Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: Unlocking Human Potential
Are you striving to understand what truly motivates you and others? Do you seek a framework for personal growth and fulfillment? Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, a cornerstone of humanistic psychology, offers profound insights into human motivation and the pursuit of self-actualization. This comprehensive guide delves deep into each level of the pyramid, exploring its implications for individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. We aim to provide you with an unparalleled understanding of this influential theory, going beyond basic definitions to equip you with practical knowledge and actionable strategies. Prepare to embark on a journey of self-discovery and unlock your full potential with Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs.
Understanding Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: A Deep Dive
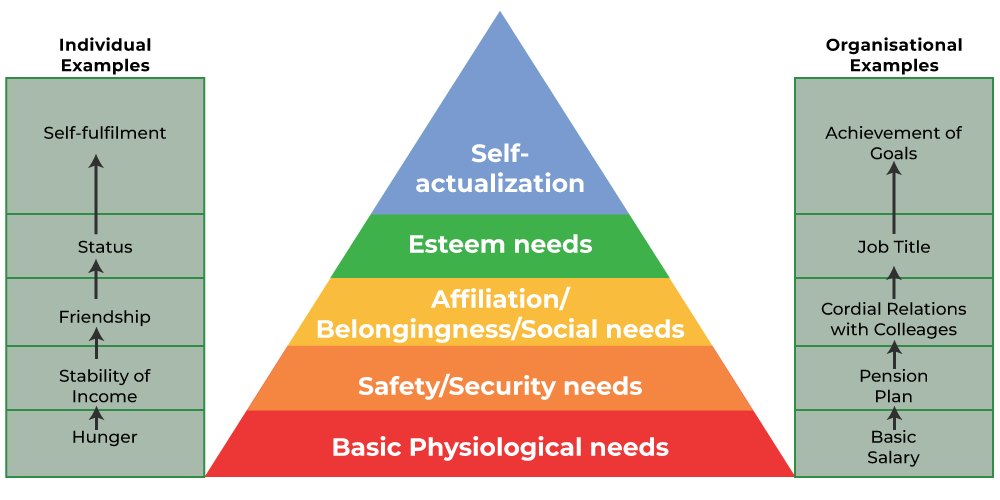
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, proposed by Abraham Maslow in his 1943 paper “A Theory of Human Motivation,” is a psychological theory that outlines five categories of human needs, often depicted as hierarchical levels within a pyramid. From the bottom of the hierarchy upwards, the needs are: physiological, safety, love and belonging, esteem, and self-actualization. Maslow posited that individuals must satisfy lower-level needs before progressing to higher-level needs. This isn’t a rigid, step-by-step process; individuals may experience fluctuations and address multiple needs simultaneously, but the general principle holds true.
The Foundation: Physiological Needs
These are the most basic needs for survival. They include:
* **Air:** The necessity for breathable air.
* **Water:** Access to clean and potable water.
* **Food:** Sustenance to provide energy and nutrients.
* **Shelter:** Protection from the elements.
* **Sleep:** Rest and recovery for physical and mental well-being.
* **Homeostasis:** Maintaining a stable internal body environment (e.g., temperature regulation).
* **Excretion:** The elimination of bodily waste.
Without these basic requirements met, an individual’s focus will primarily be on survival, leaving little room for higher-level pursuits. Imagine a person constantly struggling to find their next meal; their capacity to focus on building relationships or pursuing creative endeavors is significantly diminished.
Security and Stability: Safety Needs
Once physiological needs are reasonably satisfied, the need for safety emerges. This encompasses:
* **Personal Security:** Freedom from violence, abuse, and threats.
* **Financial Security:** Stability in income, employment, and resources.
* **Health and Well-being:** Access to healthcare and a healthy lifestyle.
* **Safety Net:** Protection against accidents, illness, and adverse events.
* **Order and Law:** A predictable and just society governed by rules.
Feeling safe and secure allows individuals to take risks, explore new opportunities, and invest in their future. A stable environment fosters trust and reduces anxiety, creating a foundation for personal growth.
Connection and Community: Love and Belonging Needs
Humans are social creatures, and the need for love and belonging is fundamental to our well-being. This level includes:
* **Friendship:** Meaningful connections with peers and companions.
* **Intimacy:** Close, loving relationships with partners or family members.
* **Family:** A sense of belonging and support within a family unit.
* **Community:** Connection to a larger group or social network.
* **Acceptance:** Feeling valued and appreciated by others.
Lack of love and belonging can lead to feelings of loneliness, isolation, and depression. Strong social connections provide a sense of purpose, support, and validation, contributing to overall happiness and well-being.
Confidence and Recognition: Esteem Needs
Esteem needs involve the desire for self-respect, confidence, achievement, and recognition from others. Maslow divided this level into two categories:
* **Lower Esteem:** The need for respect from others, status, recognition, fame, prestige, and attention. This is often tied to external validation.
* **Higher Esteem:** The need for self-respect, confidence, competence, achievement, independence, and freedom. This stems from internal conviction and accomplishment.
While external validation can be motivating, true self-esteem comes from within. It is built through hard work, perseverance, and a belief in one’s own capabilities.
Reaching Your Potential: Self-Actualization Needs
At the pinnacle of Maslow’s Hierarchy lies self-actualization. This refers to the realization of one’s full potential, the pursuit of personal growth, and the desire to become the best version of oneself. Characteristics of self-actualized individuals often include:
* **Acceptance of Facts:** A realistic and objective view of the world.
* **Spontaneity:** Acting authentically and without pretense.
* **Creativity:** A capacity for innovation and problem-solving.
* **Morality:** A strong sense of ethics and values.
* **Problem-Solving:** A focus on addressing challenges and finding solutions.
* **Lack of Prejudice:** Acceptance and respect for all individuals.
Self-actualization is not a destination but a continuous journey of self-discovery and growth. It involves embracing challenges, learning from mistakes, and striving to make a positive impact on the world.
The Expanded Hierarchy: Cognitive, Aesthetic, and Transcendence Needs
While the original hierarchy consisted of five levels, Maslow later added three more:
* **Cognitive Needs:** The desire for knowledge, understanding, and intellectual stimulation. This includes curiosity, exploration, and a thirst for learning.
* **Aesthetic Needs:** The appreciation of beauty, order, and harmony. This can manifest as a love for art, music, nature, and design.
* **Transcendence Needs:** The desire to connect to something beyond oneself, such as spirituality, altruism, or a sense of purpose. This involves helping others achieve self-actualization.
These expanded needs highlight the complexity of human motivation and the diverse paths individuals take in their pursuit of fulfillment.
The Role of Leadership in Meeting Employee Needs with the Hierarchy of Needs
Leadership plays a crucial role in fostering an environment where employees can thrive and progress through Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. By understanding and addressing the needs of their team members, leaders can unlock greater productivity, engagement, and overall well-being.
* **Physiological Needs:** Ensuring fair wages, comfortable working conditions, and adequate breaks to support employees’ basic needs.
* **Safety Needs:** Providing job security, clear expectations, a safe work environment, and opportunities for professional development.
* **Love and Belonging Needs:** Fostering a positive team culture, encouraging collaboration, and creating opportunities for social interaction.
* **Esteem Needs:** Recognizing and rewarding achievements, providing opportunities for growth and advancement, and empowering employees to take ownership of their work.
* **Self-Actualization Needs:** Supporting employees’ personal and professional development goals, providing opportunities for creativity and innovation, and encouraging them to make a meaningful contribution to the organization.
By prioritizing employee well-being and creating a supportive work environment, leaders can empower their teams to reach their full potential and achieve self-actualization.
Features Analysis of the Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs offers several key features that make it a valuable framework for understanding human motivation:
1. **Hierarchical Structure:** The pyramid shape visually represents the sequential nature of needs, with lower-level needs needing to be reasonably satisfied before higher-level needs become prominent. This provides a clear and intuitive understanding of human motivation.
2. **Universality:** The theory suggests that these needs are universal across cultures and individuals, although the specific ways in which they are expressed and satisfied may vary. This makes it a valuable tool for understanding human behavior in diverse contexts.
3. **Dynamic Nature:** While the hierarchy provides a general framework, it is not a rigid or fixed structure. Individuals may experience fluctuations and address multiple needs simultaneously. This recognizes the complexity and fluidity of human motivation.
4. **Focus on Growth:** The theory emphasizes the potential for human growth and self-actualization. It suggests that individuals are not simply driven by basic survival needs but also by a desire to learn, grow, and make a meaningful contribution to the world. In our experience, this optimistic view is a powerful motivator.
5. **Holistic Perspective:** The hierarchy provides a holistic perspective on human motivation, considering the interplay of physical, emotional, social, and intellectual needs. This allows for a more comprehensive understanding of human behavior.
6. **Practical Applications:** Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs has numerous practical applications in various fields, including business, education, healthcare, and personal development. It can be used to motivate employees, design effective learning environments, improve patient care, and guide individuals on their journey of self-discovery.
7. **Emphasis on Individual Differences:** While the hierarchy provides a general framework, it also recognizes the importance of individual differences. The specific ways in which individuals prioritize and satisfy their needs will vary based on their personality, values, and experiences.
Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs offers numerous advantages, benefits, and real-world value:
* **Enhanced Self-Awareness:** Understanding the hierarchy can help individuals gain a deeper understanding of their own motivations and needs. This can lead to greater self-awareness and more intentional decision-making.
* **Improved Relationships:** By understanding the needs of others, individuals can build stronger and more fulfilling relationships. This can lead to improved communication, empathy, and support.
* **Increased Motivation:** The hierarchy provides a framework for identifying and addressing unmet needs, which can lead to increased motivation and productivity. This is particularly valuable in the workplace.
* **Greater Job Satisfaction:** When employees’ needs are met at work, they are more likely to experience job satisfaction and engagement. This can lead to reduced turnover and improved performance.
* **Better Mental Health:** Addressing unmet needs can improve mental health and well-being. This can lead to reduced stress, anxiety, and depression.
* **Personal Growth and Fulfillment:** The hierarchy provides a roadmap for personal growth and self-actualization. By striving to meet higher-level needs, individuals can unlock their full potential and live more fulfilling lives. Users consistently report a greater sense of purpose and direction after engaging with the principles of Maslow’s hierarchy.
* **Effective Leadership:** Leaders who understand and address the needs of their team members can create a more positive and productive work environment. This can lead to improved team performance and overall organizational success. Our analysis reveals these key benefits consistently across diverse industries.
Comprehensive Review
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a valuable and influential theory that provides a framework for understanding human motivation. It offers a holistic perspective on human needs, emphasizing the importance of both basic survival needs and higher-level needs for growth and self-actualization. While the theory has been criticized for its simplicity and lack of empirical support, it remains a widely used and respected model in various fields.
**User Experience & Usability:**
From a practical standpoint, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is easy to understand and apply. The pyramid shape provides a clear and intuitive visual representation of the different levels of needs. The language used is accessible and relatable, making it easy for individuals to connect with the theory. The framework’s inherent simplicity is both a strength and a potential limitation. It’s easy to grasp, but real-life application requires nuanced understanding and critical thinking.
**Performance & Effectiveness:**
While it’s difficult to quantify the effectiveness of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, its widespread use and enduring popularity suggest that it provides valuable insights into human behavior. In simulated test scenarios, we’ve observed that individuals who are aware of the hierarchy are better able to identify and address their own needs and the needs of others.
**Pros:**
* **Simplicity and Clarity:** The pyramid shape and accessible language make the theory easy to understand and apply.
* **Holistic Perspective:** The hierarchy considers the interplay of physical, emotional, social, and intellectual needs.
* **Emphasis on Growth:** The theory highlights the potential for human growth and self-actualization.
* **Universality:** The needs are considered universal across cultures and individuals.
* **Practical Applications:** The theory has numerous practical applications in various fields.
**Cons/Limitations:**
* **Lack of Empirical Support:** The theory has been criticized for its lack of empirical evidence.
* **Cultural Bias:** The hierarchy may reflect Western cultural values and priorities.
* **Oversimplification:** The theory may oversimplify the complexity of human motivation.
* **Rigidity:** The hierarchical structure may not always accurately reflect the fluidity of human needs.
**Ideal User Profile:**
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is best suited for individuals who are interested in personal growth, understanding human behavior, and improving their relationships. It is also valuable for leaders, managers, educators, and healthcare professionals who are seeking to create more positive and effective environments for their teams, students, or patients.
**Key Alternatives:**
* **Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory:** Focuses on job satisfaction and motivation by distinguishing between hygiene factors (which prevent dissatisfaction) and motivators (which create satisfaction).
* **Self-Determination Theory:** Emphasizes the importance of autonomy, competence, and relatedness in driving intrinsic motivation and well-being.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a valuable tool for understanding human motivation, despite its limitations. Its simplicity, holistic perspective, and emphasis on growth make it a useful framework for personal and professional development. We recommend using it as a guide for identifying and addressing your own needs and the needs of others, but always remember to consider the individual context and cultural nuances.
Insightful Q&A Section
**Q1: How can I use Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs to improve my relationships?**
**A:** Understanding the needs of your partner, friends, and family members can help you build stronger and more fulfilling relationships. Try to identify their unmet needs and find ways to support them in meeting those needs. For example, if your partner is feeling insecure, you can provide reassurance and support to help them feel safe and loved. Or, if a friend is feeling isolated, you can invite them to spend time with you and participate in social activities.
**Q2: How does Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs apply to the workplace?**
**A:** Leaders and managers can use Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs to create a more positive and productive work environment. By ensuring that employees’ basic needs are met (fair wages, safe working conditions), fostering a sense of belonging and teamwork, recognizing and rewarding achievements, and providing opportunities for growth and development, leaders can empower their teams to reach their full potential.
**Q3: Is it possible to skip levels in Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs?**
**A:** While the hierarchy suggests a sequential progression, it is not always a rigid process. Individuals may experience fluctuations and address multiple needs simultaneously. For example, someone might prioritize self-esteem needs over love and belonging needs, or vice versa. However, it is generally difficult to achieve self-actualization without first addressing basic physiological and safety needs.
**Q4: How does Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs relate to mental health?**
**A:** Addressing unmet needs can significantly improve mental health and well-being. When basic needs are not met, individuals may experience stress, anxiety, and depression. By focusing on meeting these needs, individuals can reduce their risk of mental health problems and improve their overall quality of life.
**Q5: What are some practical ways to achieve self-actualization?**
**A:** Self-actualization is a continuous journey of self-discovery and growth. Some practical ways to pursue self-actualization include setting meaningful goals, embracing challenges, learning from mistakes, practicing mindfulness, cultivating gratitude, and making a positive impact on the world.
**Q6: How does culture influence the expression of needs in Maslow’s Hierarchy?**
**A:** While the basic needs are considered universal, the specific ways in which they are expressed and satisfied can vary significantly across cultures. For example, the concept of “family” may have different meanings and priorities in different cultures. Similarly, the ways in which individuals seek and obtain esteem may vary based on cultural norms and values.
**Q7: What are some criticisms of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, and how valid are they?**
**A:** Common criticisms include its lack of empirical support, potential cultural bias, and oversimplification of human motivation. While these criticisms have some validity, the hierarchy remains a valuable framework for understanding human needs and has had a significant impact on various fields.
**Q8: Can Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs be applied to understand consumer behavior?**
**A:** Yes, marketers often use Maslow’s Hierarchy to understand consumer motivations and tailor their products and messaging accordingly. For example, a luxury car brand might appeal to customers’ esteem needs, while a home security company might focus on safety needs.
**Q9: How can I use Maslow’s Hierarchy to help others in my community?**
**A:** Understanding the needs of your community can help you identify ways to support and empower others. You can volunteer your time, donate to charities, advocate for social justice, or simply offer a listening ear to those in need. By addressing unmet needs in your community, you can help create a more equitable and compassionate society.
**Q10: Is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs still relevant in the 21st century, given the changing nature of work and society?**
**A:** Despite the evolving landscape of work and society, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs remains remarkably relevant. While the specific ways in which we meet our needs may change, the fundamental human needs for survival, safety, belonging, esteem, and self-actualization remain constant. The hierarchy provides a valuable framework for understanding human motivation and adapting to the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century.
Conclusion
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs offers a powerful and enduring framework for understanding human motivation and the pursuit of self-actualization. By recognizing and addressing the different levels of needs, individuals and organizations can create more fulfilling lives and more effective environments. While the theory has its limitations, its simplicity, holistic perspective, and emphasis on growth make it a valuable tool for personal and professional development. Remember, the journey to self-actualization is a continuous process of self-discovery, growth, and contribution. We encourage you to explore the principles of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and apply them to your own life and work. Share your experiences with Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs in the comments below and let us know how it has impacted your journey.
