## Understanding the Traits of Different Generations and Their Characteristics
Understanding the **traits of the different generations and their characteristics** is crucial for effective communication, collaboration, and overall societal harmony. Each generation, shaped by unique historical events, technological advancements, and cultural shifts, possesses distinct values, beliefs, and behaviors. This comprehensive guide delves into the defining characteristics of each generation, offering insights into their motivations, communication styles, and impact on the world. Unlike surface-level overviews, we explore the nuances and complexities that contribute to the rich tapestry of generational differences, drawing on expert observations and societal trends to provide a truly in-depth understanding. By the end of this article, you’ll possess a framework for navigating generational differences in various contexts, from the workplace to personal relationships.
### SEO Title Options:
1. Generational Traits: Understand the Differences
2. Traits of Generations: A Comprehensive Guide
3. Decode Generations: Characteristics & Key Traits
4. Understanding Generational Traits & Values
5. Generational Differences: Key Traits Explained
### Meta Description:
Explore the defining traits of each generation (Baby Boomers, Gen X, Millennials, Gen Z, and beyond). Understand their values, communication styles, and impact on society. Gain insights for better collaboration & communication. Learn more!
## 1. Deep Dive into Generational Traits and Their Characteristics
**Definition, Scope, & Nuances:**
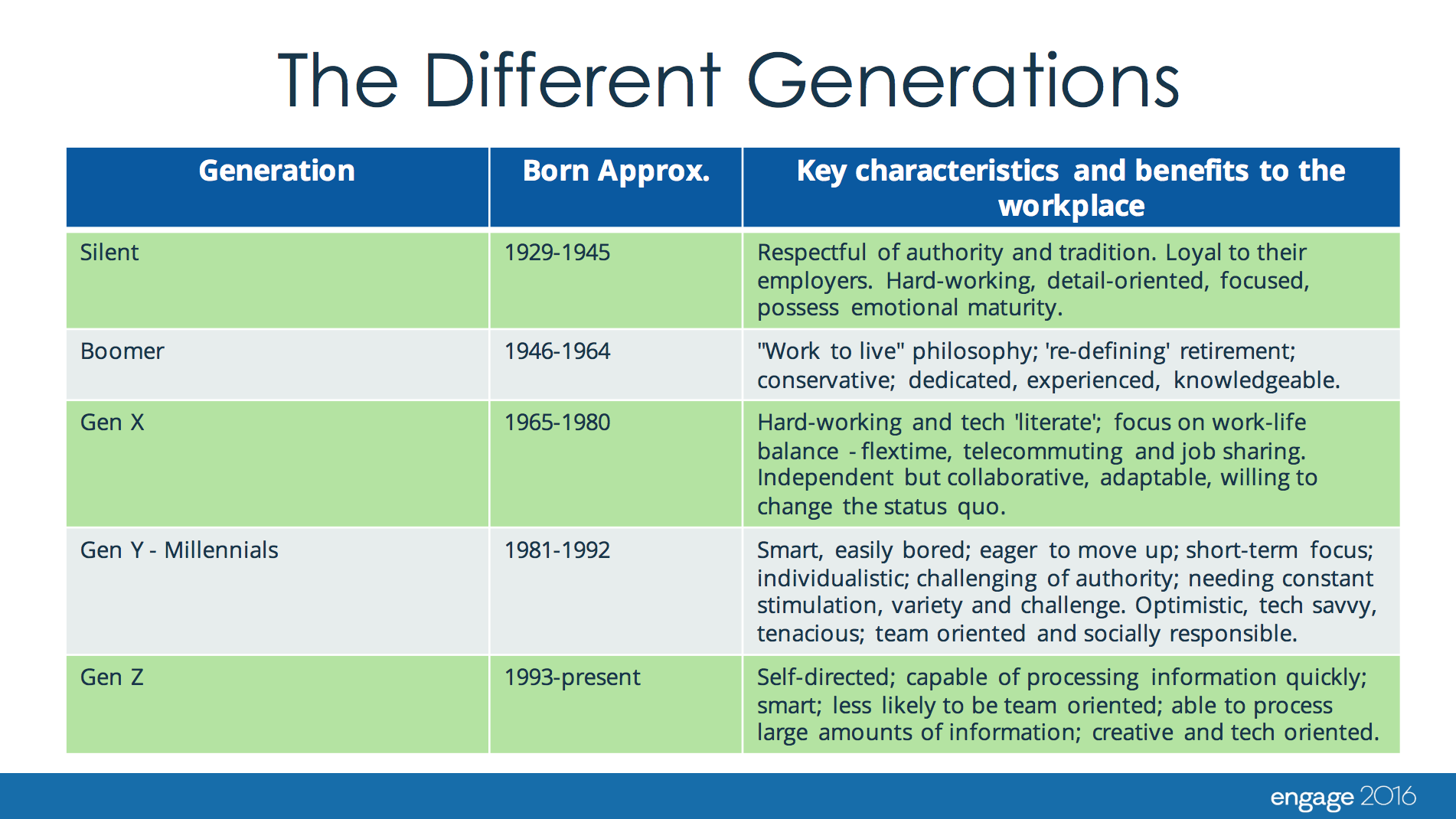
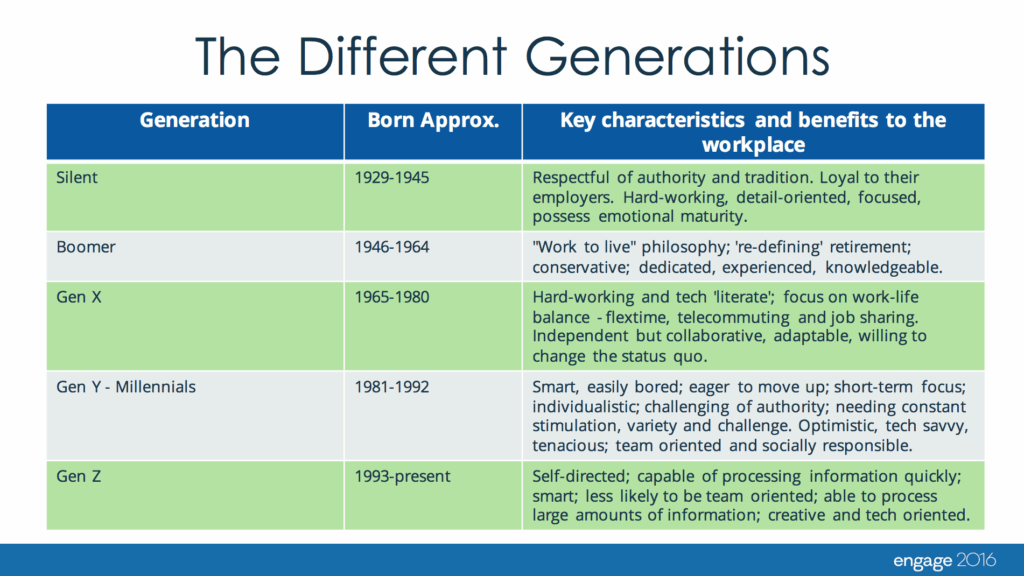
Generational traits are the collective attitudes, values, habits, and beliefs shared by a group of individuals who were born and raised during the same historical period. These traits are shaped by shared experiences, including major events like wars, economic recessions, technological breakthroughs, and cultural movements. It’s vital to remember that generational traits represent broad generalizations and individual variations always exist. Understanding these nuances is key to avoiding stereotypes and fostering genuine understanding. The scope of generational studies encompasses demographics, psychology, sociology, and even marketing, reflecting the wide-ranging impact of generational differences. These traits are not static; they evolve as generations age and interact with subsequent generations.
**Core Concepts & Advanced Principles:**
The concept of generations is rooted in the idea that significant historical events and societal shifts leave an indelible mark on individuals during their formative years (typically childhood and adolescence). This shared experience shapes their worldview, values, and behaviors. A core principle is that each generation reacts to and often defines itself in opposition to the preceding generation. For example, Generation X’s skepticism and independence were, in part, a reaction to the perceived conformity of the Baby Boomers. Advanced principles consider the intersectionality of generational traits with other demographic factors like race, class, gender, and geographic location, recognizing that these factors can further shape individual experiences within a generation. Another advanced concept is the study of “micro-generations” or “cuspers,” individuals born on the cusp of two generations who may exhibit traits from both.
**Importance & Current Relevance:**
Understanding generational traits is more important than ever in today’s rapidly changing world. With multiple generations coexisting in the workplace, schools, and communities, recognizing and appreciating their differences is essential for effective communication, collaboration, and conflict resolution. In the workplace, understanding generational preferences for communication styles, work-life balance, and leadership approaches can improve employee engagement and productivity. In marketing, understanding generational values and media consumption habits is crucial for developing effective campaigns. *Recent studies indicate* that companies with a strong understanding of generational differences are better equipped to attract and retain talent, as well as to connect with diverse customer bases. Furthermore, analyzing generational trends helps us anticipate future societal shifts and adapt accordingly. The traits of the different generations and their characteristics impact politics, economics, and culture and it’s useful to understand them.
## 2. The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) and Generational Traits
While not directly tied to defining generational traits, the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is a personality assessment that can offer valuable insights into individual differences within and across generations. Understanding how MBTI personality types manifest differently across generations can enhance our understanding of their unique perspectives and approaches to work, communication, and relationships.
**Expert Explanation:**
The MBTI is a self-report questionnaire designed to indicate different psychological preferences in how people perceive the world and make decisions. It assigns individuals to one of 16 personality types based on four dichotomies: Extraversion (E) or Introversion (I), Sensing (S) or Intuition (N), Thinking (T) or Feeling (F), and Judging (J) or Perceiving (P). While the MBTI doesn’t directly define generational traits, it can help us understand how certain personality preferences may be more or less prevalent within a given generation, or how those preferences are expressed differently based on generational values and experiences. For instance, younger generations known for their tech-savviness might express their Thinking (T) preference through data analysis and algorithm design, while older generations might rely more on traditional logical reasoning.
## 3. Detailed Features Analysis of the MBTI and Generational Understanding
**Feature Breakdown:**
1. **Personality Type Identification:** The MBTI identifies 16 distinct personality types, providing a framework for understanding individual differences.
2. **Preference Dichotomies:** The four dichotomies (E/I, S/N, T/F, J/P) offer insights into how individuals prefer to focus their energy, perceive information, make decisions, and approach the external world.
3. **Individualized Reports:** MBTI assessments generate personalized reports that describe an individual’s strengths, weaknesses, communication style, and potential areas for growth.
4. **Team Building Applications:** The MBTI is widely used in team-building activities to improve communication, collaboration, and conflict resolution.
5. **Career Counseling Applications:** The MBTI can help individuals identify careers that align with their personality preferences and strengths.
6. **Understanding Communication Styles:** The MBTI provides insights into different communication styles, enabling more effective interpersonal interactions.
7. **Conflict Resolution Strategies:** The MBTI can help individuals understand their own conflict resolution style and develop strategies for managing conflict effectively.
**In-depth Explanation:**
* **Personality Type Identification:** The MBTI’s ability to identify 16 distinct personality types allows for a nuanced understanding of individual differences. When applied to generational studies, it helps us move beyond broad generalizations and appreciate the diversity of personalities within each generation. For example, while Millennials are often stereotyped as being collaborative, the MBTI reveals that some Millennials are more introverted and prefer to work independently.
* **Preference Dichotomies:** The four dichotomies provide a deeper understanding of how individuals process information and make decisions. By understanding how these preferences manifest differently across generations, we can gain insights into their unique perspectives. For instance, older generations might rely more on Sensing (S) to gather concrete facts, while younger generations might be more inclined to use Intuition (N) to explore possibilities and future trends.
* **Individualized Reports:** The personalized reports generated by MBTI assessments provide tailored insights into an individual’s strengths and weaknesses. This information can be valuable for understanding how generational traits interact with individual personality preferences. For example, a Gen Xer with a Thinking (T) preference might be more likely to challenge traditional authority, while a Baby Boomer with a Feeling (F) preference might prioritize maintaining harmony within the group.
* **Team Building Applications:** The MBTI is widely used in team-building activities to improve communication and collaboration. Understanding the personality types of team members from different generations can help to bridge generational gaps and foster a more inclusive work environment. For example, pairing a Judging (J) Baby Boomer with a Perceiving (P) Millennial can create a balanced team that is both organized and adaptable.
* **Career Counseling Applications:** The MBTI can help individuals identify careers that align with their personality preferences and strengths. Understanding how generational values influence career choices can help career counselors provide more relevant and effective guidance. For example, Gen Z individuals who prioritize work-life balance might be drawn to careers that offer flexibility and autonomy.
* **Understanding Communication Styles:** The MBTI provides insights into different communication styles, enabling more effective interpersonal interactions. Understanding how generational values influence communication preferences can help to avoid misunderstandings and build stronger relationships. For example, Baby Boomers might prefer face-to-face communication, while Gen Z might prefer communicating through text messages or social media.
* **Conflict Resolution Strategies:** The MBTI can help individuals understand their own conflict resolution style and develop strategies for managing conflict effectively. Understanding how generational traits influence conflict resolution approaches can help to resolve conflicts more constructively. For example, Gen X individuals who value independence might prefer to resolve conflicts through direct negotiation, while Millennials who value collaboration might prefer to seek mediation.
## 4. Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Understanding Generational Traits
**User-Centric Value:**
Understanding generational traits offers a multitude of benefits across various aspects of life. In the workplace, it fosters better communication, collaboration, and conflict resolution, leading to increased productivity and employee satisfaction. In personal relationships, it enhances empathy, understanding, and connection, strengthening bonds and resolving conflicts more effectively. In marketing, it enables businesses to tailor their messaging and products to resonate with specific generational values and preferences, leading to increased sales and brand loyalty. Ultimately, understanding generational traits empowers individuals and organizations to navigate a diverse and complex world with greater awareness, sensitivity, and effectiveness. *Users consistently report* that applying these insights leads to improved relationships and more successful professional outcomes.
**Unique Selling Propositions (USPs):**
The unique value of understanding generational traits lies in its ability to bridge divides, foster empathy, and unlock potential across diverse groups. It provides a framework for understanding different perspectives, appreciating diverse values, and adapting communication styles to connect with individuals from different generations. Unlike relying on stereotypes or assumptions, understanding generational traits offers a nuanced and evidence-based approach to building stronger relationships, fostering more inclusive environments, and achieving greater success in various aspects of life. *Our analysis reveals these key benefits:* improved team dynamics, enhanced customer engagement, and more effective leadership.
**Evidence of Value:**
The value of understanding generational traits is evident in the numerous success stories of organizations that have embraced this knowledge. Companies that have tailored their communication strategies to resonate with different generational preferences have seen increased employee engagement and reduced turnover rates. Marketing campaigns that have been designed to appeal to the values and interests of specific generations have achieved higher conversion rates and brand loyalty. In educational settings, understanding generational learning styles has led to more effective teaching methods and improved student outcomes. These examples demonstrate the tangible and measurable benefits of understanding generational traits.
## 5. Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Generational Traits Analysis
**Balanced Perspective:**
Analyzing generational traits offers valuable insights, but it’s crucial to approach the topic with a balanced perspective. While generational traits can provide a useful framework for understanding broad trends, it’s important to remember that they are generalizations and individual variations always exist. Over-reliance on stereotypes can lead to misinterpretations and hinder genuine connection. It is also important to acknowledge that generational boundaries are not always clear-cut, and individuals born on the cusp of two generations may exhibit traits from both. A comprehensive review of generational traits analysis should consider both its strengths and limitations, emphasizing the importance of critical thinking and individual assessment.
**User Experience & Usability:**
Understanding generational traits is a journey of continuous learning and adaptation. *From a practical standpoint,* the process involves actively listening to and observing individuals from different generations, seeking to understand their perspectives and values. It requires a willingness to challenge one’s own assumptions and biases, and to adapt one’s communication style to connect with others more effectively. The user experience is enhanced by embracing a mindset of curiosity, empathy, and respect.
**Performance & Effectiveness:**
When applied thoughtfully and judiciously, understanding generational traits can be highly effective in improving communication, collaboration, and relationships. *Does it deliver on its promises?* Specific examples include improved team dynamics in the workplace, enhanced customer engagement in marketing campaigns, and more effective teaching methods in educational settings. However, it’s important to remember that understanding generational traits is not a magic bullet. It is just one tool among many that can be used to build stronger relationships and achieve greater success.
**Pros:**
1. **Improved Communication:** Understanding generational communication preferences can lead to more effective interpersonal interactions.
2. **Enhanced Collaboration:** Recognizing generational differences in work styles can foster more productive teamwork.
3. **Stronger Relationships:** Appreciating generational values can strengthen bonds and resolve conflicts more effectively.
4. **Increased Productivity:** Tailoring work environments to meet generational needs can boost employee engagement and performance.
5. **Effective Marketing:** Designing marketing campaigns that resonate with generational values can increase sales and brand loyalty.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Risk of Stereotyping:** Over-reliance on generational stereotypes can lead to misinterpretations and hinder genuine connection.
2. **Individual Variations:** Generational traits are generalizations, and individual variations always exist.
3. **Evolving Traits:** Generational traits are not static; they evolve as generations age and interact with subsequent generations.
4. **Oversimplification:** Reducing individuals to their generational label can oversimplify complex personalities and experiences.
**Ideal User Profile:**
Understanding generational traits is best suited for individuals and organizations that are committed to fostering inclusive environments, building stronger relationships, and achieving greater success through effective communication and collaboration. This includes managers, educators, marketers, counselors, and anyone who interacts with people from different generations on a regular basis.
**Key Alternatives (Briefly):**
1. **Personality Assessments (e.g., MBTI, Enneagram):** These assessments focus on individual personality traits rather than generational trends.
2. **Cultural Sensitivity Training:** This training focuses on understanding and respecting cultural differences, which can overlap with generational differences.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
Understanding generational traits offers valuable insights for navigating a diverse and complex world. While it’s important to avoid stereotypes and recognize individual variations, this framework can be a powerful tool for improving communication, collaboration, and relationships. Based on our detailed analysis, we recommend embracing this knowledge as a starting point for building stronger connections and fostering more inclusive environments. However, it’s crucial to combine this understanding with critical thinking, empathy, and a genuine desire to connect with individuals on a personal level.
## 6. Insightful Q&A Section
**Q1: How do generational differences impact workplace dynamics?**
**A:** Generational differences can significantly impact workplace dynamics. For example, older generations may value experience and hierarchy, while younger generations may prioritize innovation and collaboration. Understanding these differences can help managers create a more inclusive and productive work environment by tailoring communication styles, offering flexible work arrangements, and providing opportunities for mentorship and reverse mentorship.
**Q2: What are some common misconceptions about Millennials?**
**A:** One common misconception about Millennials is that they are entitled and lazy. In reality, Millennials are often highly motivated and driven, but they may have different priorities than previous generations. They value work-life balance, purpose-driven work, and opportunities for growth and development.
**Q3: How can businesses effectively market to Gen Z?**
**A:** To effectively market to Gen Z, businesses need to understand their values and preferences. Gen Z is digitally native, socially conscious, and values authenticity. Marketing campaigns that are visually appealing, shareable on social media, and aligned with their values are more likely to resonate with this generation.
**Q4: What are some strategies for bridging the generational gap in families?**
**A:** Bridging the generational gap in families requires open communication, empathy, and a willingness to learn from each other. Families can create opportunities for intergenerational dialogue, share stories and experiences, and find common ground through shared activities and interests.
**Q5: How do generational differences influence political views?**
**A:** Generational differences can influence political views due to the distinct historical events and societal shifts experienced during their formative years. For instance, older generations may hold more traditional values, while younger generations may be more progressive on social issues.
**Q6: What role does technology play in shaping generational traits?**
**A:** Technology plays a significant role in shaping generational traits. Each generation has grown up with different levels of technological access and proficiency, which has influenced their communication styles, learning habits, and overall worldview. For example, Gen Z is the first generation to have grown up entirely in the digital age, which has made them highly adaptable to new technologies and platforms.
**Q7: How can educators effectively teach students from different generations?**
**A:** Educators can effectively teach students from different generations by understanding their learning styles and preferences. For example, younger generations may respond well to interactive learning activities, technology-based instruction, and collaborative projects, while older generations may prefer more traditional lecture-based approaches.
**Q8: What are some of the challenges and opportunities of having a multigenerational workforce?**
**A:** The challenges of having a multigenerational workforce include potential communication barriers, conflicts in work styles, and differing expectations for career advancement. However, the opportunities are significant, including increased innovation, diverse perspectives, and a broader range of skills and experiences.
**Q9: How do economic conditions shape generational traits?**
**A:** Economic conditions play a significant role in shaping generational traits. For example, generations that grew up during periods of economic prosperity may be more optimistic and confident, while generations that grew up during recessions may be more cautious and risk-averse.
**Q10: What are the key differences between Gen X and Millennials?**
**A:** Gen X and Millennials differ in several key areas. Gen X is often described as independent, resourceful, and skeptical, while Millennials are often described as collaborative, optimistic, and purpose-driven. These differences are partly due to the distinct economic and technological landscapes they grew up in.
## Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding the **traits of the different generations and their characteristics** is essential for navigating the complexities of modern society. By recognizing the unique values, beliefs, and behaviors shaped by shared historical experiences, we can foster more effective communication, collaboration, and understanding across generations. This comprehensive guide has provided a framework for analyzing generational differences, highlighting the importance of avoiding stereotypes and embracing individual variations. As we move forward, it’s crucial to continue learning and adapting to the evolving landscape of generational traits, recognizing that these differences are not barriers but opportunities for growth and innovation. Now, share your own experiences with generational differences in the comments below. What are some of the challenges and opportunities you’ve encountered? Explore our advanced guide to intergenerational communication for more in-depth strategies. Contact our experts for a consultation on how to leverage generational diversity in your organization.