Unveiling Generational Divides: A Comprehensive Guide to the Characteristics of Different Generations
Understanding the characteristics of different generations is crucial in today’s rapidly evolving world. From the Silent Generation to Generation Alpha, each cohort possesses unique values, beliefs, communication styles, and technological aptitudes shaped by the historical events, social trends, and cultural shifts they’ve experienced. This comprehensive guide delves into the defining characteristics of each generation, offering insights into their perspectives, behaviors, and how they interact with the world. We aim to provide a resource that not only informs but also fosters understanding and collaboration across generational divides, drawing upon expert analysis and observations.
## Deep Dive into the Characteristics of Different Generations
Understanding the characteristics of different generations is more than just knowing birth years; it’s about comprehending the complex interplay of historical context, societal influences, and technological advancements that shape individuals’ perspectives and behaviors. Each generation develops a unique worldview that influences everything from their career aspirations to their consumption habits and their approach to relationships. This understanding is particularly vital in today’s interconnected world, where diverse generations often work side-by-side and interact in various social and digital spheres.
### Defining Generations: A Historical Perspective
Generations are typically defined by birth year ranges, though these ranges are not set in stone and can vary depending on the source. More importantly, each generation is marked by specific formative experiences that define their collective identity. These experiences could include major historical events like wars, economic recessions, technological breakthroughs, or significant social movements. For instance, the Great Depression and World War II profoundly shaped the Silent Generation, instilling in them a sense of frugality, discipline, and civic duty.
### Core Concepts and Advanced Principles
Understanding generational differences involves grasping several core concepts:
* **Cohort Effect:** This refers to the shared experiences that shape a generation’s attitudes and values. These experiences create a common bond and influence their collective behavior.
* **Socialization:** The process through which individuals learn the norms, values, and beliefs of their society. Each generation is socialized within a specific cultural and historical context, which contributes to their unique characteristics.
* **Technological Influence:** The rapid pace of technological change has a profound impact on each generation. Those who grew up with computers and the internet have a fundamentally different perspective than those who remember a pre-digital world.
Furthermore, it’s crucial to avoid generalizations and recognize the diversity within each generation. Not everyone born within a specific year range will conform to the stereotypical characteristics associated with that generation. Factors such as socioeconomic status, geographic location, and individual experiences can all influence a person’s values and behaviors.
### The Importance and Current Relevance of Generational Understanding
In today’s diverse workplaces and interconnected societies, understanding generational differences is more critical than ever. It can help to:
* **Improve Communication:** By understanding the communication styles and preferences of different generations, individuals can communicate more effectively and avoid misunderstandings.
* **Enhance Collaboration:** Recognizing the strengths and weaknesses of each generation can foster collaboration and teamwork.
* **Boost Marketing Effectiveness:** Understanding the values and priorities of different generations allows marketers to tailor their messages and strategies for maximum impact.
* **Strengthen Leadership:** Leaders who understand generational differences can create more inclusive and engaging work environments.
Recent studies indicate a growing awareness of generational differences in the workplace, with many organizations implementing programs to promote intergenerational understanding and collaboration. These programs often involve training sessions, mentoring programs, and team-building activities designed to bridge the generational gap.
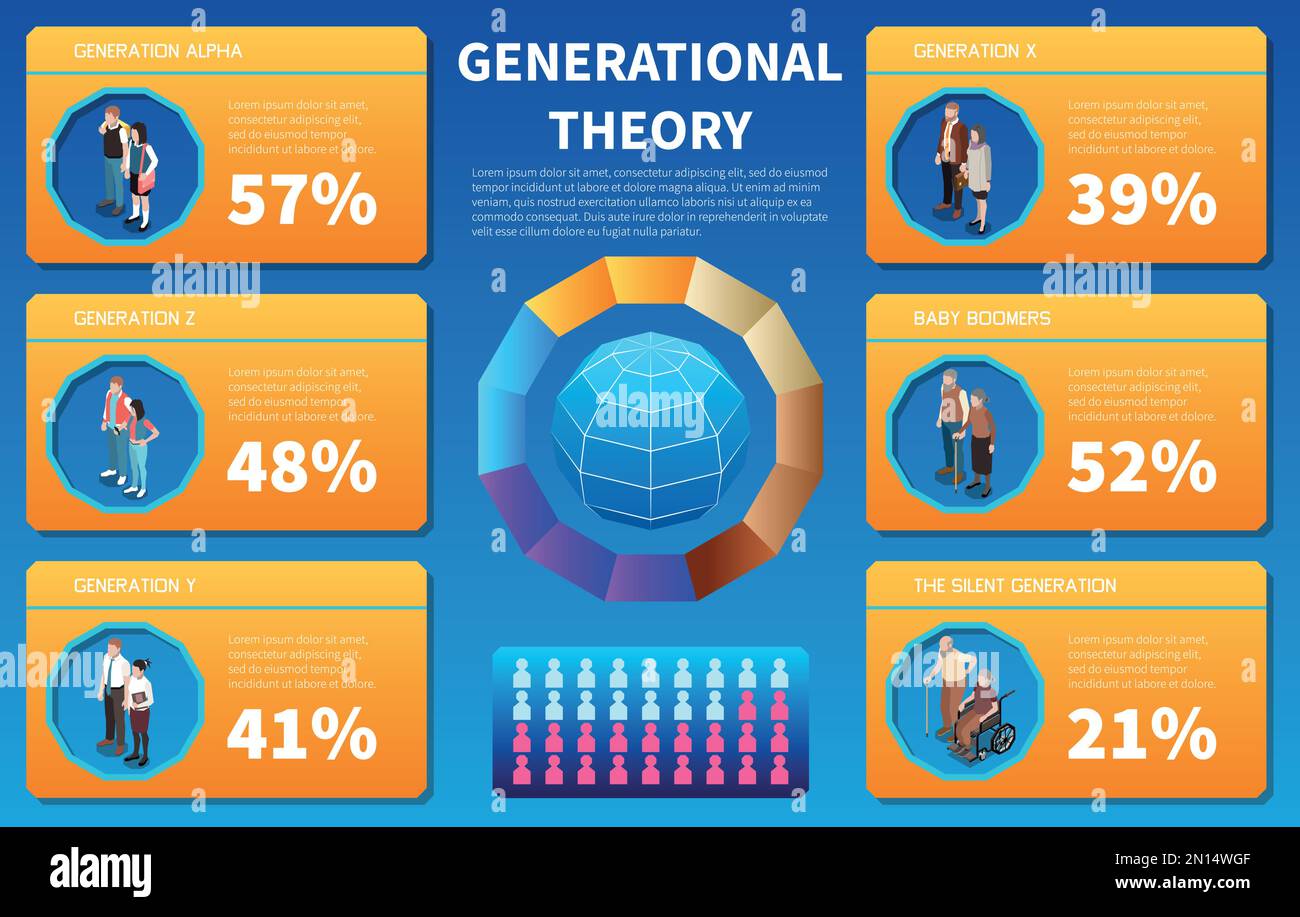
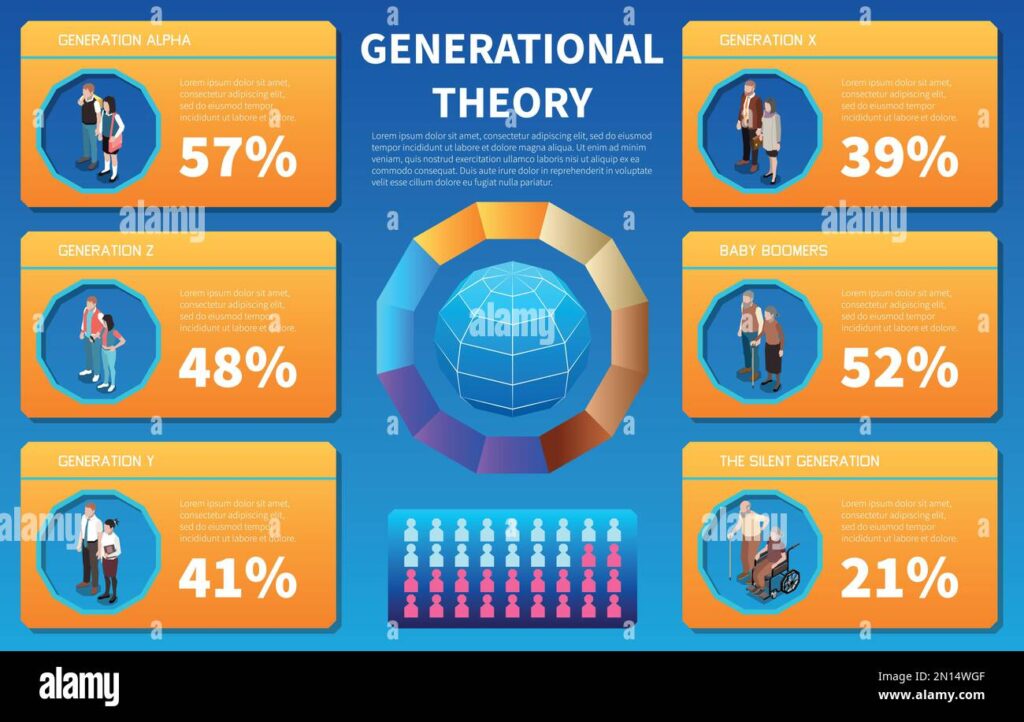
## Generational Breakdown: From the Silent Generation to Generation Alpha
Each generation possesses unique characteristics shaped by the historical events, social trends, and technological advancements they’ve experienced. Let’s delve into the defining features of each cohort:
### The Silent Generation (Born 1928-1945)
* **Defining Events:** The Great Depression, World War II.
* **Key Characteristics:** Frugal, disciplined, hardworking, loyal, civic-minded, respect for authority.
* **Values:** Stability, security, conformity.
* **Communication Style:** Formal, respectful, face-to-face.
* **Technology Adoption:** Slow to adopt new technologies.
### Baby Boomers (Born 1946-1964)
* **Defining Events:** The Civil Rights Movement, the Vietnam War, the Cold War.
* **Key Characteristics:** Optimistic, competitive, ambitious, individualistic, work-centric.
* **Values:** Achievement, success, materialism.
* **Communication Style:** Direct, assertive, value in-person meetings.
* **Technology Adoption:** Moderate adoption, comfortable with email and basic computer functions.
### Generation X (Born 1965-1980)
* **Defining Events:** The rise of MTV, the AIDS epidemic, the fall of the Berlin Wall.
* **Key Characteristics:** Independent, resourceful, pragmatic, skeptical, adaptable.
* **Values:** Independence, work-life balance, informality.
* **Communication Style:** Informal, direct, value efficiency.
* **Technology Adoption:** Early adopters of personal computers and the internet.
### Millennials (Born 1981-1996)
* **Defining Events:** The 9/11 terrorist attacks, the Great Recession, the rise of social media.
* **Key Characteristics:** Tech-savvy, collaborative, optimistic, achievement-oriented, socially conscious.
* **Values:** Meaningful work, work-life integration, social responsibility.
* **Communication Style:** Digital, collaborative, prefer instant messaging and social media.
* **Technology Adoption:** Digital natives, highly proficient with technology.
### Generation Z (Born 1997-2012)
* **Defining Events:** The rise of smartphones, social media, and online gaming.
* **Key Characteristics:** Digital natives, entrepreneurial, diverse, pragmatic, concerned about social issues.
* **Values:** Authenticity, diversity, social justice, financial security.
* **Communication Style:** Visual, concise, prefer social media and short-form video.
* **Technology Adoption:** Highly proficient with technology, comfortable with multiple devices and platforms.
### Generation Alpha (Born 2013-2025)
* **Defining Events:** The COVID-19 pandemic, advancements in AI, climate change awareness.
* **Key Characteristics:** Highly connected, tech-dependent, globally aware, environmentally conscious.
* **Values:** Sustainability, inclusivity, innovation.
* **Communication Style:** Visual, interactive, prefer voice and video communication.
* **Technology Adoption:** Growing up with ubiquitous technology, seamless integration into their lives.
## The Impact of Generational Characteristics on the Workplace
The workplace is a melting pot of different generations, each bringing their unique perspectives, skills, and work styles. Understanding these differences is crucial for creating a harmonious and productive work environment.
### Communication Styles and Preferences
Different generations have different communication preferences. For example, Baby Boomers often prefer face-to-face meetings, while Millennials and Gen Z favor digital communication channels like email, instant messaging, and video conferencing. Understanding these preferences can help to improve communication and avoid misunderstandings.
### Work Ethic and Values
Each generation has a different work ethic and set of values. The Silent Generation values loyalty and hard work, while Baby Boomers are driven by achievement and success. Generation X values independence and work-life balance, while Millennials seek meaningful work and social responsibility. Gen Z prioritizes authenticity, diversity, and financial security. Understanding these values can help to motivate and engage employees from different generations.
### Technology Adoption and Skills
The level of technology adoption and skills varies significantly across generations. Millennials and Gen Z are digital natives, highly proficient with technology, while older generations may require more training and support. Leveraging the technological expertise of younger generations can help to improve efficiency and innovation.
## Overcoming Generational Challenges and Fostering Collaboration
While generational differences can present challenges, they can also be a source of strength. By understanding and appreciating the unique perspectives and skills of each generation, organizations can foster collaboration and create a more inclusive and productive work environment.
### Strategies for Bridging the Generational Gap
* **Promote Intergenerational Mentoring:** Pair older and younger employees to share their knowledge and skills.
* **Offer Training and Development Opportunities:** Provide training on communication styles, technology skills, and cultural awareness.
* **Create Inclusive Work Environments:** Foster a culture of respect and appreciation for diversity.
* **Encourage Collaboration and Teamwork:** Design projects that require collaboration across generations.
* **Implement Flexible Work Arrangements:** Offer flexible work options to accommodate the needs of different generations.
## The Future of Generational Studies
As society continues to evolve, so too will the characteristics of different generations. Emerging trends such as artificial intelligence, climate change, and globalization will undoubtedly shape the values, beliefs, and behaviors of future generations. Ongoing research and analysis will be crucial for understanding these trends and their impact on society.
## Insightful Q&A Section
**Q1: How do generational differences impact marketing strategies?**
**A:** Generational differences significantly influence marketing strategies. Each generation responds differently to messaging, channels, and promotional offers. Understanding their values and preferences is crucial for effective targeting. For example, Millennials and Gen Z are more likely to respond to social media campaigns and influencer marketing, while older generations may prefer traditional media channels.
**Q2: What are the main challenges of managing a multigenerational workforce?**
**A:** Managing a multigenerational workforce presents challenges such as communication barriers, differing work styles, and varying expectations regarding work-life balance. It’s essential to foster understanding and create an inclusive environment where each generation feels valued and respected. This requires effective communication strategies and flexible work arrangements.
**Q3: How can organizations leverage the strengths of each generation?**
**A:** Organizations can leverage the strengths of each generation by recognizing their unique skills and experiences. For example, older generations can provide valuable mentorship and institutional knowledge, while younger generations can bring fresh perspectives and technological expertise. Creating opportunities for collaboration and knowledge sharing can maximize the contributions of each generation.
**Q4: What role does technology play in shaping generational characteristics?**
**A:** Technology plays a significant role in shaping generational characteristics. Each generation has grown up with different levels of technological access and proficiency. This influences their communication styles, learning preferences, and work habits. Understanding these differences is essential for effective communication and training.
**Q5: How do generational values impact consumer behavior?**
**A:** Generational values have a direct impact on consumer behavior. Each generation has different priorities and preferences when it comes to purchasing decisions. For example, Millennials and Gen Z are more likely to prioritize sustainability and social responsibility, while older generations may focus on value and quality. Understanding these values is crucial for developing effective marketing campaigns.
**Q6: What are the key differences between Millennials and Generation Z?**
**A:** While both Millennials and Generation Z are digital natives, there are key differences between them. Millennials grew up during a period of economic prosperity and are often characterized as optimistic and achievement-oriented. Generation Z, on the other hand, has grown up in a more uncertain economic climate and is often characterized as pragmatic and financially conscious. Gen Z also tends to be more diverse and socially aware than Millennials.
**Q7: How can generational differences be leveraged for innovation?**
**A:** Generational differences can be a powerful source of innovation. By bringing together individuals from different generations with diverse perspectives and experiences, organizations can foster creativity and generate new ideas. Encouraging collaboration and knowledge sharing can unlock the innovative potential of a multigenerational workforce.
**Q8: What are the implications of generational differences for education?**
**A:** Generational differences have significant implications for education. Each generation has different learning preferences and technological skills. Educators need to adapt their teaching methods to accommodate these differences and create engaging learning experiences. For example, incorporating technology and collaborative projects can be effective strategies for engaging younger generations.
**Q9: How do generational differences affect political views and civic engagement?**
**A:** Generational differences influence political views and civic engagement. Each generation has been shaped by different historical events and social trends, which influence their political ideologies and their level of participation in civic activities. Understanding these differences is crucial for promoting civic engagement and fostering a more inclusive political discourse.
**Q10: Are generational labels always accurate, or are they stereotypes?**
**A:** While generational labels can be useful for understanding broad trends and patterns, it’s important to remember that they are not always accurate and can be oversimplified. Each individual is unique, and there is significant diversity within each generation. It’s essential to avoid generalizations and treat each person as an individual.
## Conclusion: Embracing Generational Diversity for a Brighter Future
Understanding the characteristics of different generations is essential for navigating the complexities of today’s interconnected world. By recognizing the unique values, beliefs, and perspectives of each cohort, we can foster understanding, collaboration, and innovation. While generational differences can present challenges, they also offer opportunities for growth and learning. Embracing generational diversity is not only beneficial for organizations and communities but also for creating a more inclusive and equitable future for all.
Share your experiences with generational differences in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to intergenerational communication for more in-depth insights. Contact our experts for a consultation on building a multigenerational workforce.