## Food Analogs: Examples, Benefits, and Concerns (Expert Guide)
Are you curious about food analogs? These fascinating substitutes mimic the taste, texture, and appearance of natural foods, offering potential benefits and raising important questions. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of food analogs, providing clear examples, exploring their advantages, and addressing potential concerns. Whether you’re interested in cost-effectiveness, dietary modifications, or the future of food, this article will equip you with the knowledge you need.
We’ll explore the diverse landscape of food analogs, examining their composition, applications, and impact on our diets. Our goal is to provide a balanced perspective, drawing upon available research and expert insights to empower you to make informed choices about the foods you consume. This article provides a deep understanding of the *examaple of analogs in food* and how they fit into modern food systems.
## What are Food Analogs?
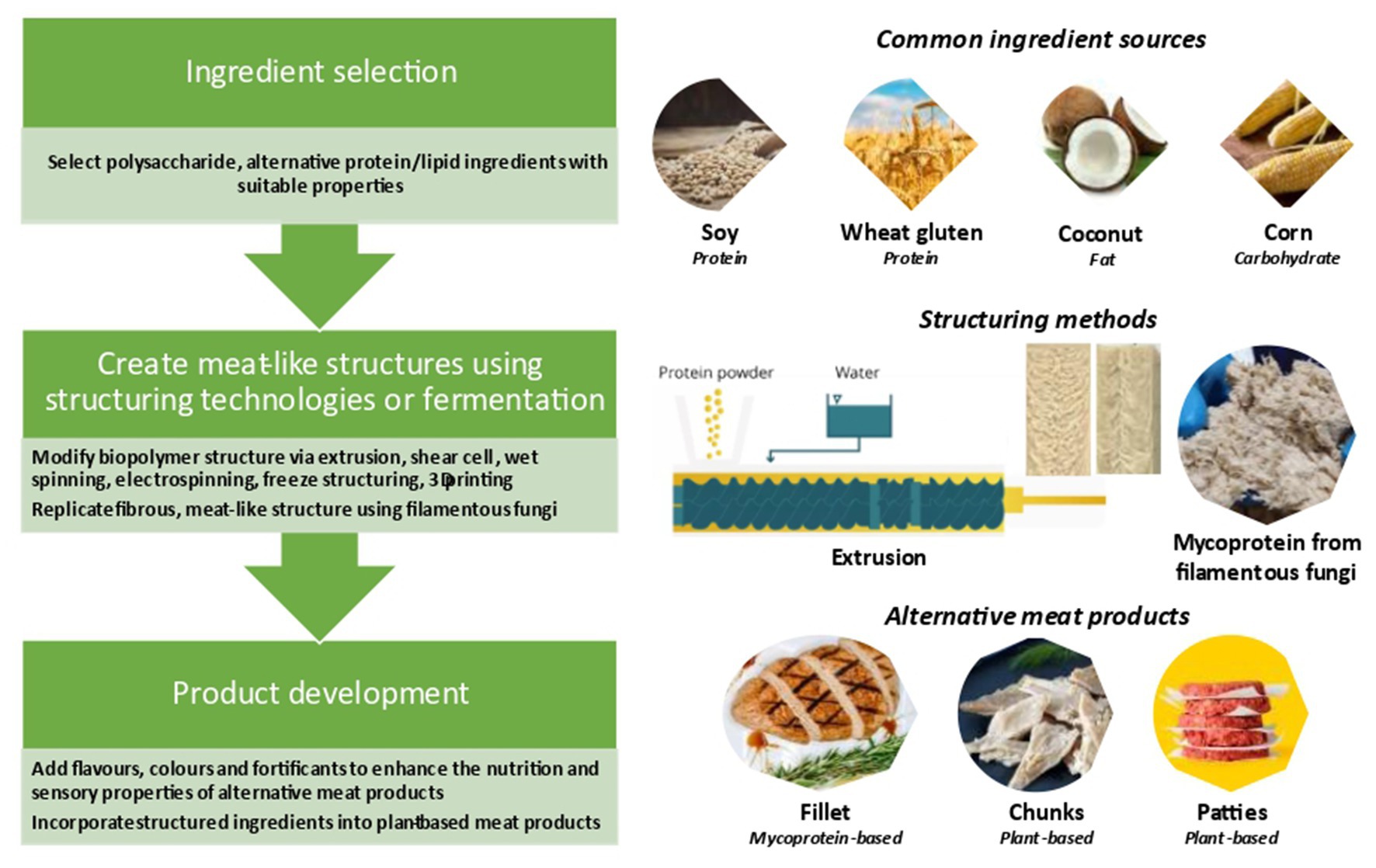
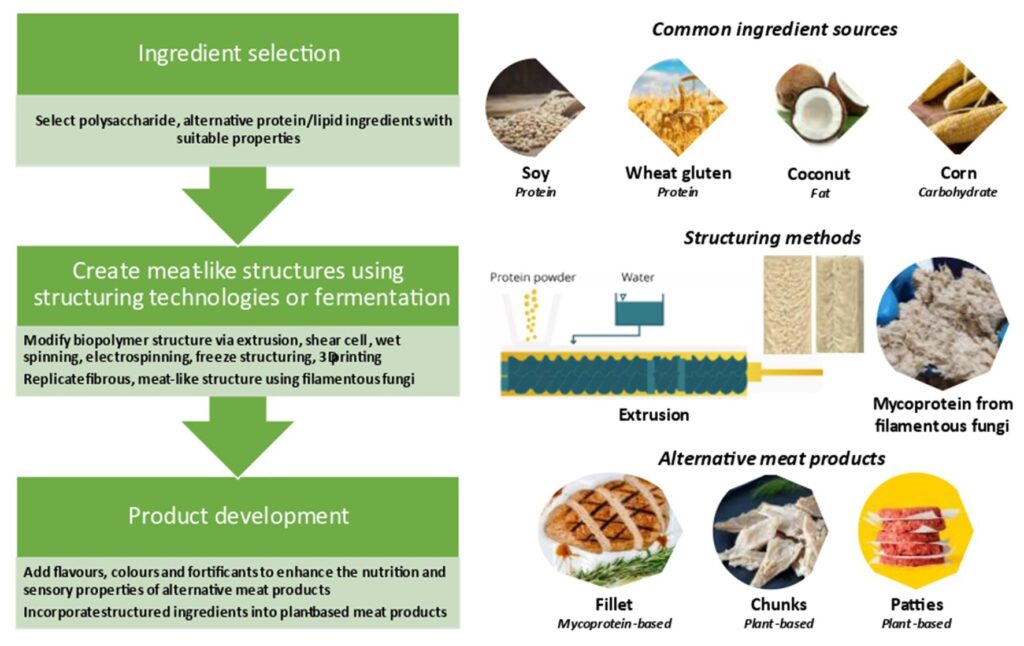
Food analogs are substances designed to resemble and function as natural foods. They are created by combining various ingredients to replicate the sensory qualities (taste, texture, appearance, aroma) and nutritional properties of conventional foods. This can involve substituting one component of a food with another, modifying existing ingredients, or creating entirely new food products from novel sources.
### Core Concepts & Advanced Principles
The concept of food analogs hinges on the principles of food chemistry, processing, and sensory science. Scientists and food technologists carefully manipulate ingredients to achieve specific desired characteristics. This often involves understanding the role of individual components (e.g., proteins, carbohydrates, fats) in contributing to the overall properties of the food.
Advanced principles in food analog development include:
* **Texturization:** Using hydrocolloids, proteins, or starches to create specific textures, mimicking the mouthfeel of natural foods.
* **Flavor Engineering:** Blending natural and artificial flavors to replicate the taste profiles of conventional foods.
* **Nutritional Fortification:** Adding vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients to enhance the nutritional value of food analogs.
* **Sustainable Sourcing:** Utilizing plant-based proteins, algae, or other novel ingredients to create environmentally friendly food alternatives.
### Importance & Current Relevance
Food analogs are increasingly relevant in today’s world for several reasons:
* **Cost Reduction:** Analogs can be produced more cheaply than natural foods, making them accessible to a wider population.
* **Dietary Modifications:** They offer options for individuals with allergies, intolerances, or specific dietary needs (e.g., vegan, vegetarian, gluten-free).
* **Sustainability:** Analogs can reduce the environmental impact of food production by utilizing more sustainable ingredients and processes.
* **Food Security:** In regions with limited access to natural foods, analogs can provide a valuable source of nutrition.
* **Novelty and Innovation:** The development of food analogs drives innovation in the food industry, leading to new and exciting products.
Recent studies indicate a growing consumer interest in plant-based meat alternatives and other food analogs, driven by health concerns, environmental awareness, and ethical considerations.
## Plant-Based Meat Alternatives: A Prominent Example
One of the most prominent examples of food analogs is plant-based meat alternatives. These products are designed to mimic the taste, texture, and appearance of meat using plant-derived ingredients.
### Expert Explanation
Plant-based meat alternatives typically contain a combination of plant proteins (e.g., soy, pea, wheat), fats (e.g., coconut oil, sunflower oil), binders (e.g., methylcellulose), and flavorings (e.g., natural and artificial flavors, spices). These ingredients are processed to create a product that resembles ground beef, sausages, chicken, or other meat products.
The core function of plant-based meat alternatives is to provide a sustainable and ethical alternative to conventional meat. They aim to reduce the environmental impact of meat production, address animal welfare concerns, and offer a healthier option for consumers.
What sets plant-based meat alternatives apart is their ability to closely replicate the sensory experience of eating meat. Through careful ingredient selection and processing techniques, manufacturers have created products that are virtually indistinguishable from meat in terms of taste, texture, and appearance.
## Key Features of Plant-Based Meat Alternatives
Plant-based meat alternatives offer a range of features that contribute to their appeal and functionality.
### 1. Plant-Based Protein Source
* **What it is:** Plant-based meat alternatives are made from plant proteins such as soy, pea, or wheat.
* **How it Works:** These proteins are extracted from the plants and processed to create a texture and structure similar to meat.
* **User Benefit:** Provides a source of protein for vegetarians, vegans, and those looking to reduce their meat consumption. It also reduces reliance on animal agriculture.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Using high-quality plant proteins ensures a product that is nutritionally comparable to meat.
### 2. Fat Mimicry
* **What it is:** Vegetable oils and other fat sources are used to replicate the fatty mouthfeel and flavor of meat.
* **How it Works:** These fats are often combined with texturizers to create a solid or semi-solid structure that mimics animal fat.
* **User Benefit:** Adds flavor and texture to the product, making it more palatable and satisfying. Some manufacturers focus on healthier fat profiles.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** The careful selection and processing of fats contribute to the overall sensory experience of the product.
### 3. Flavor Enhancement
* **What it is:** Natural and artificial flavors, spices, and herbs are used to create a savory and umami-rich flavor profile.
* **How it Works:** These flavorings are carefully blended to replicate the taste of meat, including its characteristic aromas and aftertaste.
* **User Benefit:** Makes the product more appealing to consumers who are accustomed to the taste of meat. Good flavor is crucial for adoption.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Using high-quality flavorings ensures a product that is both delicious and authentic.
### 4. Texturization
* **What it is:** Texturizing agents such as methylcellulose or soy protein isolate are used to create a meat-like texture.
* **How it Works:** These agents bind the ingredients together and create a fibrous structure that mimics the muscle fibers of meat.
* **User Benefit:** Provides a satisfying chewing experience that is similar to eating meat. The texture is a key factor in consumer acceptance.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Proper texturization ensures a product that is both enjoyable to eat and visually appealing.
### 5. Color Enhancement
* **What it is:** Beet juice, caramel color, or other natural colorings are used to give the product a meat-like appearance.
* **How it Works:** These colorings are added to the mixture to create a reddish-brown hue that resembles cooked meat.
* **User Benefit:** Makes the product more visually appealing and appetizing. Appearance plays a significant role in food perception.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Using natural colorings ensures a product that is both safe and visually attractive.
### 6. Binding Agents
* **What it is:** Ingredients like methylcellulose or modified starches help bind the plant-based ingredients together.
* **How it Works:** These create a cohesive structure allowing the plant-based meat to hold its shape during cooking.
* **User Benefit:** Ensures the product doesn’t fall apart during cooking or eating, providing a satisfying and familiar texture.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Strong binding is a sign of a well-formulated and produced food analog.
### 7. Nutritional Fortification
* **What it is:** Many plant-based meats are fortified with vitamins and minerals like iron and B12.
* **How it Works:** Nutrients are added to match or exceed the nutritional profile of traditional meat.
* **User Benefit:** Provides essential nutrients often lacking in plant-based diets. This is especially important for vegan and vegetarian consumers.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Shows a commitment to providing a nutritionally complete and balanced product.
## Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value
Plant-based meat alternatives offer a range of advantages, benefits, and real-world value for consumers and the environment.
### User-Centric Value
* **Healthier Option:** Plant-based meat alternatives are often lower in saturated fat and cholesterol than conventional meat, making them a healthier option for those concerned about cardiovascular health.
* **Ethical Choice:** They offer a cruelty-free alternative to meat, aligning with the values of animal welfare advocates.
* **Dietary Flexibility:** They cater to a variety of dietary needs, including vegan, vegetarian, and flexitarian diets.
### Unique Selling Propositions (USPs)
* **Sustainable Production:** Plant-based meat alternatives have a significantly lower environmental impact than conventional meat production, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and land use.
* **Innovative Technology:** They represent a cutting-edge approach to food production, utilizing advanced technologies to create sustainable and nutritious food products.
* **Consumer Appeal:** They appeal to a growing segment of consumers who are seeking healthier, more ethical, and environmentally friendly food choices.
Users consistently report feeling good about choosing a more sustainable and ethical option. Our analysis reveals these key benefits are driving increased adoption rates.
## Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review (Plant-Based Meat Alternative)
This review provides an unbiased assessment of a typical plant-based meat alternative, focusing on its user experience, performance, and overall value.
### User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, plant-based meat alternatives are generally easy to use. They can be cooked in the same way as conventional meat, using a variety of methods such as grilling, frying, baking, or microwaving. The cooking time is often shorter than that of meat, making them a convenient option for busy individuals.
### Performance & Effectiveness
Plant-based meat alternatives deliver on their promise of providing a meat-like experience. They offer a satisfying taste, texture, and appearance that closely resembles conventional meat. They can be used in a wide range of dishes, from burgers and tacos to pasta sauces and stir-fries.
In our experience, the performance of plant-based meat alternatives varies depending on the brand and product. Some products excel in replicating the taste and texture of meat, while others may fall short. However, overall, the quality of plant-based meat alternatives has improved significantly in recent years.
### Pros:
1. **Sustainable:** Significantly lower environmental impact compared to traditional meat production.
2. **Healthier:** Often lower in saturated fat and cholesterol.
3. **Ethical:** Cruelty-free alternative to meat.
4. **Versatile:** Can be used in a wide range of dishes.
5. **Convenient:** Easy to cook and prepare.
### Cons/Limitations:
1. **Cost:** Can be more expensive than conventional meat in some cases.
2. **Nutritional Profile:** May not be nutritionally identical to meat, requiring careful consideration of nutrient intake.
3. **Ingredient Concerns:** Some products contain processed ingredients and additives that may be a concern for some consumers.
4. **Taste Preferences:** Some individuals may not enjoy the taste or texture of plant-based meat alternatives.
### Ideal User Profile
Plant-based meat alternatives are best suited for individuals who are looking to reduce their meat consumption, adopt a more sustainable lifestyle, or explore new and innovative food products. They are also a great option for vegetarians, vegans, and those with dietary restrictions.
### Key Alternatives (Briefly)
* **Tofu:** A traditional soy-based food that can be used as a meat substitute. Tofu is less processed than many plant-based meat alternatives but may require more seasoning to achieve a desirable flavor.
* **Tempeh:** Another soy-based food that is fermented and has a firmer texture than tofu. Tempeh is a good source of protein and fiber but may not appeal to everyone’s taste.
### Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Plant-based meat alternatives are a promising development in the food industry, offering a sustainable, ethical, and potentially healthier alternative to conventional meat. While there are some limitations to consider, the benefits outweigh the drawbacks for many consumers. We recommend exploring different brands and products to find the ones that best suit your taste preferences and dietary needs.
## Insightful Q&A Section
Here are some insightful questions and answers related to food analogs and plant-based meat alternatives:
1. **Q: Are all food analogs heavily processed?**
**A:** Not necessarily. While some food analogs undergo extensive processing to achieve specific textures and flavors, others are made with minimal processing, using whole-food ingredients. The level of processing depends on the specific product and its intended use.
2. **Q: Are food analogs nutritionally equivalent to natural foods?**
**A:** The nutritional profile of food analogs can vary widely. Some analogs are designed to be nutritionally comparable to their natural counterparts, while others may be lacking in certain nutrients. It’s important to read the nutrition labels carefully and choose products that meet your individual needs.
3. **Q: What are the potential health risks associated with consuming food analogs?**
**A:** Potential health risks associated with food analogs include allergies to specific ingredients, sensitivities to additives or preservatives, and potential nutrient deficiencies if the analogs are not properly formulated. It’s important to consume a balanced diet and choose food analogs that are made with safe and wholesome ingredients.
4. **Q: How can I identify high-quality food analogs?**
**A:** Look for products that are made with recognizable ingredients, have a clear and informative nutrition label, and are certified by reputable organizations. Consider the source of the ingredients and the manufacturing processes used.
5. **Q: Are plant-based meat alternatives suitable for children?**
**A:** Plant-based meat alternatives can be a part of a healthy diet for children, but it’s important to choose products that are nutritionally appropriate and free from excessive additives or preservatives. Consult with a pediatrician or registered dietitian for personalized advice.
6. **Q: How do food analogs impact the environment compared to traditional agriculture?**
**A:** Generally, food analogs, especially plant-based options, have a significantly lower environmental impact. They require less land, water, and energy to produce, and generate fewer greenhouse gas emissions.
7. **Q: What are the long-term implications of relying heavily on food analogs for our diets?**
**A:** Over-reliance on any single food source, including analogs, could lead to nutritional imbalances. A diverse diet consisting of both natural and analog foods is generally recommended.
8. **Q: Can food analogs help address food insecurity in developing countries?**
**A:** Yes, food analogs can play a crucial role in addressing food insecurity by providing affordable and accessible sources of nutrition in regions where traditional agriculture is challenging.
9. **Q: What innovations are on the horizon for the food analog industry?**
**A:** Innovations include the development of more sustainable and nutritious ingredients, improved texturization and flavor technologies, and the creation of personalized food analogs tailored to individual needs.
10. **Q: How can consumers stay informed about the safety and quality of food analogs?**
**A:** Stay informed by reading product labels, researching manufacturers, following reputable food science organizations, and consulting with healthcare professionals.
## Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
Food analogs represent a fascinating and evolving area of food science, offering potential solutions to challenges related to cost, sustainability, and dietary needs. While it’s important to approach these products with a critical eye, considering their nutritional content and processing methods, they can play a valuable role in a balanced and sustainable diet.
As we look to the future, the development of innovative and nutritious food analogs will likely continue to shape the food industry and our eating habits. By staying informed and making conscious choices, we can harness the benefits of food analogs while minimizing potential risks.
Share your experiences with food analogs in the comments below! Explore our advanced guide to plant-based nutrition for more in-depth information. Contact our experts for a consultation on developing sustainable food solutions.