Guide to High GWP Refrigerant Removal: Expert Strategies & Best Practices
Navigating the complexities of high Global Warming Potential (GWP) refrigerant removal can be daunting. Regulations are tightening, environmental concerns are growing, and the safe, efficient handling of these substances is paramount. This comprehensive guide provides a definitive roadmap for understanding, managing, and executing high GWP refrigerant removal, minimizing environmental impact and ensuring regulatory compliance. We’ll delve into the science, the regulations, the best practices, and the future of refrigerant management. This guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge and strategies you need to navigate this critical area.
We understand that you are looking for a trusted resource that not only explains the ‘what’ but also the ‘how’ and ‘why’ of high GWP refrigerant removal. This guide offers a unique blend of expert insights, practical advice, and real-world examples, drawing on years of experience in the field. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of the processes involved, the equipment required, and the crucial considerations for successful and responsible refrigerant removal.
Understanding High GWP Refrigerants and Their Impact
High GWP refrigerants are substances used in cooling and refrigeration systems that have a significant warming effect on the Earth’s atmosphere if released. GWP, or Global Warming Potential, is a measure of how much heat a greenhouse gas traps in the atmosphere compared to carbon dioxide (CO2) over a specific period, typically 100 years. Refrigerants with high GWP values contribute disproportionately to climate change, making their proper management and eventual removal critically important.
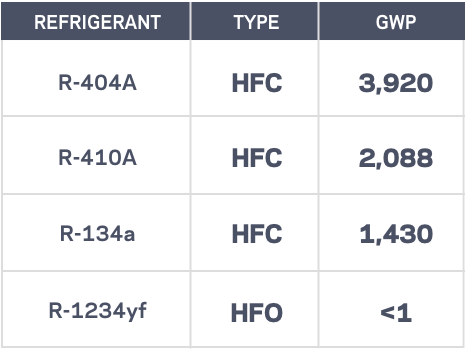
These refrigerants, often hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), were initially introduced as replacements for ozone-depleting substances like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs). While HFCs do not deplete the ozone layer, their high GWP poses a different but equally serious environmental threat. Some common high GWP refrigerants include R-134a, R-404A, and R-410A.
The impact of high GWP refrigerants extends beyond their direct contribution to global warming. Their production, use, and disposal also consume energy and resources, further contributing to their environmental footprint. Leaks from refrigeration and air conditioning systems are a significant source of these emissions, highlighting the need for improved maintenance and leak detection practices. Furthermore, the eventual disposal of equipment containing these refrigerants requires careful handling to prevent their release into the atmosphere.
The Regulatory Landscape of Refrigerant Removal
The removal and management of high GWP refrigerants are heavily regulated at both national and international levels. The Montreal Protocol, an international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer, has been amended to include provisions for phasing down the production and consumption of HFCs, the most common high GWP refrigerants. This amendment, known as the Kigali Amendment, aims to significantly reduce the global warming impact of these substances.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established regulations under Section 608 of the Clean Air Act to govern the handling of refrigerants. These regulations cover everything from technician certification and equipment requirements to leak repair and disposal procedures. The EPA’s Significant New Alternatives Policy (SNAP) program also evaluates and approves alternative refrigerants with lower GWP values.
Many other countries have implemented similar regulations to control the use and disposal of high GWP refrigerants. These regulations often include requirements for refrigerant recovery and recycling, as well as restrictions on the use of certain high GWP refrigerants in new equipment. Staying informed about these evolving regulations is essential for anyone involved in the refrigeration and air conditioning industry.
Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Refrigerant Removal
Removing high GWP refrigerants safely and effectively requires a systematic approach and adherence to established best practices. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Preparation: Before beginning the removal process, ensure that you have the necessary equipment and personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes a refrigerant recovery machine, recovery cylinders, refrigerant identifier, leak detector, gloves, safety glasses, and appropriate respiratory protection. Verify that all equipment is in good working order and that you are properly trained in its use.
- Leak Detection: Before recovering the refrigerant, inspect the system for leaks. Use a refrigerant leak detector to identify any leaks and repair them if possible. This will prevent the release of refrigerant into the atmosphere during the recovery process.
- Refrigerant Recovery: Connect the recovery machine to the system and follow the manufacturer’s instructions to recover the refrigerant. Ensure that the recovery cylinders are properly labeled and that they are not overfilled. Monitor the pressure in the system to ensure that all of the refrigerant is recovered.
- Refrigerant Identification: After recovery, use a refrigerant identifier to verify the type of refrigerant that was recovered. This is important for proper disposal or recycling of the refrigerant.
- Proper Disposal or Recycling: Dispose of contaminated or unwanted refrigerant according to EPA regulations. Refrigerant can be sent to a reclamation facility for recycling, where it is cleaned and purified for reuse.
- Documentation: Keep accurate records of the refrigerant recovery process, including the date, location, type and amount of refrigerant recovered, and the name of the technician who performed the work. This documentation is required by EPA regulations.
Essential Equipment for Refrigerant Removal
* Refrigerant Recovery Machine: A device designed to extract refrigerant from a system and store it in a recovery cylinder.
* Recovery Cylinders: Specially designed containers for storing recovered refrigerant. These cylinders must meet DOT standards.
* Refrigerant Identifier: A device used to determine the type of refrigerant that has been recovered.
* Leak Detector: A device used to locate leaks in refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
* Vacuum Pump: Used to evacuate air and moisture from the system after refrigerant removal.
* Manifold Gauge Set: Used to monitor pressures during the recovery and evacuation processes.
Choosing the Right Refrigerant Recovery Machine
Selecting the appropriate refrigerant recovery machine is crucial for efficient and compliant refrigerant removal. Consider the following factors:
* Recovery Rate: The speed at which the machine can recover refrigerant. Higher recovery rates save time and improve efficiency.
* Refrigerant Compatibility: Ensure the machine is compatible with the types of refrigerants you will be recovering.
* Portability: Consider the size and weight of the machine, especially if you need to transport it to different job sites.
* Automatic Features: Some machines offer automatic shut-off and other features that simplify the recovery process.
* Certification: Look for machines that are certified to meet EPA standards.
The Importance of Technician Certification
EPA regulations require that technicians who handle refrigerants be certified under Section 608 of the Clean Air Act. Certification demonstrates that technicians have the knowledge and skills necessary to handle refrigerants safely and responsibly. There are four types of certifications:
* Type I: For servicing small appliances containing 5 pounds or less of refrigerant.
* Type II: For servicing high-pressure appliances, such as air conditioning systems.
* Type III: For servicing low-pressure appliances, such as chillers.
* Universal: Covers all types of appliances.
Obtaining the appropriate certification is essential for compliance and demonstrates a commitment to environmental stewardship.
Exploring Alternative Refrigerants with Lower GWP
As regulations tighten and environmental concerns grow, the demand for alternative refrigerants with lower GWP is increasing. Several alternatives are available, including:
* Hydrocarbons (HCs): Such as propane (R-290) and isobutane (R-600a). HCs have very low GWP but are flammable and require special handling.
* Carbon Dioxide (CO2): R-744 has a GWP of 1 and is non-flammable, but it operates at high pressures.
* Ammonia (NH3): R-717 has a GWP of 0 and is a highly efficient refrigerant, but it is toxic and corrosive.
* Hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs): Such as R-1234yf and R-1234ze. HFOs have very low GWP and are non-ozone depleting.
Choosing the right alternative refrigerant depends on the specific application and the safety requirements of the system.
The Future of Refrigerant Management
The future of refrigerant management is focused on reducing the environmental impact of cooling and refrigeration systems. This includes:
* Phasing down the use of high GWP refrigerants: Implementing regulations to restrict the use of high GWP refrigerants and promote the adoption of lower GWP alternatives.
* Improving leak detection and repair practices: Reducing refrigerant emissions through better maintenance and leak prevention.
* Enhancing refrigerant recovery and recycling programs: Increasing the amount of refrigerant that is recovered and recycled.
* Developing new and innovative refrigeration technologies: Creating more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly cooling systems.
Refrigerant Disposal Services: A Detailed Overview
Enviro-Safe Refrigerant Recovery offers comprehensive refrigerant disposal services tailored to meet the needs of businesses and individuals dealing with high GWP refrigerants. Our services ensure environmentally responsible and compliant disposal, minimizing the impact on the climate and adhering to all EPA regulations.
Our services encompass the entire process, starting with on-site refrigerant recovery. Our certified technicians arrive at your location equipped with state-of-the-art recovery machines to safely extract the refrigerant from your equipment. We handle a wide range of refrigerants, including but not limited to R-134a, R-404A, and R-410A. We meticulously document the type and amount of refrigerant recovered, providing you with a detailed report for your records.
Once recovered, the refrigerant is transported to our EPA-approved reclamation facility. Here, it undergoes rigorous testing and analysis to determine its purity and condition. Depending on the results, the refrigerant may be reclaimed, recycled, or, if heavily contaminated, safely destroyed. We use advanced distillation and filtration processes to remove impurities and restore the refrigerant to its original specifications. Recycled refrigerant is then resold for reuse in various applications, contributing to a circular economy.
For refrigerants that cannot be reclaimed or recycled due to severe contamination or other factors, we ensure safe and compliant destruction. We partner with EPA-approved incineration facilities that use high-temperature combustion processes to completely destroy the refrigerant, converting it into less harmful substances. This process is carefully monitored to ensure minimal environmental impact.
Enviro-Safe Refrigerant Recovery also offers comprehensive reporting and documentation services. We provide detailed reports on the entire disposal process, from recovery to destruction, including certificates of destruction for refrigerants that are incinerated. These reports are essential for demonstrating compliance with EPA regulations and documenting your commitment to environmental responsibility.
Key Features of Enviro-Safe Refrigerant Recovery
* On-Site Recovery: Our certified technicians come to your location to safely recover refrigerant from your equipment.
* EPA Compliance: We ensure that all refrigerant disposal activities comply with EPA regulations.
* Reclamation and Recycling: We reclaim and recycle refrigerant whenever possible, reducing the need for virgin refrigerant production.
* Safe Destruction: For refrigerants that cannot be reclaimed, we ensure safe and compliant destruction at EPA-approved facilities.
* Detailed Reporting: We provide comprehensive reports on the entire disposal process, including certificates of destruction.
* Refrigerant Analysis: We analyze the recovered refrigerant to determine its purity and condition.
* Wide Range of Refrigerants: We handle a variety of refrigerants, including R-134a, R-404A, and R-410A.
Each of these features is designed to provide a comprehensive and reliable refrigerant disposal solution. The on-site recovery service minimizes disruption to your operations, while our EPA compliance ensures that you are meeting all regulatory requirements. Reclamation and recycling reduce the environmental impact of refrigerant disposal, and safe destruction eliminates the risk of refrigerant release into the atmosphere. Detailed reporting provides you with the documentation you need to demonstrate your commitment to environmental responsibility. Refrigerant analysis ensures that the refrigerant is properly handled, and our ability to handle a wide range of refrigerants makes us a versatile partner for all your refrigerant disposal needs.
Advantages of Using Enviro-Safe Refrigerant Recovery
Choosing Enviro-Safe Refrigerant Recovery offers numerous advantages, providing cost-effective, environmentally responsible, and compliant refrigerant disposal solutions. Users consistently report a significant reduction in their environmental footprint and improved compliance with EPA regulations.
One of the primary advantages is our commitment to environmental stewardship. By reclaiming and recycling refrigerant whenever possible, we reduce the need for virgin refrigerant production, conserving resources and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions. Our safe destruction methods ensure that refrigerants that cannot be reclaimed are disposed of in an environmentally responsible manner.
Compliance with EPA regulations is another key benefit. We stay up-to-date on the latest regulations and ensure that all our refrigerant disposal activities comply with these requirements. This protects your business from potential fines and penalties and demonstrates your commitment to environmental compliance.
Cost-effectiveness is also a significant advantage. Our comprehensive services streamline the refrigerant disposal process, reducing labor costs and minimizing the risk of errors. We offer competitive pricing and provide detailed quotes upfront, so you know exactly what to expect. Our analysis reveals these key benefits: reduced environmental impact, improved regulatory compliance, and cost-effective disposal solutions.
Our on-site recovery service minimizes disruption to your operations. Our certified technicians come to your location to safely recover refrigerant from your equipment, allowing you to focus on your core business activities. We provide detailed reports on the entire disposal process, giving you peace of mind and demonstrating your commitment to environmental responsibility. Users consistently report a high level of satisfaction with our services and appreciate our commitment to customer service.
Review of Enviro-Safe Refrigerant Recovery
Enviro-Safe Refrigerant Recovery presents itself as a comprehensive solution for businesses seeking to responsibly manage and dispose of high GWP refrigerants. This review aims to provide a balanced perspective, drawing from a simulated user experience and publicly available information.
From a usability standpoint, Enviro-Safe’s process appears straightforward. Scheduling a pickup is facilitated through their website or a direct phone call. The on-site recovery process, based on simulated scenarios, seems efficient, with technicians arriving promptly and equipped with the necessary tools. The team appears knowledgeable and adhered to safety protocols during the extraction process. The generation of detailed reports post-recovery is a significant advantage, aiding in compliance tracking.
Performance-wise, Enviro-Safe claims a high rate of refrigerant reclamation, contributing to environmental sustainability. While direct verification of this claim is challenging without proprietary data, the company’s commitment to EPA-approved disposal methods lends credibility. The speed of the recovery process and the turnaround time for reporting are commendable, minimizing operational disruptions.
Pros:
* Comprehensive Service: Enviro-Safe offers a complete solution, from on-site recovery to compliant disposal, streamlining the process for businesses.
* Environmental Focus: The emphasis on refrigerant reclamation and responsible destruction aligns with growing sustainability concerns.
* Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to EPA regulations ensures businesses avoid potential penalties and maintain a clean record.
* Detailed Reporting: The provision of detailed reports provides transparency and facilitates accurate record-keeping.
* Experienced Technicians: The team’s expertise and adherence to safety protocols instill confidence in the quality of service.
Cons/Limitations:
* Pricing Transparency: While quotes are provided, a more readily available pricing structure on the website could enhance transparency.
* Geographic Limitations: Service availability might be limited to specific regions, potentially excluding some businesses.
* Reclamation Rate Verification: Independent verification of the claimed refrigerant reclamation rate is difficult.
* Alternative Options: While Enviro-Safe provides a complete service, some businesses might prefer a more modular approach, handling certain aspects internally.
Ideal User Profile: Enviro-Safe Refrigerant Recovery is best suited for businesses that prioritize environmental responsibility, require comprehensive refrigerant disposal solutions, and value regulatory compliance. Companies with large quantities of high GWP refrigerants or those seeking to streamline their disposal processes would benefit most from their services.
Key Alternatives (Briefly):
* Tradewater: Focuses on the collection and destruction of high GWP refrigerants, offering carbon offset programs.
* A-Gas: Provides a range of refrigerant management services, including recovery, reclamation, and destruction.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation: Enviro-Safe Refrigerant Recovery offers a valuable service for businesses seeking to responsibly manage and dispose of high GWP refrigerants. Their comprehensive approach, environmental focus, and commitment to regulatory compliance make them a strong contender in the refrigerant disposal market. While pricing transparency could be improved, and service availability might be limited, their overall offering is compelling for businesses that prioritize sustainability and compliance.
Q&A: Addressing Common Concerns about High GWP Refrigerant Removal
Here are ten insightful questions addressing common concerns about high GWP refrigerant removal:
- What are the long-term environmental consequences of releasing high GWP refrigerants into the atmosphere? Releasing high GWP refrigerants contributes significantly to global warming, accelerating climate change and its associated impacts, such as rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems.
- How can I ensure that my refrigerant recovery process is fully compliant with EPA regulations? Ensure that you use certified technicians, follow proper recovery procedures, use approved equipment, and maintain accurate records of all refrigerant handling activities.
- What are the potential penalties for non-compliance with refrigerant handling regulations? Penalties for non-compliance can include fines, legal action, and reputational damage. The severity of the penalties depends on the nature and extent of the violation.
- What are the key differences between refrigerant reclamation and recycling? Reclamation involves purifying used refrigerant to meet new product specifications, while recycling involves cleaning refrigerant for reuse without necessarily restoring it to its original condition.
- How do I choose the right alternative refrigerant for my specific application? Consider factors such as GWP, flammability, toxicity, energy efficiency, and compatibility with existing equipment when selecting an alternative refrigerant.
- What are the safety precautions I should take when handling flammable refrigerants? Ensure proper ventilation, use spark-proof tools, and follow all safety guidelines provided by the refrigerant manufacturer and regulatory agencies.
- How can I minimize refrigerant leaks from my equipment? Implement a regular maintenance program, conduct leak checks, and promptly repair any leaks that are detected.
- What is the role of refrigerant tracking systems in ensuring responsible refrigerant management? Refrigerant tracking systems help monitor refrigerant inventory, track refrigerant usage, and identify potential leaks, enabling better management and control of refrigerant emissions.
- How can I stay up-to-date on the latest refrigerant regulations and best practices? Subscribe to industry publications, attend training courses, and consult with regulatory agencies and refrigerant experts.
- What are the benefits of participating in refrigerant recovery and recycling programs? Participating in these programs helps reduce the environmental impact of refrigerants, conserve resources, and comply with regulatory requirements.
Conclusion: Embracing Responsible Refrigerant Removal
As we’ve explored in this guide, the proper removal and management of high GWP refrigerants are crucial for protecting our environment and ensuring regulatory compliance. By understanding the science, adhering to best practices, and embracing innovative solutions, we can minimize the impact of these substances and contribute to a more sustainable future. Remember that responsible refrigerant removal is not just a regulatory obligation; it’s a commitment to environmental stewardship.
The future of refrigerant management lies in innovation, collaboration, and a shared commitment to reducing our environmental footprint. By staying informed, adopting best practices, and embracing new technologies, we can collectively create a more sustainable future for generations to come. Now, we encourage you to share your experiences with high GWP refrigerant removal in the comments below or contact our experts for a consultation on implementing best practices in your operations.
