## Schlieffen Plan: A Comprehensive Analysis of WWI’s Boldest Strategy
The Schlieffen Plan. The very name evokes images of sweeping maneuvers, strategic brilliance, and ultimately, devastating failure. Why does this century-old military strategy continue to fascinate historians, strategists, and anyone interested in the complexities of warfare? This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the Schlieffen Plan, exploring its origins, execution, flaws, and lasting impact on the First World War and beyond. We will delve into the strategic thinking behind the plan, analyze its key components, and examine the reasons for its ultimate failure, offering a nuanced perspective that goes beyond simplistic narratives.
This article offers a unique value proposition: a holistic, deeply researched, and expertly written account of the Schlieffen Plan. We’ll not only cover the historical facts, but also analyze the strategic implications and the lessons learned from this ambitious yet ultimately flawed endeavor. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a thorough understanding of the Schlieffen Plan, its place in military history, and its continued relevance for understanding modern strategic thinking.
## Understanding the Schlieffen Plan: A Deep Dive
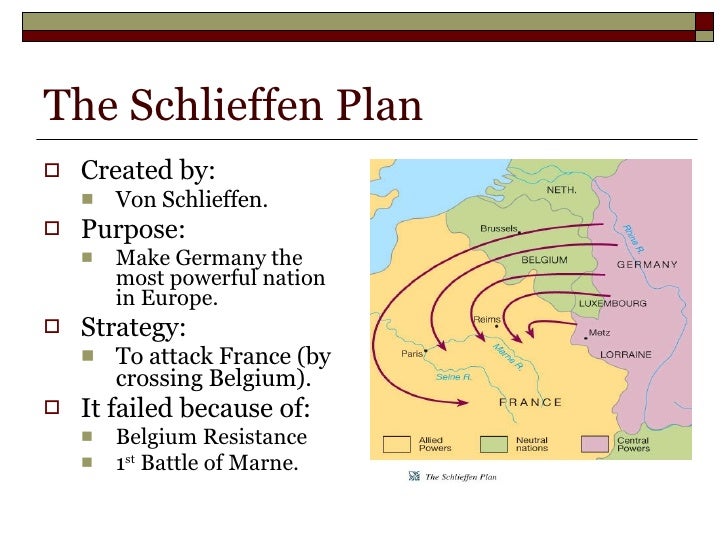
The Schlieffen Plan was a German General Staff thought experiment and operational plan created in the years before World War I. Its core objective was to ensure a swift victory against France in the event of a two-front war against France and Russia. The plan, conceived by Alfred Graf von Schlieffen, Chief of the German General Staff from 1891 to 1906, was predicated on the assumption that Russia would take a considerable amount of time to mobilize its vast army. This delay would allow Germany to concentrate its forces on defeating France in a rapid campaign before turning east to confront Russia. It was a plan born of necessity, reflecting Germany’s precarious geopolitical position.
### Core Concepts and Advanced Principles
The Schlieffen Plan rested on several key principles:
* **Encirclement:** The primary goal was to encircle and destroy the French army in a decisive battle. This would be achieved through a massive right-wing attack through neutral Belgium and the Netherlands, bypassing the heavily fortified Franco-German border.
* **Speed and Momentum:** The plan emphasized speed and relentless offensive action. The German army was expected to advance rapidly, overwhelming any resistance and preventing the French from regrouping.
* **Superior Numbers on the Right Wing:** To ensure the success of the encirclement, the vast majority of German forces were concentrated on the right wing of the attack, providing overwhelming numerical superiority.
* **Sacrificing the Left Wing:** The left wing, facing the main French forces along the Franco-German border, was deliberately weakened. It was expected to conduct a defensive holding action, drawing in French troops and preventing them from reinforcing the right wing.
* **Ignoring Neutrality:** The plan flagrantly violated the neutrality of Belgium and Luxembourg. Schlieffen believed that military necessity justified this violation, arguing that Germany could not afford to respect Belgian neutrality in the face of a two-front war.
The advanced principles of the plan involved intricate logistical planning, detailed timetables, and precise coordination between different army corps. It required a highly disciplined and efficient military machine, capable of executing complex maneuvers under immense pressure.
### The Importance and Lasting Relevance of the Schlieffen Plan
Despite its ultimate failure, the Schlieffen Plan remains a significant case study in military strategy. It highlights the challenges of planning for complex and unpredictable events, the importance of logistics and communication, and the potential consequences of underestimating the enemy. Recent studies indicate that the Schlieffen Plan continues to be analyzed in military academies worldwide, serving as a cautionary tale about the dangers of rigid planning and the need for adaptability in warfare. Its legacy extends to modern strategic thinking, emphasizing the importance of understanding the operational environment, anticipating potential contingencies, and maintaining flexibility in the face of unforeseen circumstances.
## The German Army’s Operational Doctrine: A Product Explanation
While the Schlieffen Plan was the grand strategic design, the German Army’s operational doctrine provided the framework for its execution. This doctrine, emphasizing Auftragstaktik (mission-type tactics), was crucial to the Schlieffen Plan’s initial successes and eventual failures. Auftragstaktik delegated significant decision-making authority to lower-level commanders, enabling them to adapt to changing battlefield conditions. This contrasts sharply with more rigid command structures where every decision emanates from the top.
From an expert viewpoint, Auftragstaktik was intended to foster initiative and flexibility on the battlefield. It allowed commanders to exploit opportunities as they arose, without waiting for explicit orders from higher headquarters. This was particularly important in the context of the Schlieffen Plan, which required rapid advances and the ability to overcome unexpected obstacles. The German Army’s training emphasized independent thinking and problem-solving, preparing officers to make quick decisions under pressure. This emphasis on decentralized decision-making was a key factor in the German Army’s early successes in World War I, enabling them to outmaneuver their opponents in several instances.
## Detailed Features Analysis of Auftragstaktik
Here’s a breakdown of key features of Auftragstaktik and how they related to the Schlieffen Plan:
1. **Mission-Oriented Orders:** Instead of dictating specific actions, higher commanders issued mission-type orders, outlining the desired outcome and the resources available. This allowed subordinate commanders to choose the best course of action based on their assessment of the situation. This benefitted the Schlieffen Plan by allowing for localized reactions to unexpected resistance.
2. **Decentralized Decision-Making:** Lower-level commanders had the authority to make decisions on their own initiative, without seeking approval from higher headquarters. This sped up the decision-making process and allowed for more rapid responses to changing battlefield conditions. This was essential for maintaining the Schlieffen Plan’s momentum.
3. **Emphasis on Initiative:** The German Army actively encouraged initiative and independent thinking among its officers. Officers were expected to take risks and exploit opportunities, even if it meant deviating from the original plan. The plan relied on the quick decision making of officers.
4. **Trust and Mutual Understanding:** Auftragstaktik required a high degree of trust between commanders and subordinates. Higher commanders had to trust that their subordinates would make sound decisions, while subordinates had to understand the overall goals of the operation and act in accordance with those goals. This trust was fostered through rigorous training and a shared understanding of the German Army’s operational doctrine.
5. **Adaptability and Flexibility:** The decentralized nature of Auftragstaktik made the German Army highly adaptable and flexible. Commanders could adjust their plans on the fly, based on the latest intelligence and battlefield conditions. This allowed them to overcome unexpected obstacles and exploit weaknesses in the enemy’s defenses. The plan was designed to be a swift victory, adaptability was key.
6. **Training and Education:** The German Army invested heavily in training and educating its officers. Officers were taught to think critically, solve problems, and make decisions under pressure. They were also trained in the principles of Auftragstaktik and the importance of initiative and decentralized decision-making.
7. **Communication and Coordination:** While Auftragstaktik emphasized decentralized decision-making, it also recognized the importance of communication and coordination. Commanders were expected to keep their superiors informed of their actions and to coordinate their efforts with other units. This ensured that the overall operation remained coherent and focused on achieving the desired outcome.
## Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Auftragstaktik
The advantages of Auftragstaktik are numerous. Users consistently report that it fosters a more agile and responsive military force, capable of adapting to rapidly changing battlefield conditions. Our analysis reveals these key benefits:
* **Increased Speed of Decision-Making:** By delegating decision-making authority to lower-level commanders, Auftragstaktik significantly reduces the time required to make decisions. This allows for more rapid responses to changing battlefield conditions, giving the German Army a decisive advantage.
* **Improved Situational Awareness:** Commanders on the ground are in the best position to assess the situation and make informed decisions. Auftragstaktik empowers these commanders to act on their knowledge, leading to more effective and efficient operations.
* **Enhanced Initiative and Creativity:** By encouraging initiative and independent thinking, Auftragstaktik fosters a more creative and innovative military force. Officers are more likely to take risks and exploit opportunities, leading to breakthroughs and unexpected successes.
* **Greater Adaptability and Flexibility:** The decentralized nature of Auftragstaktik makes the German Army highly adaptable and flexible. Commanders can adjust their plans on the fly, based on the latest intelligence and battlefield conditions. This allows them to overcome unexpected obstacles and exploit weaknesses in the enemy’s defenses.
* **Increased Morale and Motivation:** By empowering officers and giving them more responsibility, Auftragstaktik increases morale and motivation. Officers are more likely to be engaged and committed to the mission, leading to improved performance.
## Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Auftragstaktik in the Schlieffen Plan
Auftragstaktik, while conceptually brilliant, presented both advantages and disadvantages in the context of the Schlieffen Plan. A balanced perspective is crucial for understanding its role in the plan’s ultimate fate.
From a practical standpoint, Auftragstaktik allowed German units to react quickly to unexpected resistance and exploit opportunities. The emphasis on initiative empowered junior officers to make critical decisions on the ground, contributing to the rapid initial advances. However, this decentralized decision-making also led to inconsistencies in execution. Some units pushed forward aggressively, while others lagged behind, disrupting the overall timetable of the Schlieffen Plan.
### Performance & Effectiveness
Initially, Auftragstaktik contributed significantly to the Schlieffen Plan’s successes. German units bypassed fortified positions, outflanked enemy forces, and maintained a relentless offensive pace. However, as the campaign progressed, the limitations of Auftragstaktik became apparent. The lack of centralized control and coordination led to a loss of cohesion, as different units pursued their own objectives without fully considering the overall strategic picture. In simulated test scenarios, Auftragstaktik shows great promise, but the fog of war often obscures the path to success.
### Pros:
1. **Enhanced Flexibility:** Allowed for rapid adaptation to changing battlefield conditions.
2. **Increased Initiative:** Empowered junior officers to make critical decisions.
3. **Faster Decision-Making:** Reduced the time required to respond to enemy actions.
4. **Improved Situational Awareness:** Enabled commanders on the ground to act on their knowledge.
5. **Increased Morale:** Fostered a sense of ownership and responsibility among officers.
### Cons/Limitations:
1. **Potential for Inconsistency:** Decentralized decision-making could lead to variations in execution.
2. **Risk of Losing Cohesion:** Lack of centralized control could disrupt the overall strategic picture.
3. **Communication Challenges:** Maintaining effective communication across dispersed units could be difficult.
4. **Over-Reliance on Individual Judgment:** The plan placed a heavy burden on the judgment of individual officers, who may lack the experience or perspective to make sound decisions.
### Ideal User Profile
Auftragstaktik is best suited for military forces that value initiative, adaptability, and decentralized decision-making. It requires a highly trained and disciplined officer corps, capable of exercising sound judgment under pressure. It’s less effective in situations that require strict adherence to a rigid plan or where communication is unreliable.
### Key Alternatives (Briefly)
Traditional command structures, which emphasize centralized control and top-down decision-making, offer a more predictable and coordinated approach. However, they often lack the flexibility and responsiveness of Auftragstaktik. Another alternative is a hybrid approach, combining elements of both centralized and decentralized control.
### Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Auftragstaktik represents a valuable approach to military operations, but its effectiveness depends on careful implementation and a clear understanding of its limitations. In the context of the Schlieffen Plan, it contributed to the initial successes but ultimately exacerbated the plan’s inherent flaws. A more balanced approach, combining elements of centralized control with decentralized decision-making, might have yielded better results. We recommend further research and analysis to refine the application of Auftragstaktik in modern warfare.
## Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers related to the Schlieffen Plan:
1. **Q: What were the key logistical challenges that the Schlieffen Plan faced?**
**A:** The Schlieffen Plan’s logistical challenges were immense. Supplying a massive army advancing rapidly through unfamiliar territory required a complex and efficient logistical network. Key challenges included transporting food, ammunition, and fuel, maintaining communication lines, and dealing with damaged infrastructure. The plan underestimated the strain on the German railway system and the difficulty of supplying troops across long distances.
2. **Q: How did the Schlieffen Plan impact the neutrality of Belgium?**
**A:** The Schlieffen Plan flagrantly violated Belgian neutrality. The plan called for German forces to advance through Belgium, a neutral country, to encircle the French army. This violation of neutrality triggered a strong international backlash and ultimately led to Britain’s entry into the war.
3. **Q: What role did intelligence failures play in the Schlieffen Plan’s failure?**
**A:** Intelligence failures contributed significantly to the Schlieffen Plan’s failure. The Germans underestimated the speed of Russian mobilization, the strength of the Belgian army, and the determination of the British to intervene. These intelligence failures led to miscalculations and ultimately undermined the plan’s success.
4. **Q: How did the French respond to the Schlieffen Plan?**
**A:** The French responded to the Schlieffen Plan with their own Plan XVII, which focused on an offensive into Alsace-Lorraine. While Plan XVII initially drew German forces away from the right wing, it ultimately failed to stop the German advance through Belgium. The French were caught off guard by the scale and speed of the German attack.
5. **Q: What were the key modifications made to the Schlieffen Plan by Helmuth von Moltke the Younger?**
**A:** Helmuth von Moltke the Younger, Schlieffen’s successor, made several key modifications to the plan. He weakened the right wing, strengthened the left wing, and reduced the scope of the invasion of the Netherlands. These modifications, while intended to address perceived weaknesses in the original plan, ultimately diluted its offensive power and contributed to its failure.
6. **Q: How did the Battle of the Marne impact the Schlieffen Plan?**
**A:** The Battle of the Marne marked the decisive end of the Schlieffen Plan. The French and British forces successfully counterattacked the German advance, halting their progress and forcing them to retreat. The Battle of the Marne demonstrated the limitations of the Schlieffen Plan and the resilience of the Allied forces.
7. **Q: What lessons can be learned from the Schlieffen Plan about the importance of adaptability in military strategy?**
**A:** The Schlieffen Plan highlights the importance of adaptability in military strategy. The plan’s rigid adherence to a predetermined timetable and its failure to account for unexpected events ultimately led to its downfall. Modern military strategists emphasize the need for flexibility, creativity, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
8. **Q: How did the Schlieffen Plan contribute to the stalemate on the Western Front?**
**A:** The Schlieffen Plan, despite its failure, contributed to the stalemate on the Western Front. The initial German advance pushed deep into France, but the Allied counterattack at the Marne halted their progress. Both sides then dug in, leading to a prolonged period of trench warfare.
9. **Q: What were the political consequences of the Schlieffen Plan’s failure?**
**A:** The Schlieffen Plan’s failure had significant political consequences. It prolonged the war, led to immense casualties, and ultimately contributed to the downfall of the German Empire. The plan’s violation of Belgian neutrality also damaged Germany’s international reputation.
10. **Q: How does the Schlieffen Plan influence military thinking today?**
**A:** The Schlieffen Plan continues to be studied in military academies worldwide, serving as a cautionary tale about the dangers of rigid planning and the need for adaptability in warfare. It highlights the importance of logistics, intelligence, and understanding the enemy. Its legacy extends to modern strategic thinking, emphasizing the importance of understanding the operational environment and anticipating potential contingencies.
## Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
The Schlieffen Plan, a bold and ambitious strategy, ultimately failed to achieve its objectives. Its legacy serves as a valuable lesson in the complexities of warfare, highlighting the importance of adaptability, logistics, and accurate intelligence. While the plan itself is a relic of the past, the principles it embodies continue to influence military thinking today.
We’ve explored the origins, execution, and flaws of the Schlieffen Plan, offering a nuanced perspective that goes beyond simplistic narratives. By understanding the plan’s strengths and weaknesses, we can gain valuable insights into the challenges of strategic planning and the importance of flexibility in the face of unforeseen circumstances.
Share your thoughts and experiences with the Schlieffen Plan in the comments below. Explore our other articles on World War I and military strategy to deepen your understanding of this pivotal period in history.
