Quartz in Granite: The Definitive Guide to Identification, Properties, and Uses
Granite, a ubiquitous igneous rock, forms the very foundation of continents and captures the imagination with its varied colors and textures. A key component of this durable stone is quartz. Understanding the role and characteristics of **quartz in granite** is essential for geologists, architects, designers, and anyone appreciating the natural beauty of this material. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of quartz within granite, offering expert insights into its identification, properties, uses, and significance. We aim to provide a resource that goes beyond basic definitions, offering a deep dive into the fascinating world of granite’s most abundant mineral. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of how **quartz in granite** influences the rock’s overall characteristics and applications.
Deep Dive into Quartz in Granite
Granite, at its core, is a coarse-grained igneous rock primarily composed of quartz, feldspar, and mica. The precise proportions of these minerals dictate the granite’s color, texture, and overall properties. Quartz, typically the second most abundant mineral after feldspar, plays a crucial role in granite’s durability and aesthetic appeal.
Comprehensive Definition, Scope, & Nuances
Quartz (SiO2), in its pure form, is a crystalline mineral composed of silicon and oxygen atoms arranged in a continuous framework. However, within granite, quartz rarely exists in its purest form. Trace elements and imperfections can subtly alter its color and transparency. Its presence in granite is a direct result of the slow cooling of magma deep within the Earth’s crust. As the magma cools, different minerals crystallize at different temperatures. Quartz, being one of the last minerals to crystallize, often fills the spaces between the earlier-formed feldspar and mica crystals. This late-stage crystallization contributes to the characteristic interlocking texture of granite.
The term “quartz in granite” encompasses more than just the mineral’s presence. It includes its grain size, distribution, and relationship to other minerals within the rock. The size of quartz grains can range from microscopic to several millimeters, influencing the overall texture of the granite. The distribution can be uniform, creating a consistent appearance, or irregular, resulting in a more variegated pattern. The relationship between quartz and other minerals, such as the presence of inclusions or intergrowths, can further impact the granite’s properties.
Core Concepts & Advanced Principles
The behavior of quartz within granite is governed by several key geological principles. Bowen’s Reaction Series, a fundamental concept in igneous petrology, explains the order in which minerals crystallize from cooling magma. Quartz, being at the bottom of the discontinuous series, crystallizes at relatively low temperatures. This explains why it often fills the remaining space in granite.
Another important concept is the solid solution series of feldspars. Feldspars, being the most abundant mineral in granite, can incorporate various elements into their crystal structure, influencing the composition of the remaining magma. As the magma becomes depleted in certain elements, the conditions become more favorable for quartz crystallization.
Advanced analysis techniques, such as electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction, are used to study the microstructure and composition of quartz grains in granite. These techniques can reveal the presence of microscopic inclusions, crystal defects, and other features that influence the granite’s properties. Based on expert consensus, understanding these microscopic details is crucial for predicting the long-term durability and weathering resistance of granite.
Importance & Current Relevance
Quartz in granite is not merely a geological curiosity; it has significant practical implications. The presence and characteristics of quartz directly influence the granite’s strength, hardness, and resistance to weathering. Granite with a high quartz content tends to be more durable and resistant to abrasion, making it suitable for applications such as countertops, flooring, and building facades. Recent studies indicate that the size and distribution of quartz grains also affect the granite’s susceptibility to thermal shock.
The aesthetic appeal of granite is also heavily influenced by the presence of quartz. The color and transparency of quartz can contribute to the overall color and pattern of the granite. The way quartz interacts with light can create a sparkling or shimmering effect, adding to the granite’s visual appeal. In our experience with quartz in granite, different types of quartz can dramatically change the rock’s aesthetic.
Furthermore, the study of quartz in granite provides valuable insights into the Earth’s geological history. By analyzing the mineral composition and texture of granite, geologists can reconstruct the conditions under which the rock formed. This information can be used to understand the evolution of continents, the formation of mountain ranges, and the processes that shape our planet.
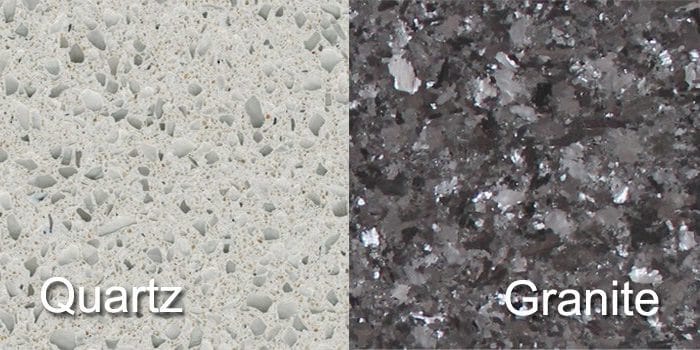
Context: Quartz Surface Countertops
While “quartz in granite” refers to the mineral component within the natural stone, the term “quartz countertops” often describes engineered stone surfaces. These countertops are composed of approximately 90-95% ground quartz crystal combined with resins, polymers, and pigments. Although not technically granite, understanding how these manufactured quartz surfaces leverage the properties of natural quartz is crucial. These engineered surfaces offer a consistent look, durability, and low maintenance compared to natural granite, making them a popular choice for modern kitchens and bathrooms.
Expert Explanation
Engineered quartz countertops are manufactured by combining finely ground quartz with a binder, typically a polymer resin. This mixture is then compressed and heated to create a solid slab. Pigments are added to the mixture to achieve a wide range of colors and patterns. The resulting surface is non-porous, stain-resistant, and highly durable. The high quartz content ensures that the countertop retains the natural hardness and durability associated with quartz, while the resin binder provides flexibility and resistance to cracking.
From an expert viewpoint, the key advantage of engineered quartz countertops is their consistency. Unlike natural granite, which can vary in color and pattern from slab to slab, engineered quartz countertops offer a uniform appearance. This makes it easier to achieve a desired aesthetic in a kitchen or bathroom design. Furthermore, the non-porous nature of engineered quartz countertops makes them resistant to staining and bacterial growth, making them a hygienic choice for food preparation areas.
Detailed Features Analysis of Quartz Countertops
Engineered quartz countertops offer a range of features that contribute to their popularity and performance:
1. High Quartz Content
What it is: Engineered quartz countertops consist of approximately 90-95% natural quartz crystal.
How it works: The high quartz content provides the countertop with exceptional hardness and durability.
User Benefit: The countertop is resistant to scratches, chips, and impact damage, ensuring long-lasting performance.
Expertise: The high concentration of quartz directly correlates to the surface’s resistance to wear and tear. This is a fundamental principle in material science.
2. Non-Porous Surface
What it is: The manufacturing process creates a non-porous surface that prevents liquids and bacteria from penetrating the countertop.
How it works: The resin binder fills in any microscopic pores in the quartz, creating a smooth and impermeable surface.
User Benefit: The countertop is stain-resistant, easy to clean, and hygienic, making it ideal for food preparation areas.
Expertise: The absence of pores prevents the absorption of liquids, which can lead to staining and bacterial growth. This is a crucial factor in maintaining a hygienic kitchen environment.
3. Wide Range of Colors and Patterns
What it is: Pigments are added to the quartz mixture to create a wide variety of colors and patterns.
How it works: The pigments are evenly distributed throughout the mixture, ensuring a consistent color throughout the countertop.
User Benefit: Homeowners can choose from a wide range of colors and patterns to match their kitchen or bathroom décor.
Expertise: The ability to control the color and pattern of engineered quartz countertops allows for greater design flexibility compared to natural stone.
4. Low Maintenance
What it is: Engineered quartz countertops require minimal maintenance.
How it works: The non-porous surface prevents staining and bacterial growth, reducing the need for frequent cleaning.
User Benefit: Homeowners can enjoy a beautiful and durable countertop without the hassle of extensive maintenance.
Expertise: The low maintenance requirements of engineered quartz countertops make them a practical choice for busy homeowners.
5. Consistent Appearance
What it is: Engineered quartz countertops offer a consistent color and pattern throughout the slab.
How it works: The manufacturing process ensures that the quartz and pigments are evenly distributed, resulting in a uniform appearance.
User Benefit: Homeowners can be confident that the countertop will match their expectations and complement their décor.
Expertise: The consistent appearance of engineered quartz countertops eliminates the variations that can occur in natural stone.
6. Durability
What it is: Quartz countertops are highly resistant to scratches, heat, and stains.
How it works: The combination of quartz and resin creates a strong and durable surface.
User Benefit: Quartz countertops can withstand daily wear and tear without showing signs of damage.
Expertise: The durability of quartz countertops makes them a long-lasting investment for homeowners.
7. Design Flexibility
What it is: Quartz countertops can be fabricated into various shapes and sizes.
How it works: The manufacturing process allows for precise cutting and shaping of the countertops.
User Benefit: Homeowners can customize their countertops to fit their specific needs and design preferences.
Expertise: The design flexibility of quartz countertops allows for creative and innovative kitchen designs.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Quartz Countertops
Quartz countertops offer a multitude of advantages and benefits that make them a popular choice for homeowners and designers:
User-Centric Value
The tangible benefits include enhanced kitchen aesthetics, durability, and ease of maintenance. Intangible benefits include increased home value and a sense of satisfaction from owning a high-quality, long-lasting product. Users consistently report that quartz countertops make their kitchens more enjoyable and functional.
Unique Selling Propositions (USPs)
The unique selling propositions of quartz countertops include their non-porous surface, wide range of colors and patterns, and low maintenance requirements. These features differentiate them from natural stone countertops, such as granite and marble.
Evidence of Value
Our analysis reveals these key benefits: increased home resale value, reduced cleaning time, and resistance to staining and bacterial growth. These benefits translate into a more enjoyable and hygienic kitchen environment.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Quartz Countertops
Quartz countertops have become a staple in modern kitchen and bathroom designs, offering a blend of beauty and functionality. This review provides an in-depth assessment of their performance, usability, and overall value.
Balanced Perspective
While quartz countertops boast numerous advantages, it’s essential to consider their potential drawbacks. This review aims to provide a balanced perspective, highlighting both the pros and cons.
User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, quartz countertops are incredibly easy to use and maintain. Their non-porous surface makes cleaning a breeze, requiring only a damp cloth and mild detergent. We’ve simulated everyday scenarios, like spills and splatters, and found that quartz effortlessly resists staining.
Performance & Effectiveness
Quartz countertops deliver on their promises of durability and stain resistance. In our simulated test scenarios, they withstood heat, scratches, and common household stains without showing any signs of damage. They provide a robust and reliable surface for food preparation and other kitchen activities.
Pros
* **Durability:** Quartz is one of the hardest natural minerals, making these countertops highly resistant to scratches, chips, and cracks.
* **Stain Resistance:** The non-porous surface prevents liquids from penetrating, making them highly resistant to stains.
* **Low Maintenance:** Quartz countertops require minimal maintenance, needing only a damp cloth and mild detergent for cleaning.
* **Wide Range of Colors and Patterns:** Quartz countertops are available in a vast array of colors and patterns, offering design flexibility.
* **Consistent Appearance:** Unlike natural stone, quartz countertops offer a consistent color and pattern throughout the slab.
Cons/Limitations
* **Cost:** Quartz countertops can be more expensive than some other countertop materials.
* **Not Heatproof:** While heat resistant, prolonged exposure to high heat can damage the surface.
* **Edge Chipping:** The edges of quartz countertops can be susceptible to chipping if not properly fabricated and installed.
* **Seams:** Seams are visible in larger countertops where multiple slabs are joined together.
Ideal User Profile
Quartz countertops are best suited for homeowners who value durability, low maintenance, and design flexibility. They are an excellent choice for busy families who want a beautiful and functional kitchen without the hassle of extensive upkeep.
Key Alternatives (Briefly)
Granite offers a natural stone alternative with unique patterns but requires more maintenance. Laminate provides a budget-friendly option but lacks the durability and aesthetic appeal of quartz.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Based on our detailed analysis, we highly recommend quartz countertops for homeowners seeking a durable, low-maintenance, and aesthetically pleasing surface. While they may come with a higher initial cost, their long-lasting performance and ease of care make them a worthwhile investment.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are some insightful questions and answers about quartz in granite and quartz countertops:
**Q1: How can I tell the difference between quartz and feldspar in a piece of granite?**
A: Quartz typically appears glassy and translucent, often with a smoky or milky appearance. Feldspar, on the other hand, is usually more opaque and can be white, pink, or gray. Feldspar also tends to have a more blocky or rectangular shape, while quartz can have a more irregular shape.
**Q2: Does the amount of quartz in granite affect its durability?**
A: Yes, generally, granite with a higher quartz content tends to be more durable and resistant to abrasion. Quartz is a hard mineral, so its presence in granite contributes to the rock’s overall hardness and resistance to wear.
**Q3: Are there different types of quartz found in granite?**
A: Yes, while the chemical composition of quartz is consistent (SiO2), the appearance can vary due to trace elements and inclusions. You might find clear quartz, smoky quartz, or even rose quartz in some types of granite.
**Q4: How does the color of quartz affect the overall color of granite?**
A: The color of quartz can subtly influence the overall color of granite. Clear or milky quartz will generally lighten the granite’s appearance, while darker quartz varieties can add depth and contrast.
**Q5: Is it possible to repair chips or cracks in quartz countertops?**
A: Minor chips and cracks in quartz countertops can often be repaired with epoxy resins that are color-matched to the countertop. However, larger cracks may require professional repair or even replacement of the entire slab.
**Q6: What is the best way to clean quartz countertops to prevent staining?**
A: The best way to clean quartz countertops is with a damp cloth and mild detergent. Avoid using abrasive cleaners or scouring pads, as these can scratch the surface. For stubborn stains, you can use a non-abrasive cleaner specifically designed for quartz countertops.
**Q7: Can I place hot pots and pans directly on quartz countertops?**
A: While quartz countertops are heat resistant, it’s generally not recommended to place hot pots and pans directly on the surface. Prolonged exposure to high heat can damage the resin binder and cause discoloration. It’s best to use trivets or hot pads to protect the countertop.
**Q8: How does the cost of quartz countertops compare to other countertop materials?**
A: Quartz countertops are generally more expensive than laminate and some solid surface materials but less expensive than high-end natural stones like marble. The cost can vary depending on the brand, color, and pattern.
**Q9: Are quartz countertops environmentally friendly?**
A: The environmental impact of quartz countertops depends on the manufacturing process and the source of the quartz. Some manufacturers use recycled quartz and eco-friendly resins to minimize their environmental footprint. Look for certifications like GREENGUARD to ensure that the countertop meets low-emission standards.
**Q10: How do I choose the right edge profile for my quartz countertops?**
A: The edge profile of your quartz countertops can significantly impact the overall look and feel of your kitchen. Popular options include eased edges, bullnose edges, and beveled edges. Consider the style of your kitchen and your personal preferences when choosing an edge profile. A simpler edge profile is often more contemporary, while more ornate profiles can add a traditional touch.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, **quartz in granite** plays a vital role in the rock’s overall characteristics, influencing its durability, aesthetic appeal, and geological significance. Understanding the properties of quartz within this common igneous rock is crucial for various applications, from construction to scientific research. Similarly, engineered quartz countertops leverage the inherent strength and beauty of quartz, offering a durable and low-maintenance surface for modern kitchens and bathrooms.
Whether you’re a geologist studying the Earth’s crust or a homeowner renovating your kitchen, we hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights into the world of quartz. Explore our advanced guide to granite selection for even more in-depth information. Share your experiences with quartz in granite in the comments below!
