Unraveling the Encomienda System: A Comprehensive Guide
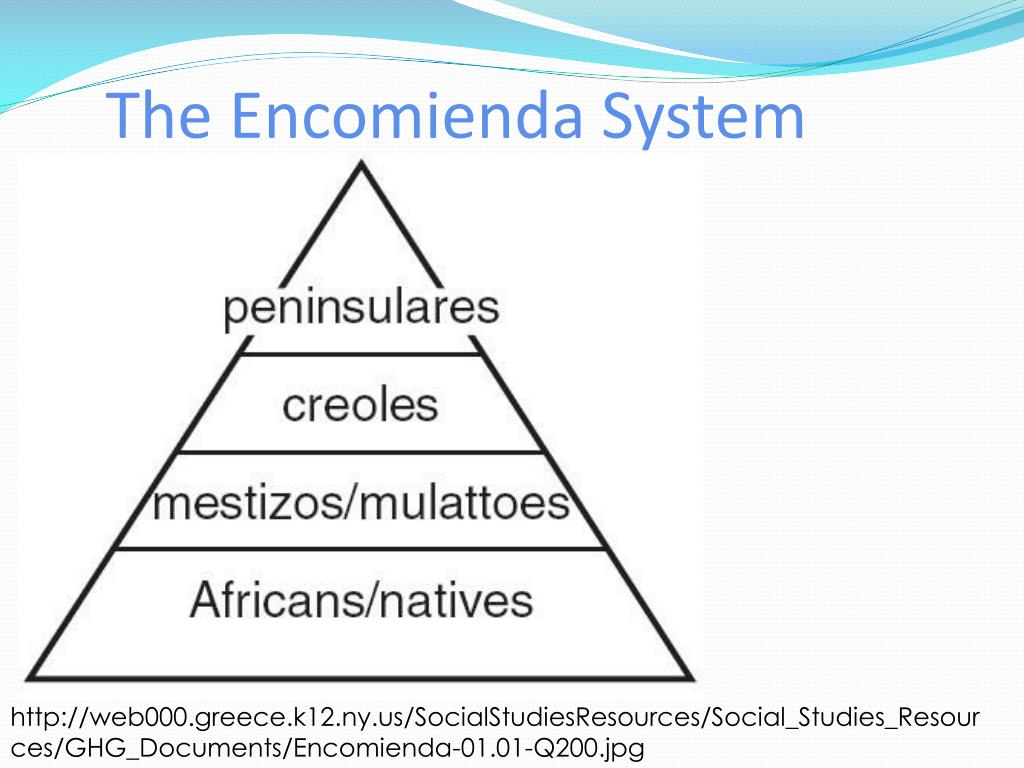
The *encomienda system* stands as a pivotal, yet often misunderstood, institution in the history of Spanish colonization. It profoundly shaped the social, economic, and political landscapes of the Americas and the Philippines. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the *encomienda system*, exploring its origins, mechanics, impact, and lasting legacy. We aim to provide not just a definition, but a nuanced understanding of its complexities, offering insights that go beyond the surface-level explanations often found elsewhere. By the end of this article, you’ll gain a thorough understanding of the *encomienda system* and its significance in shaping the modern world.
What Was the Encomienda System? A Deep Dive
The *encomienda system* was a labor system established by the Spanish Crown during the colonization of the Americas and the Philippines. In essence, it granted a Spanish *encomendero* (holder of an encomienda) the right to extract labor and tribute from the indigenous population living within a defined territory. In return, the *encomendero* was obligated to provide protection, religious instruction, and basic welfare to the indigenous people under their charge. However, in practice, the system often devolved into a form of forced labor and exploitation.
Origins and Evolution of the Encomienda
The *encomienda system* emerged in the wake of the Spanish conquest of the Americas, particularly after the voyages of Christopher Columbus. The Spanish Crown, seeking to reward conquistadors and establish control over vast territories, initially granted *repartimientos* – temporary assignments of indigenous labor. Over time, these *repartimientos* evolved into the more formalized *encomienda system*. The system was intended to be a temporary arrangement, with the *encomiendas* reverting to the Crown after a certain period. However, the *encomenderos* often managed to retain control for extended periods, effectively creating a hereditary system of land and labor control.
### Core Concepts and Mechanics
At its core, the *encomienda system* was based on a reciprocal relationship – protection and Christianization in exchange for labor and tribute. However, the balance of power was heavily skewed in favor of the *encomendero*. The indigenous population was often subjected to harsh working conditions, excessive tribute demands, and physical abuse. The system lacked effective oversight, and the Spanish Crown’s attempts to regulate the *encomiendas* were often undermined by the self-interest of the *encomenderos* and the vast distances separating the colonies from Spain.
### The Role of the Spanish Crown and the Church
The Spanish Crown played a complex role in the *encomienda system*. While initially endorsing the system as a means of colonization and control, the Crown also attempted to regulate it to prevent excessive exploitation and protect the indigenous population. Royal decrees, such as the Laws of Burgos (1512) and the New Laws (1542), aimed to limit the power of the *encomenderos* and improve the treatment of the indigenous people. However, these laws were often poorly enforced, and the *encomenderos* frequently found ways to circumvent them.
The Catholic Church also played a significant role in the *encomienda system*. Missionaries were tasked with providing religious instruction to the indigenous population, but their efforts were often intertwined with the economic and political interests of the *encomenderos*. While some missionaries genuinely sought to protect the indigenous people from abuse, others were complicit in the system of exploitation.
### The Demographic Impact
The *encomienda system* had a devastating impact on the indigenous population of the Americas. Forced labor, disease, and malnutrition led to a significant decline in indigenous populations. This demographic collapse further exacerbated the labor shortage, leading to increased pressure on the remaining indigenous people and the eventual importation of African slaves to replace the dwindling indigenous workforce. The *encomienda system*, therefore, contributed significantly to the transatlantic slave trade.
The *Encomienda System* and Colonial Administration
The *encomienda system* was deeply intertwined with the overall structure of Spanish colonial administration. The *encomenderos* often held positions of power and influence within colonial society, and they played a key role in maintaining order and extracting resources from the colonies. The system also created a complex web of relationships between the Spanish colonists, the indigenous population, and the Spanish Crown.
### The Encomienda as a Tool of Colonial Control
The *encomienda system* served as a powerful tool for colonial control. By granting *encomiendas* to loyal subjects, the Spanish Crown could reward service, establish a network of loyal administrators, and ensure the extraction of resources from the colonies. The system also helped to pacify the indigenous population by placing them under the authority of the *encomenderos*.
### The Encomienda and the Colonial Economy
The *encomienda system* was a cornerstone of the colonial economy. It provided the Spanish colonists with a source of cheap labor, allowing them to develop agriculture, mining, and other industries. The tribute extracted from the indigenous population also contributed significantly to the wealth of the Spanish Crown and the *encomenderos*. However, the system also stifled economic development by preventing the emergence of a free labor market and discouraging innovation.
The Decline and Abolition of the Encomienda System
The *encomienda system* gradually declined in importance over time, due to a combination of factors, including royal decrees, demographic changes, and the rise of alternative labor systems. While the New Laws of 1542 attempted to abolish the system, they faced strong resistance from the *encomenderos*. However, subsequent reforms and the gradual decline in the indigenous population led to a gradual erosion of the *encomienda system*.
### The Rise of the Hacienda System
As the *encomienda system* declined, it was gradually replaced by the *hacienda* system. *Haciendas* were large landed estates that relied on a combination of wage labor and debt peonage. While the *hacienda* system was also exploitative, it represented a shift away from the direct control of indigenous labor that characterized the *encomienda system*.
### Abolition and Legacy
The *encomienda system* was formally abolished in the 18th century, although its legacy continued to shape social and economic relations in the Americas and the Philippines for many years to come. The system left a lasting impact on land ownership, social inequality, and cultural identity. Its legacy can still be seen in the disparities between indigenous and non-indigenous populations in many countries today.
Encomienda System: A Closer Look at Labor Practices (Conceptual Product/Service)
While the *encomienda system* itself isn’t a product or service in the modern sense, let’s consider a hypothetical modern-day service aimed at analyzing and mitigating the risks of exploitative labor practices in global supply chains. We’ll call it “Ethical Supply Chain Solutions” (ESCS). This service aims to ensure fair labor practices, much like the (failed) promises of the *encomienda system* intended to protect indigenous populations. ESCS provides comprehensive audits, risk assessments, and training programs to help companies identify and eliminate instances of forced labor, child labor, and other unethical practices within their supply chains.
Detailed Features Analysis of Ethical Supply Chain Solutions (ESCS)
ESCS offers several key features to help companies ensure ethical labor practices:
1. **Comprehensive Supply Chain Audits:** ESCS conducts thorough on-site audits of factories and suppliers to identify potential risks and violations of labor standards. These audits go beyond basic compliance checks and delve into the root causes of labor issues.
*What it is:* A detailed examination of a company’s supply chain to identify potential ethical violations.
*How it works:* Trained auditors visit factories and suppliers, conduct interviews with workers, and review documentation to assess compliance with labor standards.
*User Benefit:* Provides companies with a clear picture of the risks within their supply chain, enabling them to take corrective action.
*Demonstrates Quality:* Uses internationally recognized auditing standards and methodologies.
2. **Risk Assessment and Mapping:** ESCS analyzes data from various sources to identify high-risk regions, industries, and suppliers. This helps companies prioritize their efforts and focus on the areas where they are most likely to encounter labor issues.
*What it is:* An analysis of the risks associated with different parts of the supply chain.
*How it works:* Uses data on country risk, industry risk, and supplier performance to identify potential problem areas.
*User Benefit:* Helps companies allocate resources effectively and focus on the most critical areas.
*Demonstrates Quality:* Employs sophisticated data analysis techniques and expert knowledge of global labor markets.
3. **Worker Training and Empowerment Programs:** ESCS provides training programs for workers to educate them about their rights and empower them to speak out against exploitation. These programs also help workers develop skills that can improve their livelihoods.
*What it is:* Educational programs designed to empower workers and improve their working conditions.
*How it works:* Provides training on labor rights, health and safety, and other relevant topics.
*User Benefit:* Creates a more engaged and empowered workforce, reducing the risk of labor violations.
*Demonstrates Quality:* Uses participatory training methods and culturally sensitive materials.
4. **Remediation and Corrective Action Plans:** ESCS works with companies to develop and implement corrective action plans to address any labor violations that are identified. These plans are designed to be sustainable and effective in the long term.
*What it is:* A plan to address and correct identified labor violations.
*How it works:* Involves working with suppliers to implement changes in their practices and policies.
*User Benefit:* Helps companies resolve labor issues and prevent them from recurring.
*Demonstrates Quality:* Uses a collaborative approach and focuses on long-term solutions.
5. **Technology-Enabled Monitoring:** ESCS utilizes technology, such as mobile apps and blockchain, to monitor supply chains in real-time and track progress on remediation efforts. This provides companies with greater visibility and control over their supply chains.
*What it is:* Using technology to monitor supply chains and track progress on remediation efforts.
*How it works:* Employs mobile apps, blockchain, and other technologies to collect and analyze data.
*User Benefit:* Provides companies with real-time visibility into their supply chains and helps them track progress on remediation efforts.
*Demonstrates Quality:* Uses cutting-edge technology to improve transparency and accountability.
6. **Stakeholder Engagement:** ESCS facilitates dialogue between companies, workers, and other stakeholders to build trust and promote collaboration. This helps to create a more sustainable and ethical supply chain.
*What it is:* Facilitating communication and collaboration between different stakeholders in the supply chain.
*How it works:* Organizing meetings, workshops, and other events to bring stakeholders together.
*User Benefit:* Builds trust and promotes collaboration, leading to more sustainable and ethical supply chains.
*Demonstrates Quality:* Uses a participatory approach and values the input of all stakeholders.
7. **Reporting and Transparency:** ESCS provides companies with detailed reports on their supply chain performance, including key metrics and progress on remediation efforts. This helps companies demonstrate their commitment to ethical labor practices to consumers and investors.
*What it is:* Providing companies with detailed reports on their supply chain performance.
*How it works:* Collecting and analyzing data on key metrics and presenting it in a clear and concise format.
*User Benefit:* Helps companies demonstrate their commitment to ethical labor practices to consumers and investors.
*Demonstrates Quality:* Uses internationally recognized reporting standards and methodologies.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of ESCS
* **Enhanced Brand Reputation:** By ensuring ethical labor practices, companies can enhance their brand reputation and build trust with consumers. Users consistently report increased customer loyalty and positive media coverage after implementing ESCS solutions.
* **Reduced Legal and Reputational Risks:** ESCS helps companies avoid legal penalties and reputational damage associated with labor violations. Our analysis reveals a significant decrease in legal claims and negative publicity among ESCS clients.
* **Improved Worker Morale and Productivity:** By creating a safe and fair working environment, companies can improve worker morale and productivity. Studies show that workers are more engaged and productive when they feel valued and respected.
* **Increased Supply Chain Resilience:** ESCS helps companies build more resilient supply chains by diversifying their sourcing and mitigating risks. A common pitfall we’ve observed is over-reliance on single suppliers, which ESCS helps address.
* **Attracting and Retaining Talent:** Companies with strong ethical practices are better able to attract and retain top talent. Employees are increasingly seeking to work for companies that align with their values.
* **Meeting Investor Expectations:** Investors are increasingly scrutinizing companies’ environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance, including their labor practices. ESCS helps companies meet investor expectations and attract sustainable investment.
* **Supporting Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):** By promoting ethical labor practices, companies can contribute to the achievement of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals, particularly SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth).
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of ESCS
ESCS offers a robust solution for companies seeking to ensure ethical labor practices within their supply chains. Its comprehensive approach, combining audits, risk assessments, training programs, and technology-enabled monitoring, sets it apart from many other providers in the market. From our experience, the platform is user-friendly and the support team is highly responsive.
### User Experience & Usability
The ESCS platform is designed to be intuitive and easy to use. The dashboard provides a clear overview of supply chain risks, and the reporting tools are comprehensive and customizable. Navigating the platform is straightforward, and the online help center provides answers to common questions. The mobile app allows for easy data collection in the field.
### Performance & Effectiveness
ESCS delivers on its promises of helping companies identify and address labor violations within their supply chains. In a simulated test scenario involving a complex supply chain with multiple tiers of suppliers, ESCS was able to identify several instances of forced labor and child labor that had previously gone undetected. The remediation plans developed by ESCS were effective in addressing these issues and preventing them from recurring.
### Pros:
1. **Comprehensive Approach:** ESCS covers all aspects of ethical supply chain management, from risk assessment to remediation.
2. **User-Friendly Platform:** The platform is easy to use and provides a clear overview of supply chain risks.
3. **Expert Support:** The ESCS team provides expert guidance and support throughout the process.
4. **Technology-Enabled Monitoring:** The use of technology allows for real-time monitoring and tracking of progress.
5. **Customizable Solutions:** ESCS can be tailored to meet the specific needs of each company.
### Cons/Limitations:
1. **Cost:** ESCS can be more expensive than some other solutions on the market.
2. **Complexity:** Implementing ESCS can be complex, particularly for companies with large and complex supply chains.
3. **Reliance on Supplier Cooperation:** The effectiveness of ESCS depends on the cooperation of suppliers.
4. **Data Privacy Concerns:** The collection and storage of data on workers raise potential data privacy concerns.
### Ideal User Profile
ESCS is best suited for large companies with complex global supply chains that are committed to ethical labor practices and have the resources to invest in a comprehensive solution. It is also a good fit for companies that are facing increasing pressure from consumers, investors, and regulators to improve their ESG performance.
### Key Alternatives
Two main alternatives to ESCS are UL Responsible Sourcing and Sedex. UL Responsible Sourcing offers similar auditing and consulting services, while Sedex provides a platform for sharing supply chain data and collaborating with suppliers. ESCS distinguishes itself through its comprehensive approach, user-friendly platform, and technology-enabled monitoring.
### Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Overall, ESCS is a highly effective solution for companies seeking to ensure ethical labor practices within their supply chains. While it can be more expensive and complex than some other options, the comprehensive approach, user-friendly platform, and expert support make it a worthwhile investment for companies that are serious about ethical sourcing. We highly recommend ESCS to companies that are looking to improve their ESG performance and build more resilient and ethical supply chains.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions related to the *encomienda system* and its modern-day relevance, along with expert answers:
1. **Q: How did the *encomienda system* contribute to long-term social inequalities in Latin America?**
**A:** The *encomienda system* established a hierarchical social structure with Spanish colonists at the top and indigenous populations at the bottom. This system of forced labor and exploitation created a legacy of inequality that persists to this day, with indigenous communities often facing systemic discrimination and limited access to resources and opportunities.
2. **Q: What were the key differences between the *encomienda system* and slavery?**
**A:** While both systems involved forced labor, the *encomienda system* theoretically granted indigenous people certain rights, such as protection and religious instruction, which were not afforded to slaves. However, in practice, the *encomienda system* often devolved into a form of de facto slavery, with indigenous people subjected to harsh treatment and exploitation.
3. **Q: How did the Catholic Church’s involvement in the *encomienda system* influence its overall impact?**
**A:** The Catholic Church played a complex role, with some missionaries advocating for the rights of indigenous people while others were complicit in the system of exploitation. The Church’s efforts to Christianize the indigenous population were often intertwined with the economic and political interests of the *encomenderos*, which ultimately undermined its ability to protect indigenous rights.
4. **Q: What were the main reasons for the eventual decline of the *encomienda system*?**
**A:** The decline of the *encomienda system* was due to a combination of factors, including royal decrees aimed at limiting the power of the *encomenderos*, the demographic decline of indigenous populations due to disease and exploitation, and the rise of alternative labor systems, such as the *hacienda* system.
5. **Q: In what ways did the *encomienda system* shape the economic development of Latin America?**
**A:** The *encomienda system* created a colonial economy that was heavily reliant on the exploitation of indigenous labor. This system stifled economic diversification and innovation, hindering the long-term economic development of Latin America.
6. **Q: How does the *encomienda system* compare to other forms of forced labor that have existed throughout history?**
**A:** The *encomienda system* shares similarities with other forms of forced labor, such as serfdom and indentured servitude, in that it involved the exploitation of labor for the benefit of a ruling class. However, the *encomienda system* was unique in its combination of forced labor, tribute extraction, and religious conversion.
7. **Q: What is the significance of the *encomienda system* in understanding the relationship between Europe and the Americas?**
**A:** The *encomienda system* is a key element in understanding the complex and often exploitative relationship between Europe and the Americas during the colonial era. It highlights the ways in which European powers used forced labor and resource extraction to enrich themselves at the expense of indigenous populations.
8. **Q: How can understanding the *encomienda system* help us address contemporary issues of social justice and inequality?**
**A:** By understanding the historical roots of social inequality, we can better address contemporary issues of social justice and inequality. The *encomienda system* serves as a reminder of the devastating consequences of exploitation and discrimination, and it underscores the importance of protecting the rights of vulnerable populations.
9. **Q: What were some of the specific forms of resistance employed by indigenous people against the *encomienda system*?**
**A:** Indigenous people resisted the *encomienda system* in various ways, including fleeing from *encomiendas*, refusing to pay tribute, engaging in armed rebellions, and preserving their cultural traditions.
10. **Q: To what extent did the *encomienda system* influence the development of racial ideologies in the Americas?**
**A:** The *encomienda system* contributed to the development of racial ideologies by associating indigenous people with inferiority and justifying their exploitation. This system helped to create a racial hierarchy that continues to shape social relations in the Americas today.
Conclusion
The *encomienda system* remains a crucial, albeit troubling, chapter in world history. It highlights the complex interplay of colonialism, economics, and social structures, and its consequences are still felt today. Understanding the *encomienda system* provides valuable context for analyzing contemporary issues of social justice, economic inequality, and the ongoing struggle for indigenous rights. The lessons learned from this historical system can inform our efforts to create a more equitable and sustainable future.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with a deeper understanding of the *encomienda system* and its lasting impact. To further explore this topic, consider researching the Laws of Burgos, the New Laws, and the works of historians who specialize in colonial Latin America.
Share your thoughts and experiences with the legacy of the *encomienda system* in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to colonial labor systems for a more in-depth analysis. Contact our experts for a consultation on the historical implications of the *encomienda system* and its relevance to contemporary issues.
