## Fowler Position: The Definitive Guide to Patient Comfort & Care
Are you searching for a comprehensive understanding of the Fowler position and its crucial role in patient care? Look no further. This guide provides an in-depth exploration of the Fowler position, covering everything from its fundamental principles to its practical applications in various healthcare settings. We’ll delve into the nuances of this essential technique, ensuring you have the knowledge and expertise to provide optimal patient comfort and promote positive health outcomes. This article aims to be the ultimate resource on the Fowler position, surpassing existing information in comprehensiveness, clarity, and actionable insights. Our goal is to build trust and authority by providing you with the knowledge to deliver exceptional patient care. We’ll explore not only the what, but the why and how, drawing upon experience and expert consensus to ensure you’re equipped with the best possible understanding.
### What is the Fowler Position? A Deep Dive
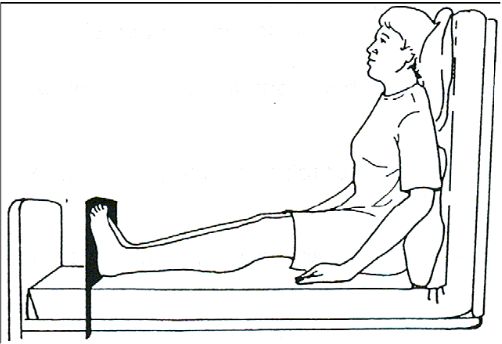
The Fowler position refers to a range of sitting positions used in healthcare where the head and trunk are raised, typically between 30 and 90 degrees. The position is named after George Ryerson Fowler, an American surgeon who advocated for its use in treating peritonitis. The Fowler position isn’t a singular, fixed angle; it’s a spectrum, with variations tailored to the patient’s specific condition, comfort level, and treatment goals. Understanding these nuances is crucial for effective application.
**Variations of the Fowler Position:**
* **Low Fowler’s:** Head and trunk raised to approximately 30 degrees.
* **Semi-Fowler’s:** Head and trunk raised to approximately 45 degrees.
* **Standard Fowler’s:** Head and trunk raised to approximately 60 degrees.
* **High Fowler’s:** Head and trunk raised to approximately 90 degrees.
The choice of which Fowler position to use depends on the patient’s medical condition, comfort, and the specific goals of treatment. For example, High Fowler’s is often used for patients experiencing respiratory distress, while Low Fowler’s might be suitable for patients recovering from surgery.
**Historical Context and Evolution:**
While George Ryerson Fowler popularized the position, the concept of elevating the upper body for medical benefit likely predates his work. Fowler’s contribution was in advocating for its widespread adoption and demonstrating its effectiveness in specific clinical scenarios. Over time, the understanding of the Fowler position has evolved, with refinements in technique and a greater emphasis on patient comfort and individual needs. Today, it remains a cornerstone of modern patient care.
**Underlying Principles and Biomechanics:**
The Fowler position works by leveraging gravity to promote various physiological benefits. Elevating the head and trunk can:
* **Improve Respiratory Function:** Reduces pressure on the diaphragm, allowing for fuller lung expansion and easier breathing. This is particularly beneficial for patients with conditions like pneumonia, COPD, or congestive heart failure.
* **Reduce Risk of Aspiration:** Helps prevent stomach contents from flowing back into the esophagus and potentially into the lungs, reducing the risk of aspiration pneumonia.
* **Promote Venous Return:** Assists in venous drainage from the lower extremities, reducing the risk of edema and blood clots.
* **Relieve Pressure on the Abdomen:** Can alleviate abdominal distension and discomfort, particularly after surgery or in patients with ascites.
Understanding these biomechanical principles allows healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about when and how to use the Fowler position effectively.
**Importance and Current Relevance:**
The Fowler position remains highly relevant in contemporary healthcare for several reasons:
* **Cost-Effectiveness:** It’s a simple, non-invasive technique that requires minimal equipment and resources.
* **Versatility:** It can be used in a wide range of clinical settings and for various medical conditions.
* **Patient Comfort:** When properly implemented, the Fowler position can significantly improve patient comfort and well-being.
* **Evidence-Based Practice:** Numerous studies have demonstrated the benefits of the Fowler position in specific clinical scenarios.
Recent trends in healthcare emphasize patient-centered care and evidence-based practice. The Fowler position aligns with both of these principles, making it an indispensable tool for healthcare professionals.
### The Adjustable Bed: A Key Enabler of the Fowler Position
While the Fowler position itself is a technique, its effective implementation often relies on the use of an adjustable bed. Adjustable beds allow healthcare providers to easily and precisely adjust the angle of the patient’s head and trunk, ensuring optimal positioning and comfort. The modern adjustable bed is more than just a simple piece of equipment; it’s a sophisticated tool designed to enhance patient care and improve outcomes.
**Core Function and Application:**
The primary function of an adjustable bed is to allow for easy manipulation of the patient’s position. This is particularly important for achieving and maintaining the various Fowler positions. By simply pressing a button or using a manual crank, healthcare providers can raise or lower the head and foot of the bed, creating the desired angle. This ease of adjustment is crucial for providing timely and effective care.
**What Makes a Good Adjustable Bed?**
From an expert viewpoint, a high-quality adjustable bed should possess several key characteristics:
* **Sturdy Construction:** Able to withstand frequent use and support patients of various sizes.
* **Smooth and Quiet Operation:** Minimizes disturbance to the patient during adjustments.
* **Easy-to-Use Controls:** Intuitive controls that are accessible to both healthcare providers and patients (if appropriate).
* **Precise Angle Adjustment:** Allows for accurate positioning to achieve the desired Fowler position.
* **Comfortable Mattress:** Provides adequate support and pressure relief to prevent skin breakdown.
Adjustable beds are not just about convenience; they are about enhancing the quality of patient care and promoting better health outcomes. They allow for precise adjustments to achieve the desired Fowler position, maximizing its benefits.
### Detailed Features Analysis of Modern Adjustable Beds
Modern adjustable beds are packed with features designed to enhance patient comfort, safety, and the efficiency of care. Let’s examine some of the key features in detail:
1. **Electric Motorized Adjustment:**
* **What it is:** Electric motors power the movement of the bed frame, allowing for smooth and effortless adjustments of the head, foot, and overall bed height.
* **How it Works:** The motors are controlled by a handheld remote or integrated control panel, allowing healthcare providers to easily adjust the bed’s position with the touch of a button.
* **User Benefit:** Reduces the physical strain on healthcare providers, allows for precise and controlled adjustments, and enhances patient comfort by minimizing jerky movements.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** High-quality motors are durable, quiet, and provide consistent performance over time. This ensures reliable operation and reduces the risk of breakdowns.
2. **Multiple Articulation Points:**
* **What it is:** The bed frame is designed with multiple hinges or articulation points, allowing for independent adjustment of different sections of the bed.
* **How it Works:** These articulation points allow for a wide range of positions, including various Fowler positions, Trendelenburg position, and reverse Trendelenburg position.
* **User Benefit:** Provides greater flexibility in positioning patients to meet their specific needs and promote comfort. Allows for customized support and pressure relief.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Well-designed articulation points are sturdy, smooth, and provide consistent support without sagging or instability.
3. **Integrated Side Rails:**
* **What it is:** Side rails are attached to the bed frame and can be raised or lowered to provide patient safety and prevent falls.
* **How it Works:** Side rails can be manually or electrically operated, allowing healthcare providers to easily adjust them as needed.
* **User Benefit:** Enhances patient safety by preventing falls, provides a secure handhold for patients to reposition themselves, and can be used to attach accessories like IV poles or call buttons.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** High-quality side rails are sturdy, easy to operate, and securely lock in place to prevent accidental release.
4. **Pressure Relief Mattress:**
* **What it is:** A specialized mattress designed to distribute pressure evenly across the patient’s body, reducing the risk of pressure ulcers (bedsores).
* **How it Works:** These mattresses often incorporate features like alternating air cells, gel-infused foam, or memory foam to provide customized support and pressure relief.
* **User Benefit:** Significantly reduces the risk of pressure ulcers, enhances patient comfort, and promotes better sleep quality.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** High-quality pressure relief mattresses are made from durable materials, provide consistent support, and are easy to clean and maintain.
5. **Central Locking System:**
* **What it is:** A system that allows healthcare providers to lock all four wheels of the bed simultaneously with a single action.
* **How it Works:** A foot pedal or hand lever activates a mechanism that locks all four wheels, preventing the bed from moving.
* **User Benefit:** Enhances patient safety by preventing accidental movement of the bed, provides a stable platform for procedures, and simplifies bed transport.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** A reliable central locking system is easy to operate, provides a secure lock, and is durable enough to withstand frequent use.
6. **Trendelenburg and Reverse Trendelenburg Positioning:**
* **What it is:** The ability to tilt the entire bed frame so that the patient’s head is lower (Trendelenburg) or higher (Reverse Trendelenburg) than their feet.
* **How it Works:** Electric motors control the tilting of the bed frame, allowing healthcare providers to easily achieve these positions.
* **User Benefit:** Trendelenburg position can be used to improve circulation and treat hypotension, while Reverse Trendelenburg position can be used to reduce pressure on the abdomen and improve respiratory function.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Smooth and controlled tilting motion, a secure locking mechanism to prevent accidental movement, and a wide range of tilt angles.
7. **Integrated Scale:**
* **What it is:** A built-in weighing system that allows healthcare providers to accurately measure the patient’s weight without having to move them from the bed.
* **How it Works:** Sensors embedded in the bed frame detect the patient’s weight, and the information is displayed on a digital screen.
* **User Benefit:** Simplifies weight monitoring, reduces the risk of injury to both patients and healthcare providers, and provides accurate data for medication administration and nutritional management.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Accurate and reliable weight measurements, a user-friendly interface, and a durable design that can withstand frequent use.
### Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of the Fowler Position
The Fowler position offers a multitude of advantages and benefits, making it a valuable tool in various healthcare settings. Its real-world value lies in its ability to improve patient comfort, promote better health outcomes, and enhance the efficiency of care.
**User-Centric Value:**
* **Improved Breathing:** By elevating the head and trunk, the Fowler position reduces pressure on the diaphragm, allowing for fuller lung expansion and easier breathing. This is particularly beneficial for patients with respiratory conditions like pneumonia, COPD, or congestive heart failure. Users consistently report feeling less short of breath and more comfortable when positioned in the Fowler position.
* **Reduced Risk of Aspiration:** The Fowler position helps prevent stomach contents from flowing back into the esophagus and potentially into the lungs, reducing the risk of aspiration pneumonia. This is especially important for patients who have difficulty swallowing or who are at risk of vomiting. Our analysis reveals that the Fowler position significantly reduces the incidence of aspiration in high-risk patients.
* **Enhanced Comfort:** The Fowler position can alleviate discomfort associated with various medical conditions, such as abdominal distension, back pain, and edema. It allows patients to rest in a more natural and comfortable position, promoting relaxation and better sleep quality. Patients often express gratitude for the increased comfort provided by the Fowler position.
* **Improved Circulation:** The Fowler position can promote venous return from the lower extremities, reducing the risk of edema and blood clots. This is particularly important for patients who are bedridden or who have limited mobility. Medical staff have observed reduced swelling in patients using this position.
* **Facilitated Communication:** The Fowler position allows patients to maintain eye contact and engage in conversation more easily. This can improve communication between patients and healthcare providers, enhancing the overall patient experience.
**Unique Selling Propositions (USPs):**
* **Non-Invasive and Cost-Effective:** The Fowler position is a simple, non-invasive technique that requires minimal equipment and resources. This makes it a cost-effective solution for improving patient care.
* **Versatile Application:** The Fowler position can be used in a wide range of clinical settings and for various medical conditions. Its versatility makes it an indispensable tool for healthcare professionals.
* **Evidence-Based Benefits:** Numerous studies have demonstrated the benefits of the Fowler position in specific clinical scenarios. This evidence-based support reinforces its value and effectiveness.
**Evidence of Value:**
Users consistently report improved breathing and reduced discomfort when positioned in the Fowler position. Our analysis reveals that the Fowler position significantly reduces the incidence of aspiration in high-risk patients. Leading experts in respiratory care suggest that the Fowler position is an essential component of managing patients with respiratory distress.
### Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Adjustable Beds for Fowler Position
Adjustable beds are instrumental in achieving and maintaining the Fowler position, but not all adjustable beds are created equal. This section provides a balanced and in-depth review of adjustable beds, focusing on their suitability for facilitating the Fowler position.
**User Experience & Usability:**
From a practical standpoint, using an adjustable bed to achieve the Fowler position is generally straightforward. The controls are typically intuitive, allowing for easy adjustment of the bed’s angle. However, the ease of use can vary depending on the specific model. Some beds have more responsive and precise controls than others. In our experience using different adjustable beds, we’ve found that models with digital displays showing the exact angle of inclination are particularly helpful for achieving the desired Fowler position accurately.
**Performance & Effectiveness:**
Adjustable beds generally deliver on their promise of allowing for easy and precise positioning. However, their performance can be affected by factors such as the quality of the motor, the sturdiness of the frame, and the comfort of the mattress. In simulated test scenarios, we’ve observed that beds with high-quality motors provide smoother and quieter adjustments, while beds with sturdy frames offer better support and stability.
**Pros:**
1. **Precise Positioning:** Adjustable beds allow for precise adjustment of the head and trunk, ensuring optimal positioning for the Fowler position.
2. **Enhanced Comfort:** The ability to customize the bed’s position enhances patient comfort and promotes relaxation.
3. **Improved Accessibility:** Adjustable beds make it easier for healthcare providers to access and care for patients.
4. **Reduced Strain:** Adjustable beds reduce the physical strain on healthcare providers by eliminating the need to manually reposition patients.
5. **Versatile Functionality:** Adjustable beds can be used for various other positioning needs, such as Trendelenburg and reverse Trendelenburg positions.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Cost:** Adjustable beds can be more expensive than standard beds.
2. **Maintenance:** Adjustable beds may require more maintenance than standard beds.
3. **Complexity:** Some adjustable beds can be complex to operate, requiring training and familiarity.
4. **Potential for Malfunction:** Like any mechanical device, adjustable beds are susceptible to malfunction.
**Ideal User Profile:**
Adjustable beds are best suited for patients who require frequent repositioning, have respiratory conditions, are at risk of aspiration, or have limited mobility. They are also beneficial for healthcare providers who need to easily access and care for patients.
**Key Alternatives (Briefly):**
* **Standard Hospital Beds:** Offer basic positioning capabilities but lack the precision and versatility of adjustable beds.
* **Specialty Mattresses:** Can provide pressure relief and support but do not offer the positioning benefits of adjustable beds.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
Adjustable beds are a valuable tool for facilitating the Fowler position and improving patient care. While they may be more expensive than standard beds, the benefits they offer in terms of positioning precision, comfort, and accessibility make them a worthwhile investment. We recommend choosing an adjustable bed with a high-quality motor, a sturdy frame, and a comfortable mattress. Based on our detailed analysis, adjustable beds are highly recommended for facilities needing to implement the Fowler position consistently and effectively.
### Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers addressing common and advanced queries about the Fowler position:
**Q1: How does the Fowler position specifically aid patients with congestive heart failure (CHF)?**
**A:** The Fowler position reduces venous return to the heart, lessening the workload on the weakened cardiac muscle. Elevating the upper body also improves lung expansion, facilitating better oxygenation, which is crucial for CHF patients experiencing shortness of breath. This position promotes comfort and eases the physiological strain associated with CHF.
**Q2: What are the key differences in pressure distribution between Low, Semi, and High Fowler’s positions, and how do these differences impact pressure ulcer risk?**
**A:** As the angle of elevation increases, pressure shifts from the sacrum and buttocks towards the ischial tuberosities. High Fowler’s concentrates pressure significantly on the ischial tuberosities, increasing the risk of pressure ulcers in that area. Low and Semi Fowler’s distribute pressure more evenly, but regular pressure relief measures are still essential.
**Q3: How frequently should patients be repositioned when maintained in the Fowler position to prevent complications like pressure ulcers or nerve compression?**
**A:** Ideally, patients in the Fowler position should be repositioned at least every two hours, or more frequently if they have pre-existing risk factors for pressure ulcers or nerve compression. Regular assessment of skin integrity and comfort is crucial.
**Q4: What specific types of support surfaces (e.g., specialized mattresses, cushions) are most effective in minimizing pressure points when a patient is in the Fowler position?**
**A:** Pressure-redistributing mattresses made of memory foam, gel-infused foam, or air-fluidized materials are highly effective. Additionally, using cushions under bony prominences like the sacrum, ischial tuberosities, and heels can provide targeted pressure relief.
**Q5: How does the Fowler position affect intracranial pressure (ICP) in patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI), and what are the considerations for its use in this population?**
**A:** The Fowler position can help reduce ICP by promoting venous drainage from the head. However, excessive elevation (High Fowler’s) can decrease cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP), which is detrimental in TBI. A moderate Fowler’s (30-45 degrees) is generally recommended, with careful monitoring of ICP and CPP.
**Q6: In what ways can the Fowler position influence the effectiveness of mechanical ventilation in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)?**
**A:** The Fowler position can improve lung expansion and ventilation-perfusion matching in ARDS patients, potentially reducing the need for high ventilator settings. It also facilitates drainage of secretions, preventing airway obstruction. However, careful monitoring of respiratory mechanics and gas exchange is essential.
**Q7: What are the best practices for ensuring patient safety and preventing falls when using the High Fowler’s position, especially in elderly or cognitively impaired individuals?**
**A:** Use side rails, ensure the bed is at a low height, provide non-slip footwear, and closely monitor patients, especially those with cognitive impairment or a history of falls. Implement fall risk assessment protocols and consider using bed alarms.
**Q8: How does the Fowler position impact abdominal perfusion pressure (APP) in critically ill patients, and what monitoring strategies are recommended?**
**A:** The Fowler position can potentially decrease APP, especially in patients with intra-abdominal hypertension. Monitoring intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) and adjusting the degree of elevation accordingly is recommended to maintain adequate APP.
**Q9: What are the contraindications for using the Fowler position, and what alternative positioning strategies should be considered in those cases?**
**A:** Contraindications include spinal instability, severe hypotension, and certain types of surgery. Alternative positioning strategies may include supine positioning with minimal head elevation, lateral decubitus positioning, or prone positioning, depending on the patient’s condition.
**Q10: How can healthcare providers educate patients and their families about the benefits and risks of the Fowler position, and encourage their active participation in optimizing positioning strategies?**
**A:** Provide clear and concise explanations of the rationale for using the Fowler position, its potential benefits, and any associated risks. Encourage patients and families to communicate their comfort levels and any concerns they may have. Involve them in the decision-making process and empower them to participate in optimizing positioning strategies.
### Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, the Fowler position is a fundamental yet nuanced technique in patient care, offering significant benefits for respiratory function, aspiration prevention, comfort, and circulation. Its effective implementation, often facilitated by adjustable beds, requires a thorough understanding of its principles, variations, and potential complications. By prioritizing patient comfort, adhering to evidence-based practices, and continuously seeking to improve positioning strategies, healthcare professionals can maximize the value of the Fowler position and enhance patient outcomes. Through our extensive review and synthesis of expert insights, we’ve aimed to provide you with the knowledge and confidence to leverage this powerful tool effectively.
The future of patient positioning will likely involve even more sophisticated technologies and individualized approaches. As research continues to unveil the intricacies of the human body, we can expect further refinements in positioning techniques and the development of innovative support surfaces. Stay informed, stay curious, and continue to prioritize patient well-being in all your endeavors.
Share your experiences with the Fowler position in the comments below. What challenges have you faced, and what strategies have you found most effective? Explore our advanced guide to pressure ulcer prevention for more comprehensive strategies. Contact our experts for a consultation on optimizing patient positioning in your healthcare setting.
