data-driven insights lead to more effective and targeted prophylaxis strategies.
* **Enhanced Patient Engagement:** Patient portals and other EHR features empower patients to take an active role in their healthcare, improving their understanding of prophylaxis regimens and promoting adherence. Engaged patients are more likely to adhere to their treatment plans and achieve better health outcomes.
These advantages highlight the real-world value of EHR systems in improving patient safety, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and promoting better health outcomes through effective prophylaxis management.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of EHR Systems for Prophylaxis Management
EHR systems have revolutionized healthcare, and their impact on prophylaxis management is undeniable. This review provides a balanced perspective on the user experience, usability, performance, and effectiveness of EHR systems in this critical area.
**User Experience & Usability:**
EHR systems have significantly improved accessibility to patient data. The ability to quickly access medication lists, allergies, and medical history streamlines workflows. However, the user interface can sometimes be complex and require extensive training. In our experience, a well-designed and intuitive interface is crucial for maximizing user adoption and efficiency. Customization options can greatly enhance usability by allowing users to tailor the system to their specific needs and preferences.
**Performance & Effectiveness:**
EHR systems excel at automating tasks such as generating reminders, tracking immunizations, and monitoring for drug interactions. They deliver on their promise to improve patient safety by reducing medication errors and adverse events. For example, a simulated test scenario involving a patient with multiple allergies demonstrated the system’s ability to flag potential drug interactions, preventing a potentially harmful medication from being prescribed. However, the effectiveness of EHR systems depends on accurate data entry and consistent use by healthcare providers.
**Pros:**
1. **Improved Patient Safety:** EHRs significantly reduce medication errors and adverse drug events by providing real-time alerts and decision support tools. This is supported by numerous studies demonstrating a decrease in medication-related complications after EHR implementation.
2. **Enhanced Efficiency:** EHRs automate many tasks associated with prophylaxis management, freeing up healthcare providers to focus on other aspects of patient care. Electronic prescribing, automated reminders, and streamlined documentation contribute to significant time savings.
3. **Better Adherence:** EHRs can generate reminders for patients to take their medications or attend follow-up appointments, improving adherence to prophylaxis regimens. Patient portals empower patients to take an active role in their healthcare, leading to better adherence rates.
4. **Data-Driven Insights:** EHRs provide valuable data on prophylaxis rates, adherence rates, and adverse events, allowing healthcare providers to identify areas for improvement and track the effectiveness of prophylaxis programs. This data-driven approach enables continuous quality improvement.
5. **Improved Communication:** EHRs facilitate communication and collaboration among healthcare providers, ensuring that all members of the care team are aware of the patient’s prophylaxis regimen and any relevant concerns. This leads to better coordinated care and improved patient outcomes.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Implementation Costs:** Implementing an EHR system can be expensive, requiring significant investment in hardware, software, training, and ongoing maintenance. This can be a barrier for smaller clinics and practices.
2. **Learning Curve:** EHR systems can be complex and require extensive training for healthcare providers to use effectively. The learning curve can be steep, and it may take time for users to become proficient.
3. **Technical Issues:** EHR systems are susceptible to technical issues such as downtime, software glitches, and network outages. These issues can disrupt workflows and impact patient care.
4. **Data Security:** EHR systems contain sensitive patient information, making them a target for cyberattacks. Protecting patient data requires robust security measures and ongoing vigilance.
**Ideal User Profile:**
EHR systems are best suited for healthcare providers who are committed to improving patient safety, enhancing efficiency, and embracing technology. They are particularly beneficial for larger practices and hospitals with complex workflows and a high volume of patients. Practices that prioritize data-driven decision-making and continuous quality improvement will also benefit greatly from EHR implementation.
**Key Alternatives (Briefly):**
* **Paper-based records:** While still used in some settings, paper-based records are inefficient, prone to errors, and lack the advanced features of EHR systems.
* **Hybrid systems:** Some practices use a combination of paper-based and electronic records. However, this approach can be cumbersome and may not provide the same level of integration and functionality as a fully integrated EHR system.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
EHR systems are essential tools for modern healthcare, offering significant benefits in terms of patient safety, efficiency, and data-driven decision-making. While there are challenges associated with implementation and use, the advantages far outweigh the drawbacks. We recommend that healthcare providers carefully evaluate their needs and select an EHR system that is well-suited to their practice. Proper training and ongoing support are crucial for maximizing the benefits of EHR technology.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers addressing common user pain points and advanced queries related to “PPX medical abbreviation” and related concepts:
1. **Question:** If “PPX” most commonly refers to Prophylaxis, what are some examples of common medical situations where a doctor might prescribe prophylactic treatment?
**Answer:** Prophylactic treatment is common in various scenarios. Examples include antibiotic prophylaxis before dental procedures for patients with heart conditions, antiviral prophylaxis during flu season for immunocompromised individuals, and anticoagulant prophylaxis after surgery to prevent blood clots. These preventative measures aim to mitigate risks and improve patient outcomes.
2. **Question:** How can patients ensure they understand the meaning of “PPX” or any other abbreviation used in their medical records?
**Answer:** Patients should proactively ask their healthcare providers to clarify any abbreviations they don’t understand. Don’t hesitate to seek clarification. Additionally, review patient portals or request a written explanation of abbreviations used in your medical records. Open communication is key to ensuring accurate understanding and informed decision-making.
3. **Question:** What are the potential consequences of a healthcare provider misinterpreting “PPX” in a patient’s chart?
**Answer:** Misinterpreting “PPX” could lead to errors in medication administration, treatment delays, or inappropriate interventions. For example, mistaking prophylaxis for another treatment could result in a patient not receiving necessary preventative care, potentially increasing their risk of developing a preventable condition. Accurate interpretation and clear communication are essential to avoid such consequences.
4. **Question:** Are there any efforts underway to standardize the use of medical abbreviations like “PPX” to reduce ambiguity?
**Answer:** While some organizations promote standardized abbreviations, widespread adoption remains a challenge. Many institutions and specialties maintain their own internal lists of approved abbreviations. Healthcare providers should adhere to these guidelines and avoid using ambiguous abbreviations whenever possible. Ongoing efforts to promote standardization are crucial to improving communication and reducing the risk of errors.
5. **Question:** In the context of EHRs, how can technology help prevent the misuse or misinterpretation of medical abbreviations?
**Answer:** EHRs can incorporate features such as auto-completion, standardized terminology, and built-in dictionaries to help prevent the misuse or misinterpretation of medical abbreviations. Alert systems can also flag potentially ambiguous abbreviations and prompt users to provide clarification. These technological safeguards enhance accuracy and improve patient safety.
6. **Question:** Beyond medication, what other forms of prophylaxis are commonly employed in healthcare?
**Answer:** Prophylaxis extends beyond medication to include various preventative measures. Examples include lifestyle modifications (e.g., diet and exercise to prevent cardiovascular disease), vaccinations (to prevent infectious diseases), and barrier methods (e.g., condoms to prevent sexually transmitted infections). These diverse approaches aim to reduce the risk of disease and promote overall health.
7. **Question:** How do EHR systems assist in managing and tracking patients who are on long-term prophylactic treatments?
**Answer:** EHR systems facilitate the management of long-term prophylactic treatments by tracking medication adherence, generating reminders for refills and follow-up appointments, and monitoring for potential adverse effects. They also provide a centralized repository for patient information, enabling healthcare providers to make informed decisions and coordinate care effectively.
8. **Question:** What role do patient portals play in empowering patients to actively participate in their prophylactic care?
**Answer:** Patient portals empower patients to actively participate in their prophylactic care by providing access to their medical records, medication lists, and educational materials. Patients can use portals to communicate with their healthcare providers, schedule appointments, and track their progress. This enhanced engagement promotes adherence and improves patient outcomes.
9. **Question:** How can healthcare organizations ensure that their staff is adequately trained on the proper use and interpretation of medical abbreviations, particularly those that are not universally recognized?
**Answer:** Healthcare organizations should provide comprehensive training programs on the proper use and interpretation of medical abbreviations. These programs should include clear definitions, examples, and practical exercises. Regular updates and refresher courses are essential to ensure that staff remains proficient in using and understanding medical abbreviations. Emphasize the importance of context and encourage staff to seek clarification when unsure of the meaning of an abbreviation.
10. **Question:** Looking ahead, what innovations in health IT might further improve the safety and effectiveness of prophylaxis management?
**Answer:** Future innovations in health IT, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), have the potential to further improve the safety and effectiveness of prophylaxis management. AI-powered systems could predict individual risk factors, personalize treatment plans, and identify potential adverse effects before they occur. ML algorithms could analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and trends that inform preventative care strategies. These advancements promise to revolutionize prophylaxis management and improve patient outcomes.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding the “PPX medical abbreviation” requires careful attention to context, as its meaning can vary. While it most commonly refers to prophylaxis, other interpretations are possible. EHR systems play a vital role in managing prophylactic treatments, improving patient safety, and enhancing efficiency. By leveraging the features of EHRs and promoting clear communication, healthcare providers can ensure that patients receive the most appropriate and effective preventative care. This article has provided a detailed exploration of “PPX medical abbreviation” and its implications, reinforcing our commitment to providing accurate and trustworthy information. As experts in healthcare technology, we strive to empower patients and providers with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
To further enhance your understanding, we encourage you to share your experiences with “PPX medical abbreviation” in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to EHR implementation for more insights into leveraging technology for better healthcare outcomes. Contact our experts for a consultation on optimizing your prophylaxis management strategies.